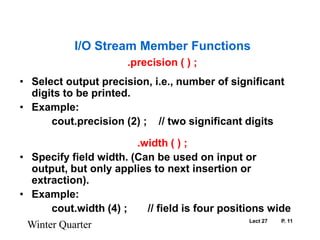
This document provides information about C++ stream input/output (I/O) manipulation over 17 pages. It discusses the standard header files for stream I/O, the class hierarchy for stream I/O in C++, stream manipulators for formatting output, stream format states for controlling formatting, and various member functions for manipulating streams and performing formatted I/O. It also provides an example program demonstrating the use of manipulators and member functions for stream I/O.




![Lect 27 P. 9ios::eofbit set when eof encountered [ stream.eof() ]ios::failbit set when format error occurred on the stream, but no characters were lost [ stream.fail() or simply ! stream ]ios::badbit set when stream error occurs that results in a loss of data [ stream.bad() ]ios::goodbit set when none of the bits eofbit,failbit, or badbit are set [ stream.good() ]Winter QuarterStream I/O Format State Flags](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciomanipulation-110321061140-phpapp02/85/C-io-manipulation-9-320.jpg)



![Lect 27 P. 14#include <iostream> // No “.h” (standard header)#include <iomanip> // No “.h” (standard header)using namespace std; // To avoid “std::”int main ( ){int a, b, c = 8, d = 4 ;float k ;char name[30] ;cout<< "Enter your name" <<endl; cin.getline (name, 30);cout<< "Enter two integers and a float " <<endl; cin>> a >> b >> k ;Winter QuarterUsing Manipulators & Member Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciomanipulation-110321061140-phpapp02/85/C-io-manipulation-14-320.jpg)



![Lect 27 P. 18Winter QuarterMore Input Stream Member Functions.get (array_name, max_size) ;Example:char name[40] ;cin.get(name, 40) ; // Gets up to 39 characters // and inserts a null at the end of the // string "name". If a delimiter is // found, the read terminates. The // delimiter is not stored in the array, // but it is left in the stream.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciomanipulation-110321061140-phpapp02/85/C-io-manipulation-18-320.jpg)
![Lect 27 P. 19.getline (array_name, max_size) ;Example:char name[40] ;cin.getline(name, 40) ; // Gets up to 39 characters // and assigns the string to "name". A // null is inserted at the end of the string. // Note that if a delimiter is found, // it is removed from the stream, but it is // not stored in the character array. Winter QuarterMore Input Stream Member Functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciomanipulation-110321061140-phpapp02/85/C-io-manipulation-19-320.jpg)


![Lect 27 P. 22More I/O Stream Member FunctionsWinter Quarter.read( ) ; .write( ) ;Ex:char gross[144] ;cin.read(gross,144); // reads 144 characters from // input stream. Does NOT // append '\0'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ciomanipulation-110321061140-phpapp02/85/C-io-manipulation-22-320.jpg)
