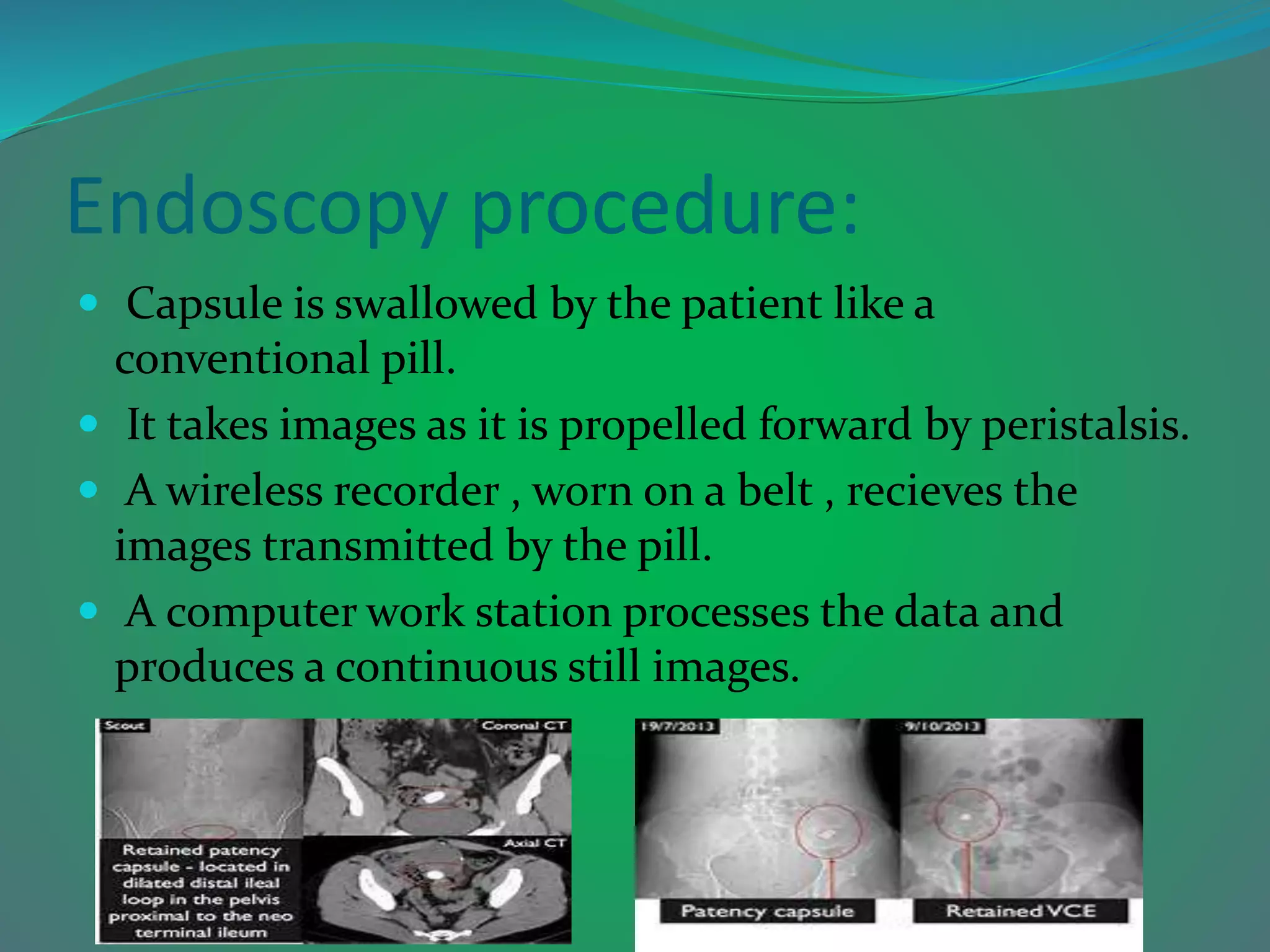
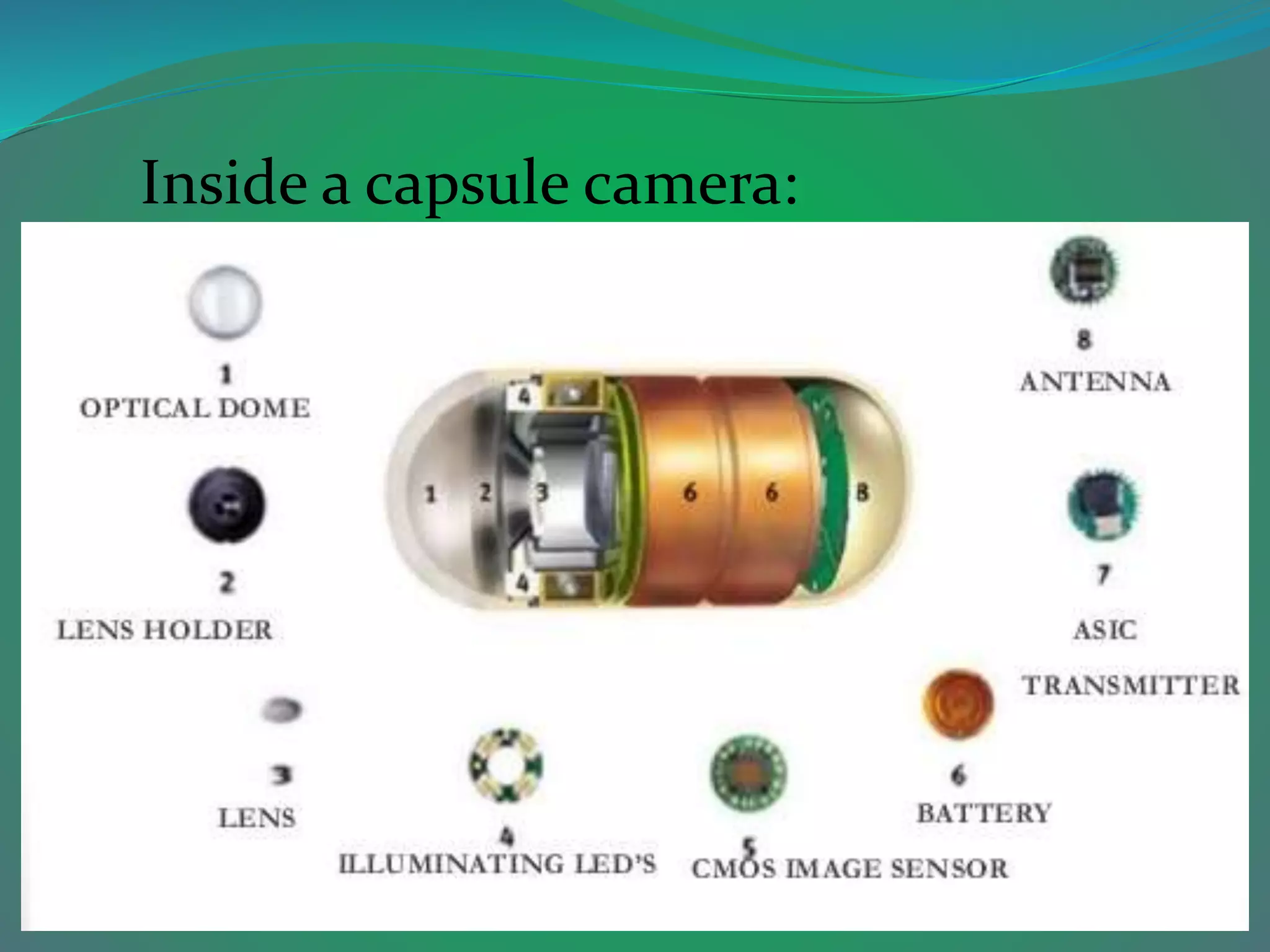
Capsule endoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that enables doctors to examine the lining of the small intestine using a pill-sized video camera swallowed by the patient, which captures and transmits images to a recording device. Introduced in 1999, the capsule captures images via optical fibers and sends them to a wireless recorder, with the data processed for interpretation. While useful for diagnosing conditions like Crohn's disease and tumors, capsule endoscopy has limitations including slower motility, image quality concerns, and dependence on the observer's interpretation.