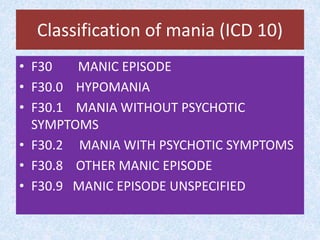
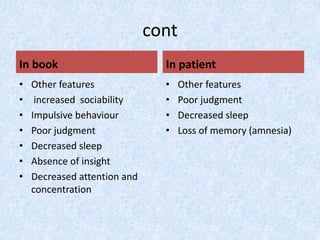
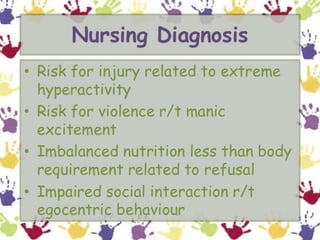
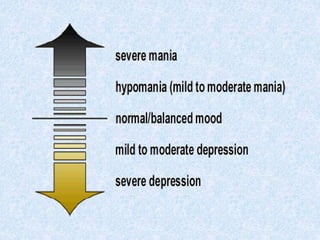
This document presents the case of a 23-year-old male patient presenting with symptoms of mania including irritability, wandering behavior, muttering to self, suspiciousness, loud speech, auditory hallucinations, and grandiosity. The patient has a 4-year history of untreated psychiatric illness with similar symptoms in the past requiring hospitalization. A family history of psychiatric illness is denied. The document defines mania and provides classification, etiology, clinical features, and objective/subjective symptoms of mania based on this patient's presentation and ICD-10 criteria.