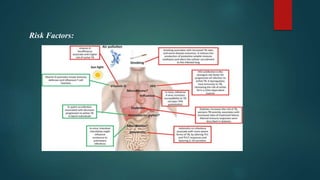
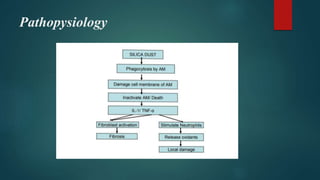
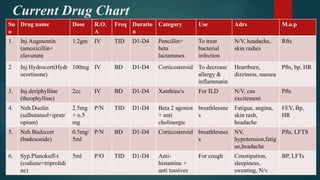
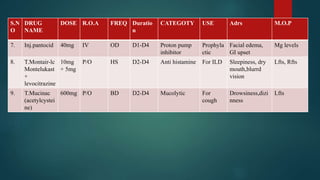
A 55-year-old male patient presented with cough, sputum, and breathlessness for 2 months. He had a history of silica dust exposure at work. Tests revealed right-sided pleural effusion and interstitial lung disease. He was diagnosed with silico-tuberculosis based on his occupational exposure history and imaging findings. He was started on antibiotics, bronchodilators, steroids, antitussives, and other supportive medications. Pharmacist interventions included recommending drugs missing from the treatment chart and providing education on silico-tuberculosis and lifestyle modifications to reduce silica exposure.