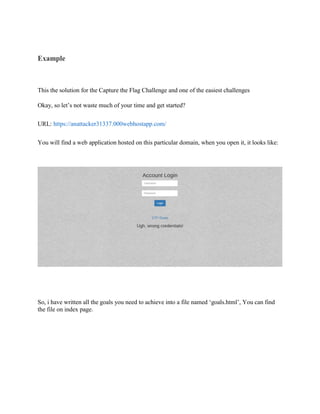
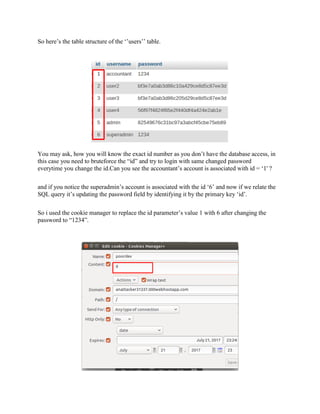
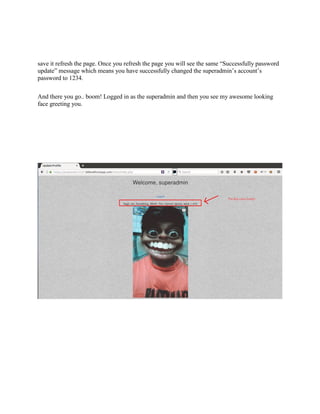
The document provides an overview of Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions in cybersecurity, detailing how they work, types of challenges, and their real-world benefits for participants. CTFs serve as valuable training tools for both students and professionals, enhancing technical skills and soft skills while fostering networking opportunities. It also discusses preparedness, participation guidelines, tools for various tasks, and common rules to ensure fair play during competitions.