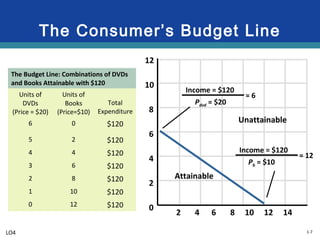
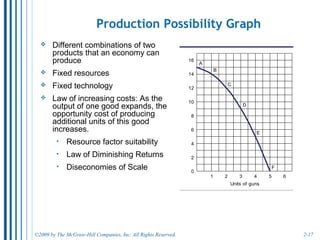
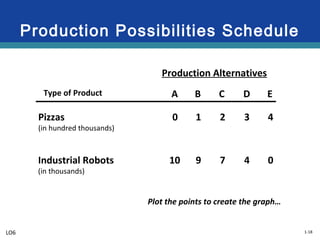
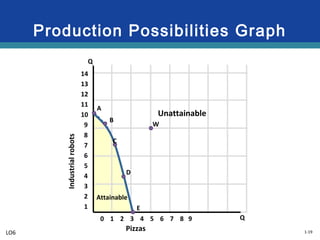
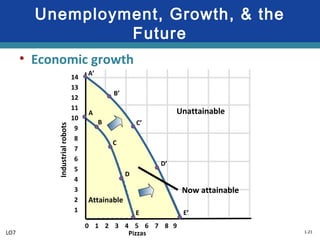
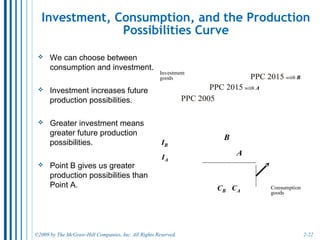
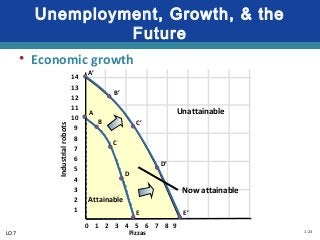
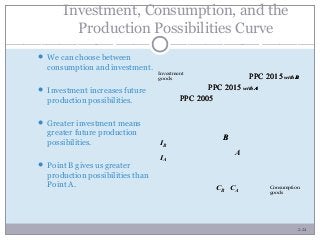
The document discusses key economic concepts related to resource utilization and scarcity. It begins by defining scarcity as the fundamental economic problem, as resources are limited but human wants are unlimited. This requires making choices that involve weighing costs and benefits, including opportunity costs of forgone alternatives. The four main economic resources are identified as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship, each earning a type of income. The concept of productive and allocative efficiency is introduced, along with the production possibilities curve which illustrates the tradeoffs between different goods that can be produced. Economic growth can shift the curve by expanding resources and technology.