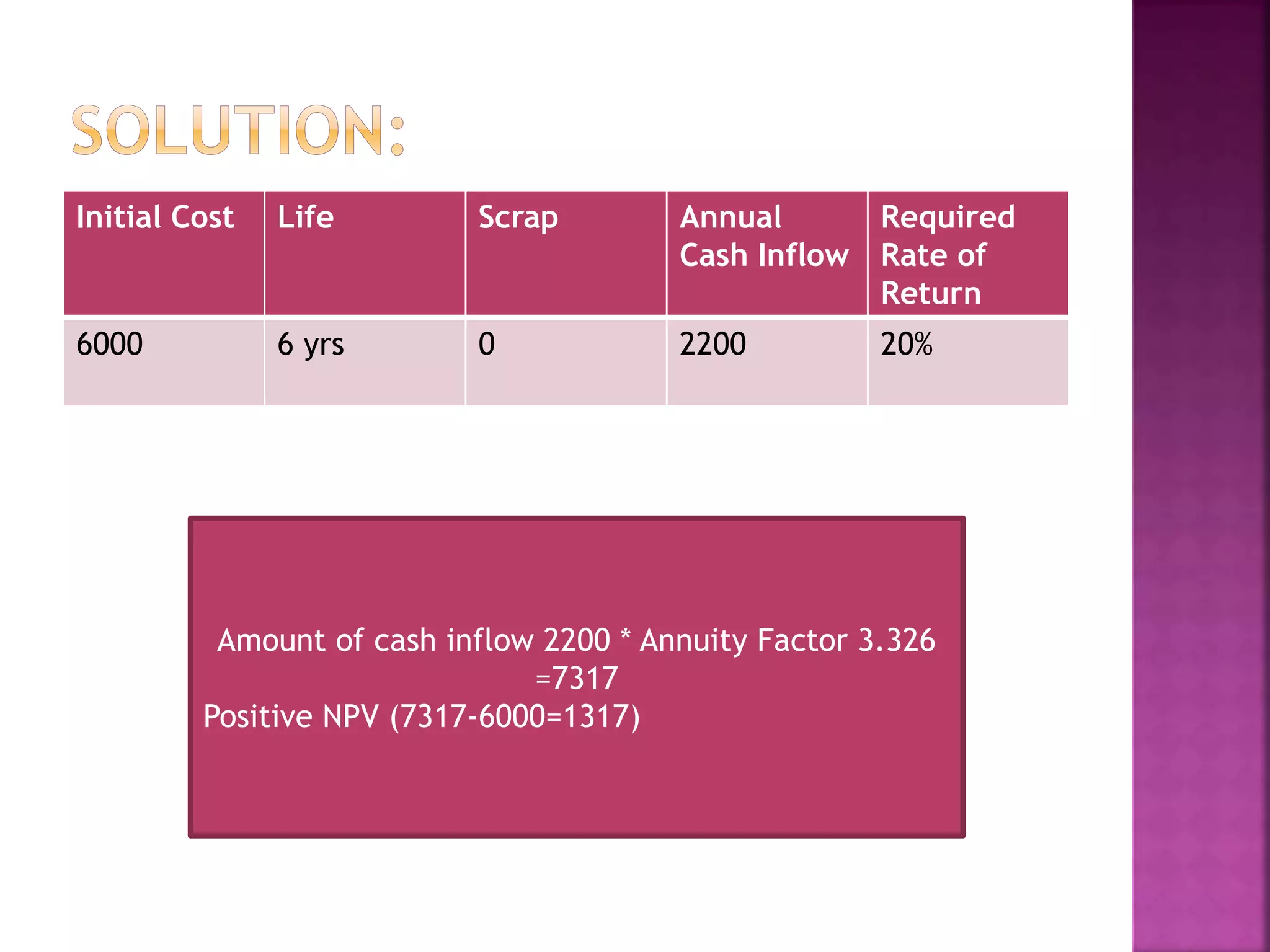
The document discusses capital budgeting, outlining the process of making investment decisions for long-term projects. It covers evaluation techniques including payback period, net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), and profitability index (PI) to assess the viability of investments. Key metrics for decision-making are emphasized, such as cash inflows versus outflows, the time value of money, and acceptance criteria based on calculated returns.