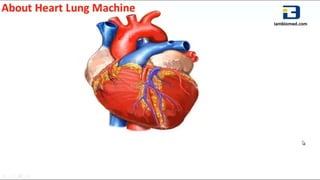
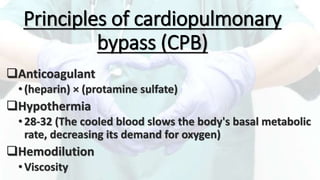
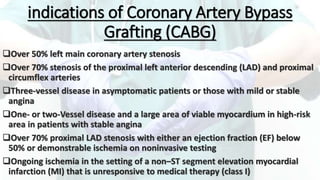
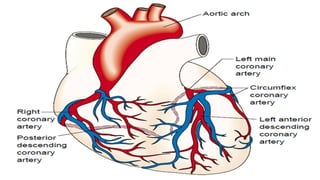
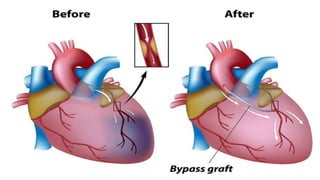
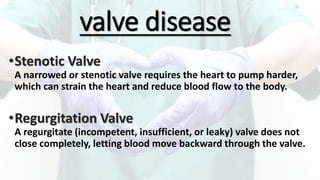
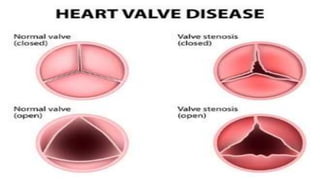
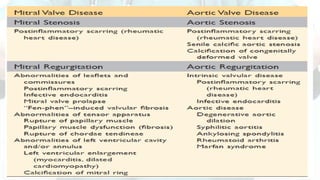
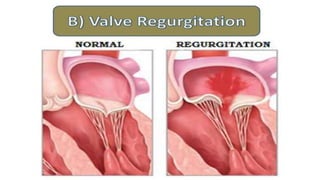
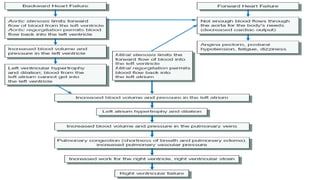
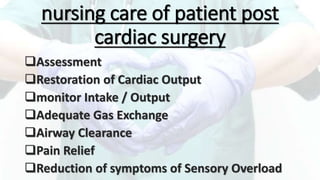
Mohamed Ragab Abdelhakam is a student at Misr University for Science and Technology who is studying cardiopulmonary bypass, coronary artery bypass grafting, valve disorders, and the pre- and post-operative nursing care of cardiac surgery patients. The document outlines the principles of cardiopulmonary bypass including anticoagulation, hypothermia, and hemodilution. It also discusses indications and contraindications for coronary artery bypass grafting and the differences between valve regurgitation and stenosis. Preoperative nursing care includes assessment, medication management, and patient education, while postoperative care focuses on restoring cardiac output, gas exchange, airway clearance, pain relief, and reducing sensory overload.