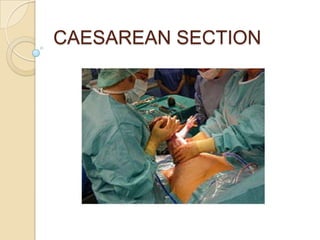
1. Caesarean section is a surgical procedure where the fetus, placenta, and membranes are delivered through an incision in the abdominal wall and uterus.
2. The incidence of caesarean sections has steadily increased over the last decade from around 10% to 30% due to improved safety, identification of risk factors, and increased awareness of fetal well-being.
3. Indications for caesarean include cephalopelvic disproportion, previous uterine scar, fetal distress, and malpresentations; contraindications include a dead fetus or one that is too premature.