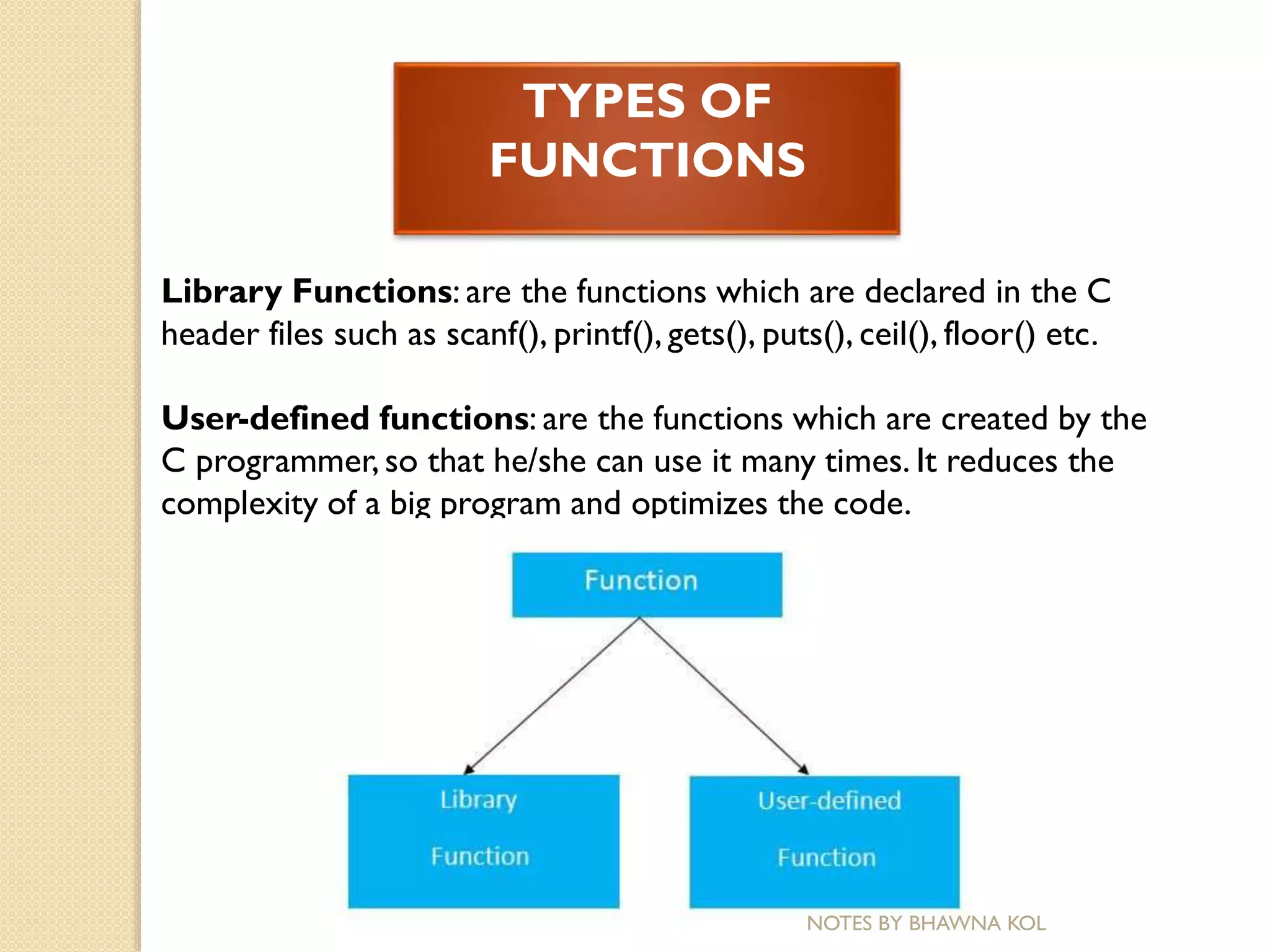
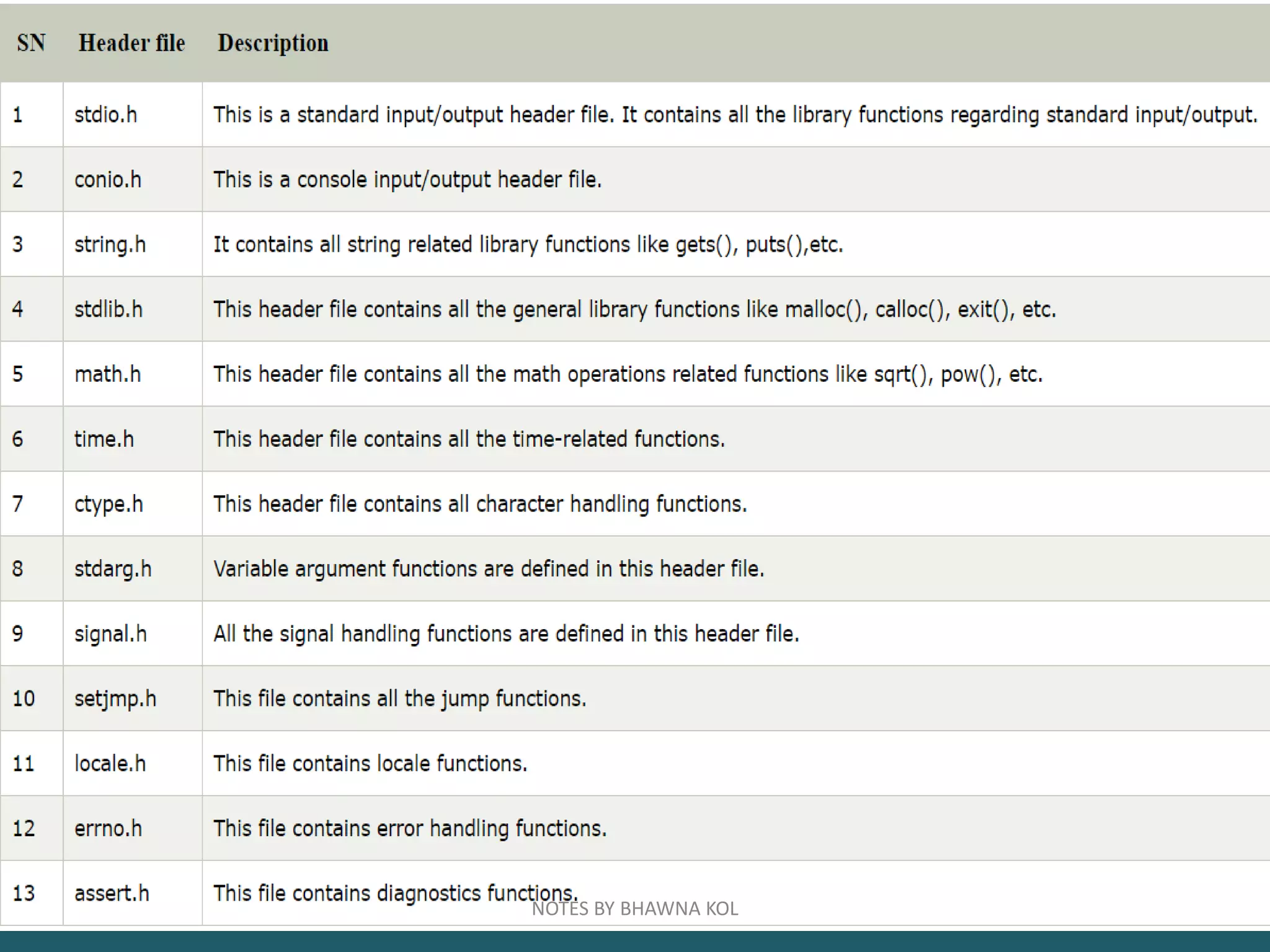
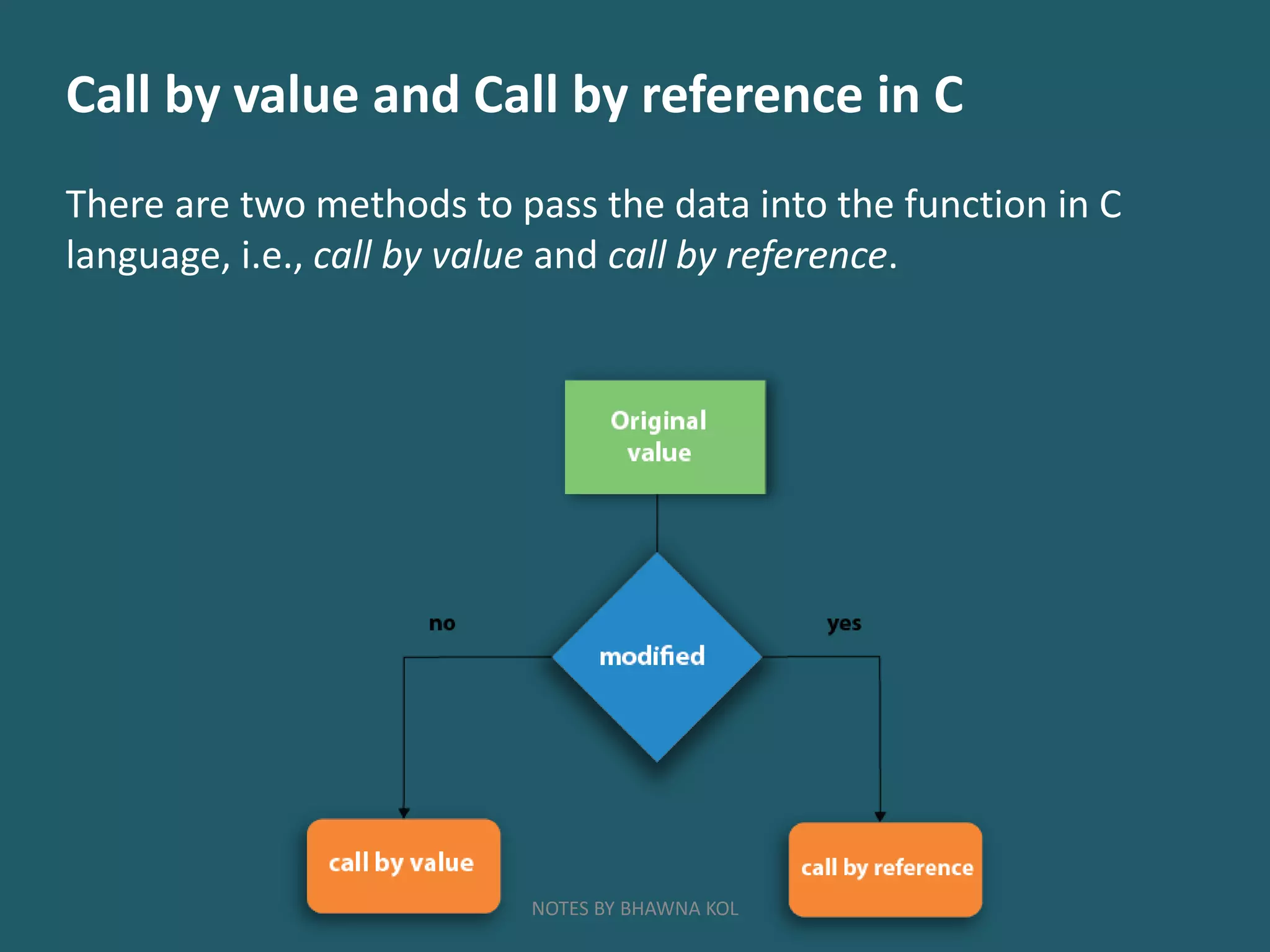
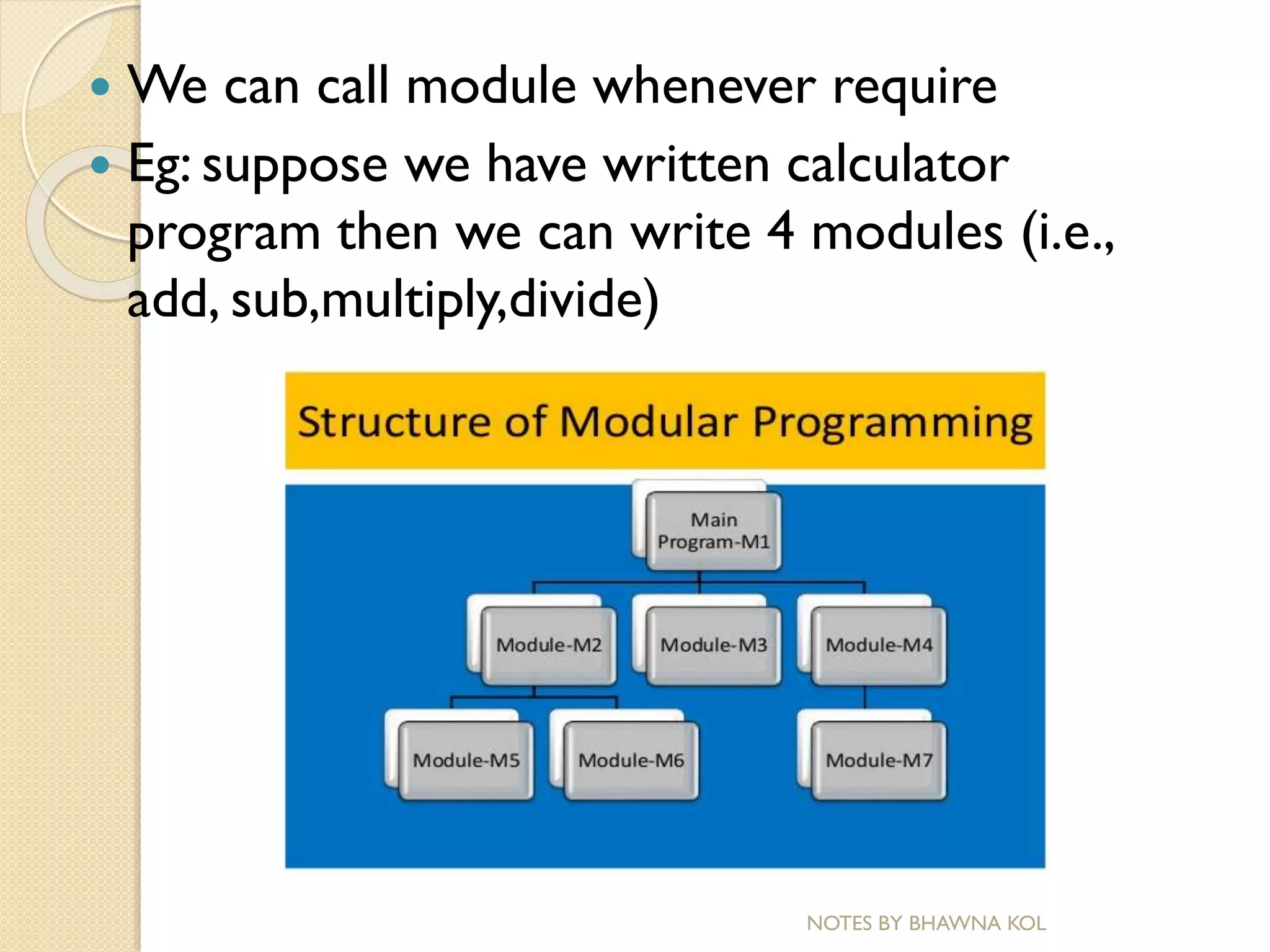
The document discusses modular programming in C. Modular programming involves breaking a large program into smaller sub-programs or modules. This makes the program easier to use, maintain and reuse code. Functions are a key part of modular programming in C. Functions allow breaking a program into reusable modules that perform specific tasks. Functions can be called anywhere in a program to perform tasks without rewriting code. Modular programming improves readability, reduces errors and makes programs easier to maintain and modify.



![Functions in C
A function is a set of statements that take inputs, do some
specific computation and produces output.
The idea is to put some commonly or repeatedly done task
together and make a function so that instead of writing the
same code again and again for different inputs, we can call
the function.
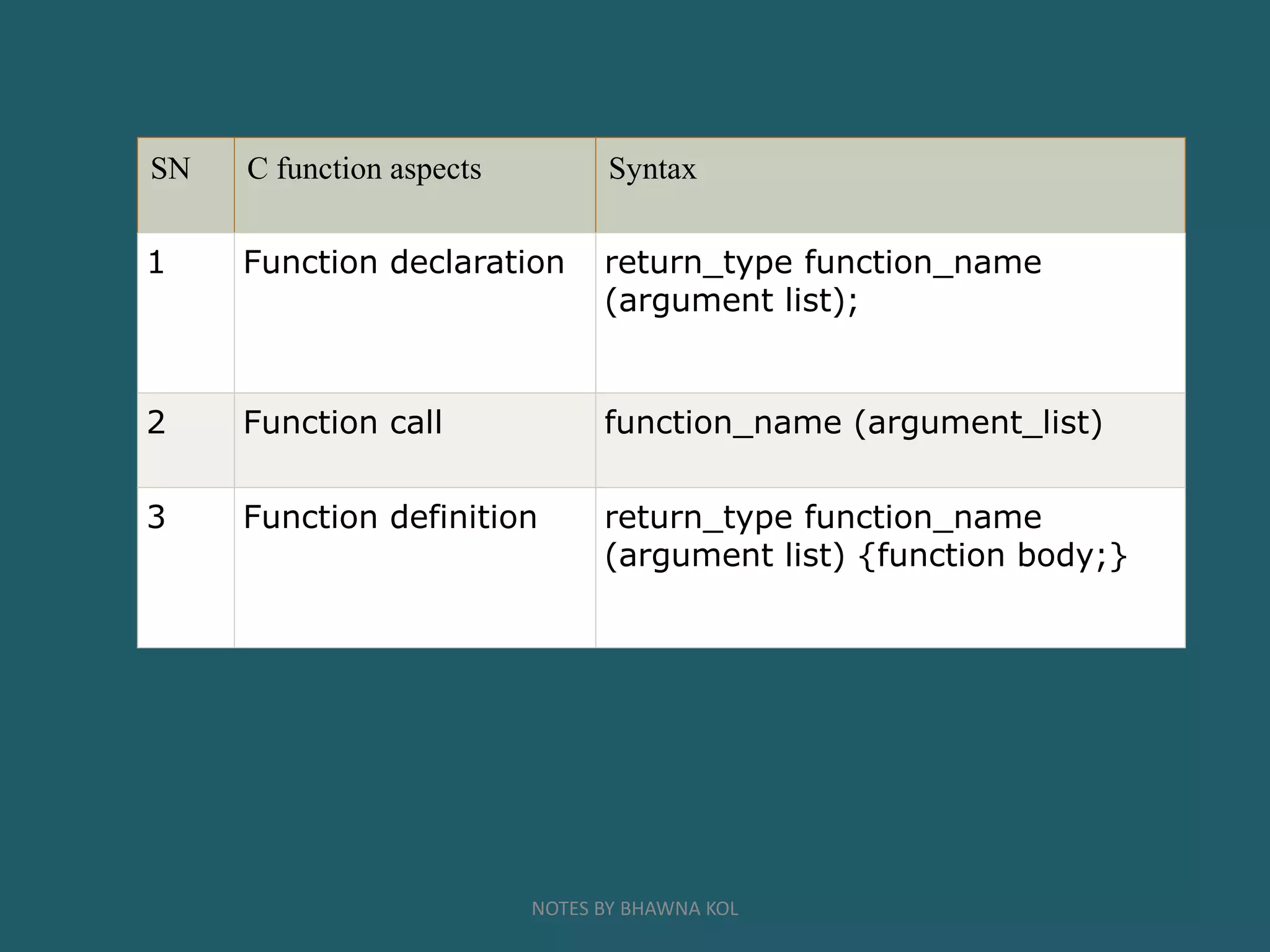
The general form of a function is:
return_type function_name([ arg1_type arg1_name, ... ])
{ code }
NOTES BY BHAWNA KOL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3-210524132901/75/Modular-Programming-in-C-6-2048.jpg)