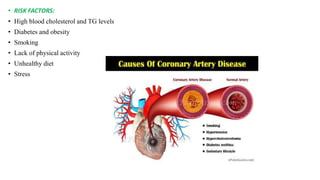
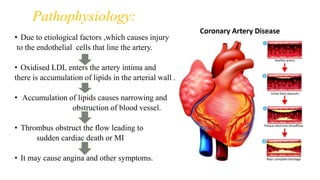
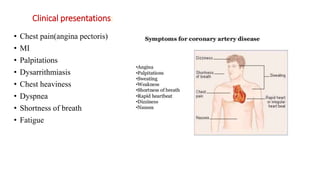
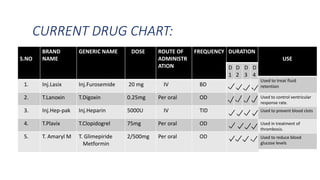
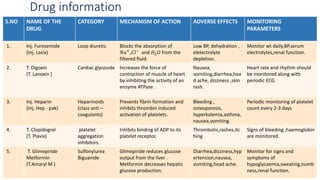
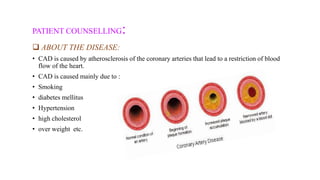
A 65-year-old male with a history of diabetes was admitted with shortness of breath, palpitations, and urinary frequency. Coronary angiography revealed mild coronary artery disease with triple vessel involvement. He was diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD) likely caused by his diabetes. He was treated medically with drugs including furosemide, digoxin, heparin, clopidogrel, glimepiride, and metformin. The goals of treatment were to alter disease progression, reduce complications, and manage symptoms through lifestyle modifications and pharmacological therapy.





![• DIAGNOSTIC TEST :
• Coronary angiogram report:
n Impression:CAD mild [MCA + critical triple vessel disease]
Left anterior descending artery
Left Circumflex artery
Right coronary
artery
parameter profile Abnormal values Normal values
TSH 5.540 mic IU/ml ( ) 0.4 - 4 mic IU/ml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cponcad-190205152521/85/Case-presentation-on-CAD-6-320.jpg)