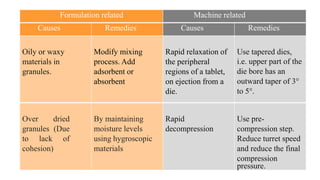
This document presents a case study on corrective and preventive action (CAPA) for tablet defects. It describes a problem where tablets were separating into layers during manufacturing. The defect was identified as lamination, caused by over-dried granules lacking cohesion. To address this, corrective action involved adding hygroscopic materials to maintain moisture levels. Preventive actions included improved training, self-inspections, process validation and revised standard operating procedures to prevent future lamination issues.