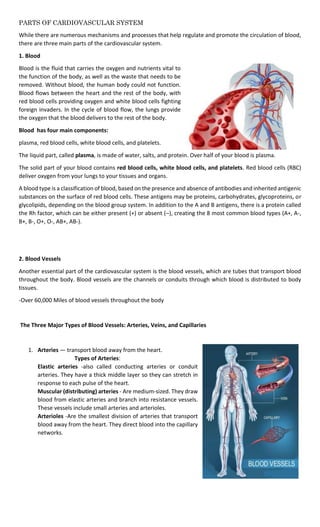
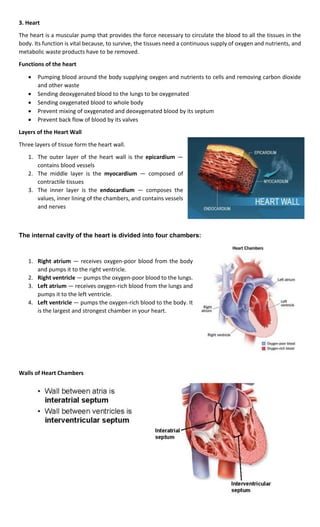
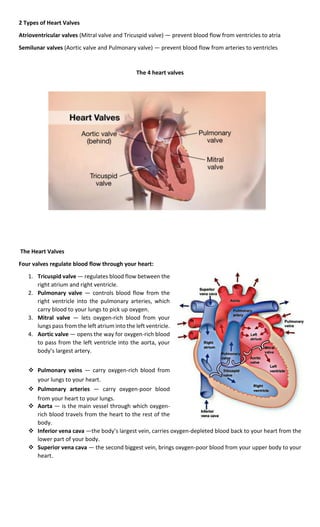
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and blood vessels, and has three main functions:
1. Circulate oxygenated blood to tissues and organs via the circulatory system
2. Transport nutrients to and remove waste from all body cells
3. Maintain homeostasis in the body through regulated blood flow
The three main components are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. The heart pumps blood through a closed
system of arteries, veins, and capillaries to provide cells with oxygen and nutrients while removing carbon
dioxide and other wastes.