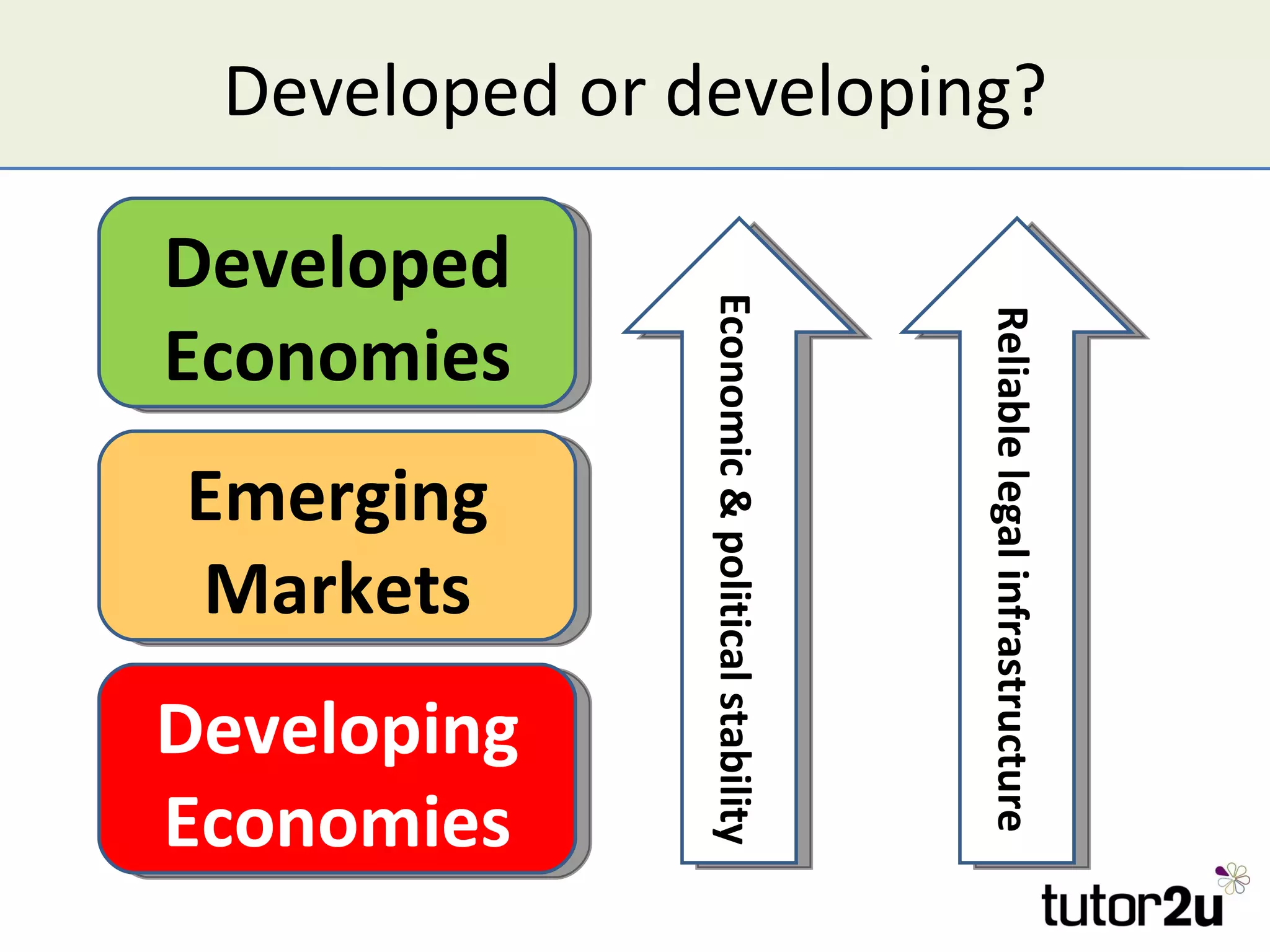
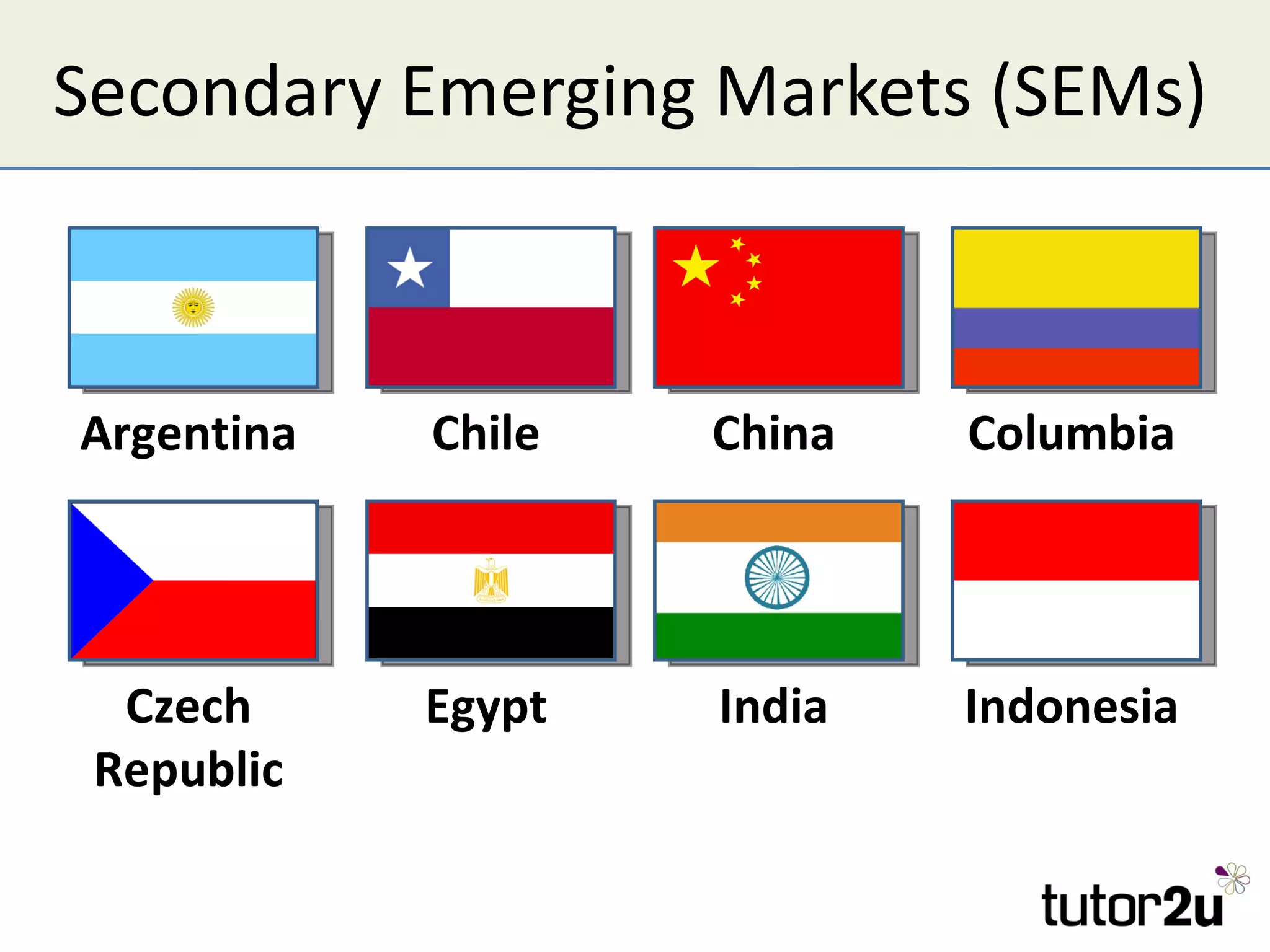
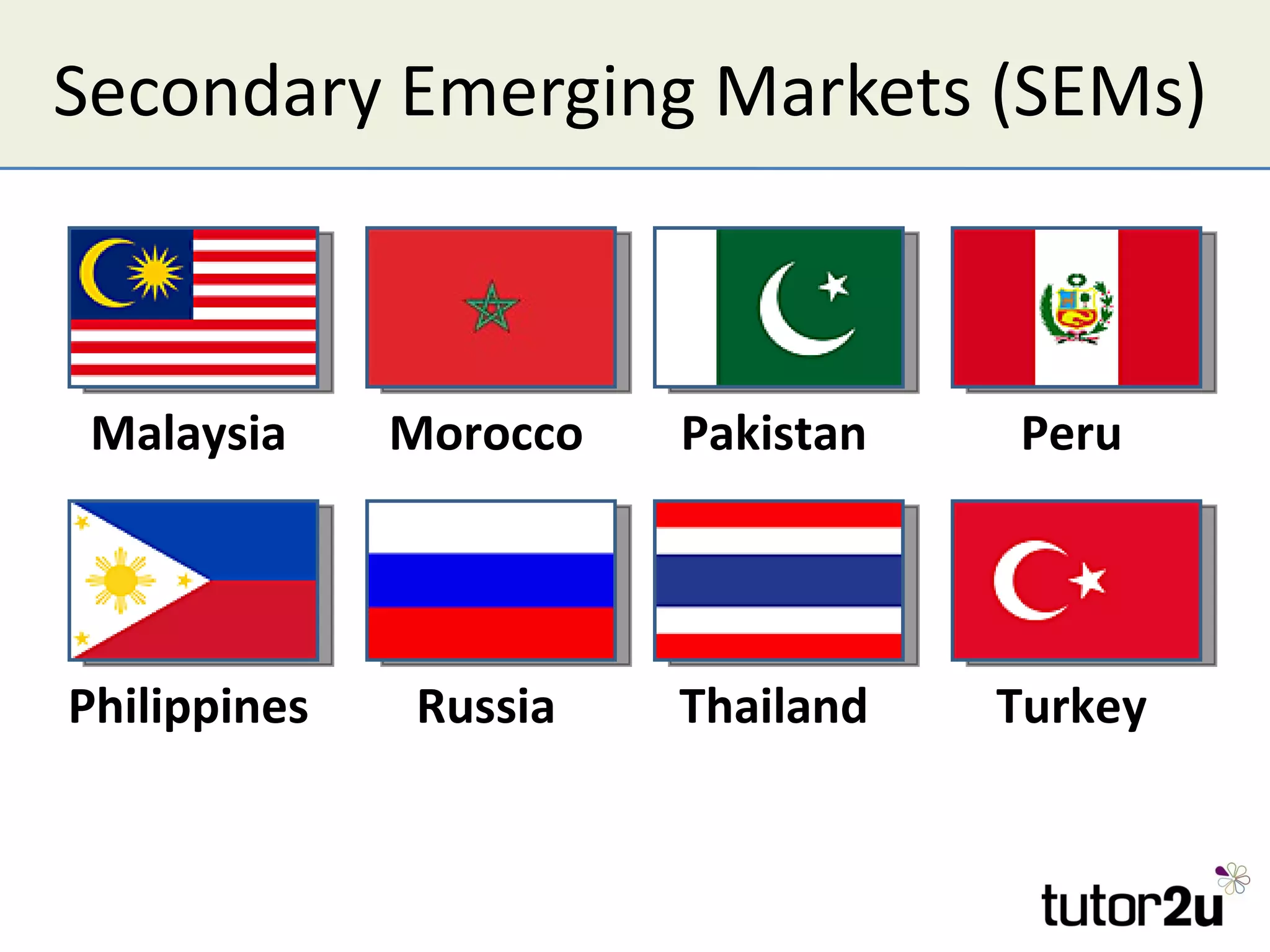
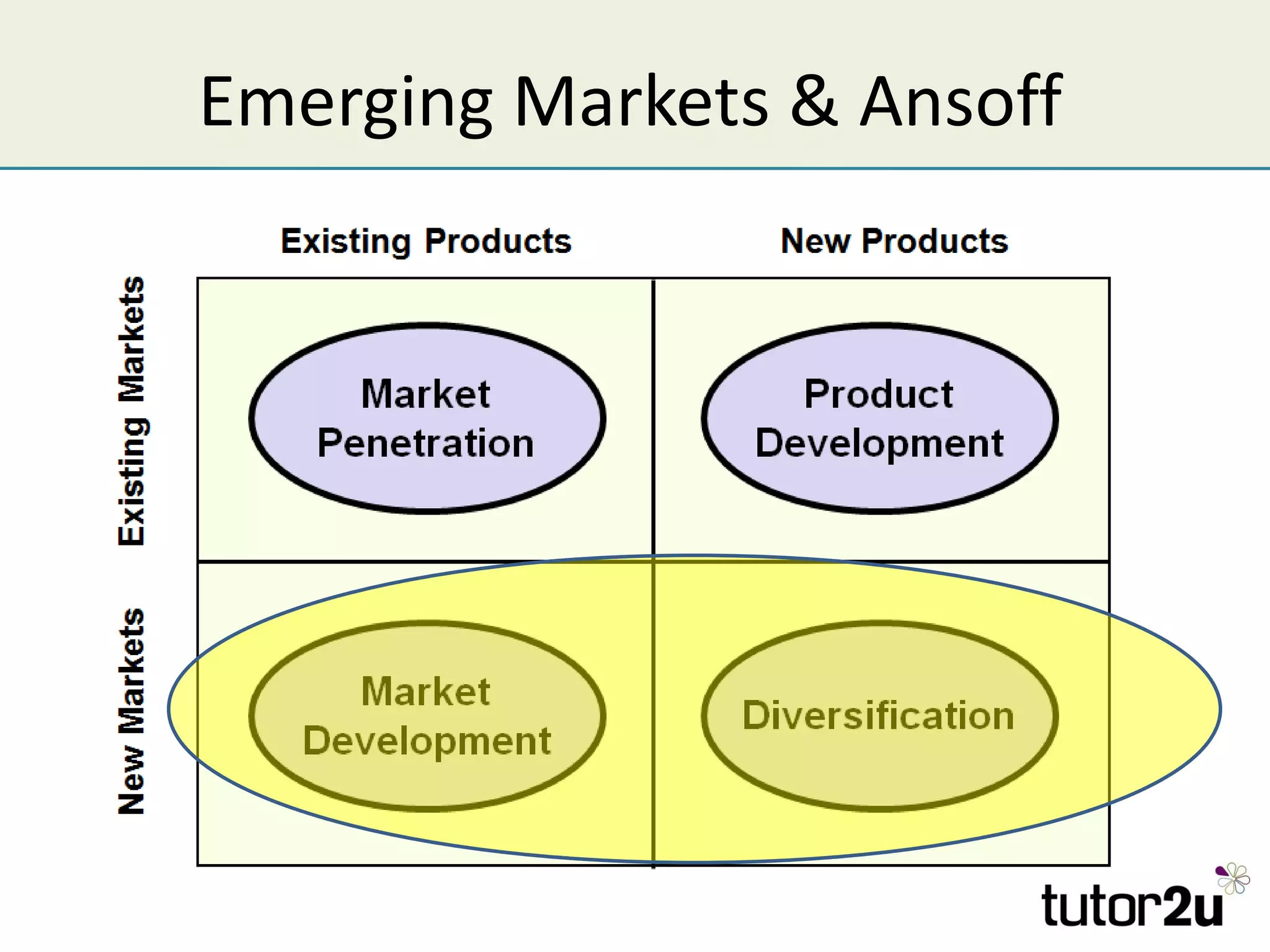
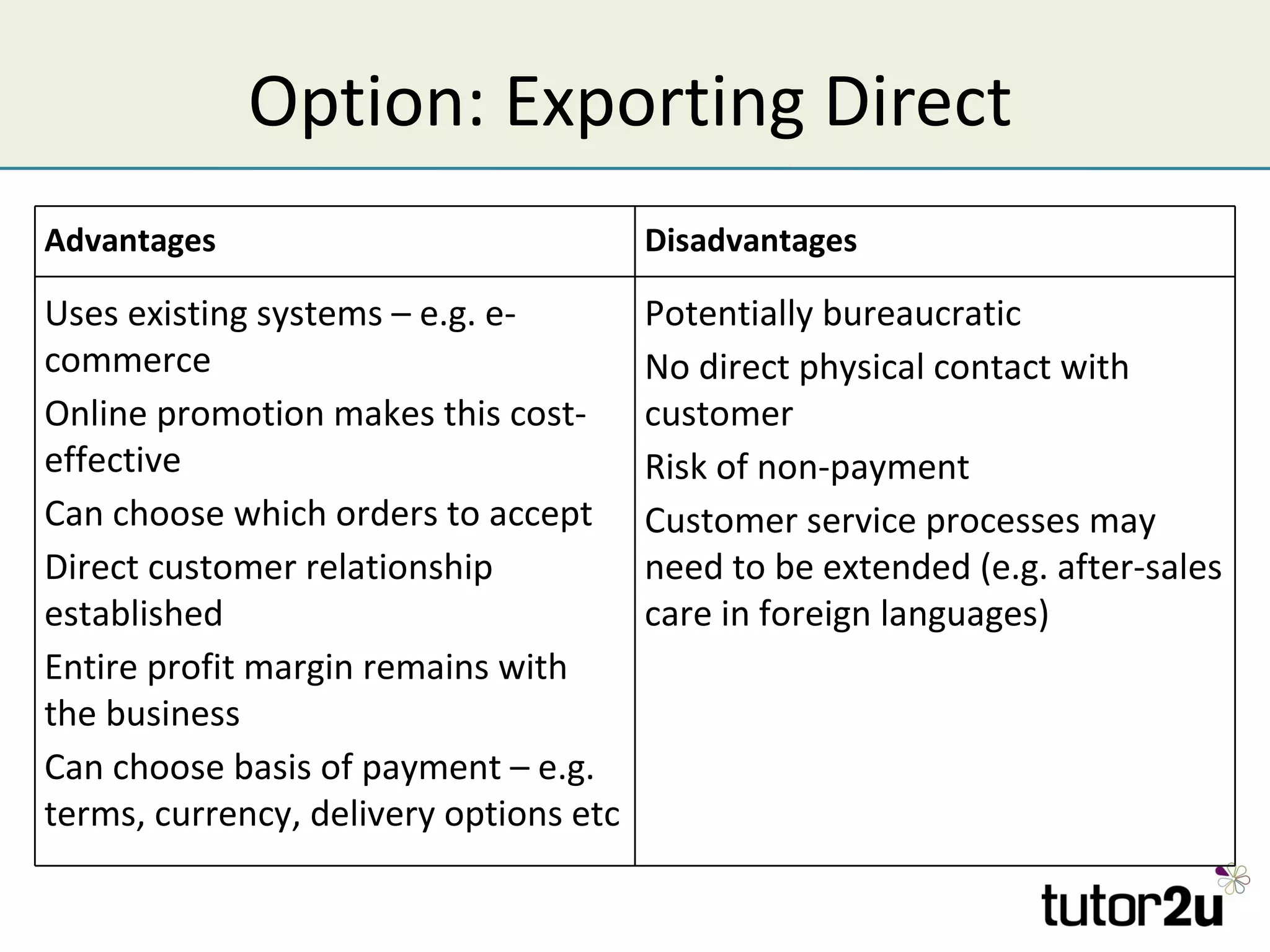
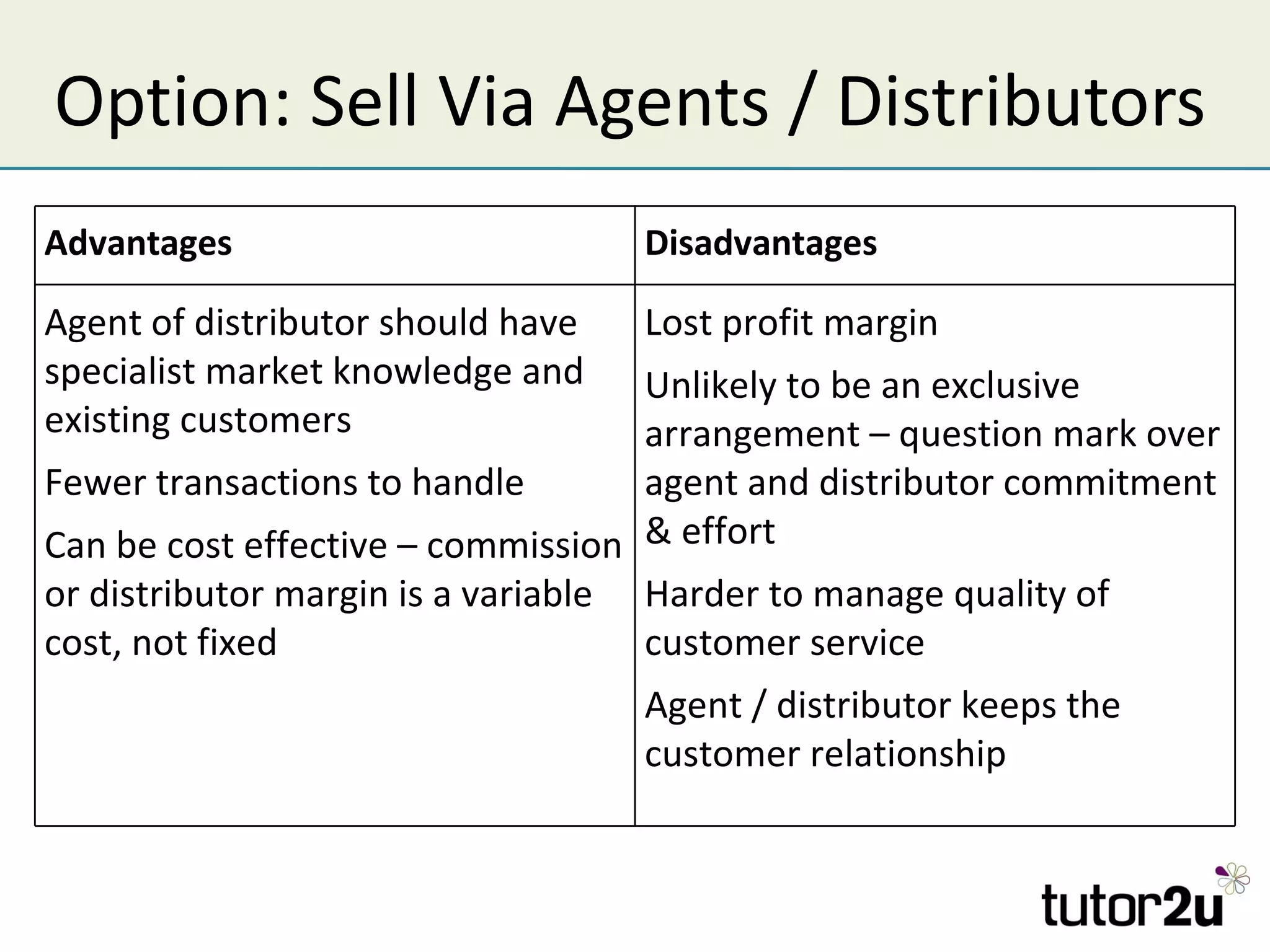
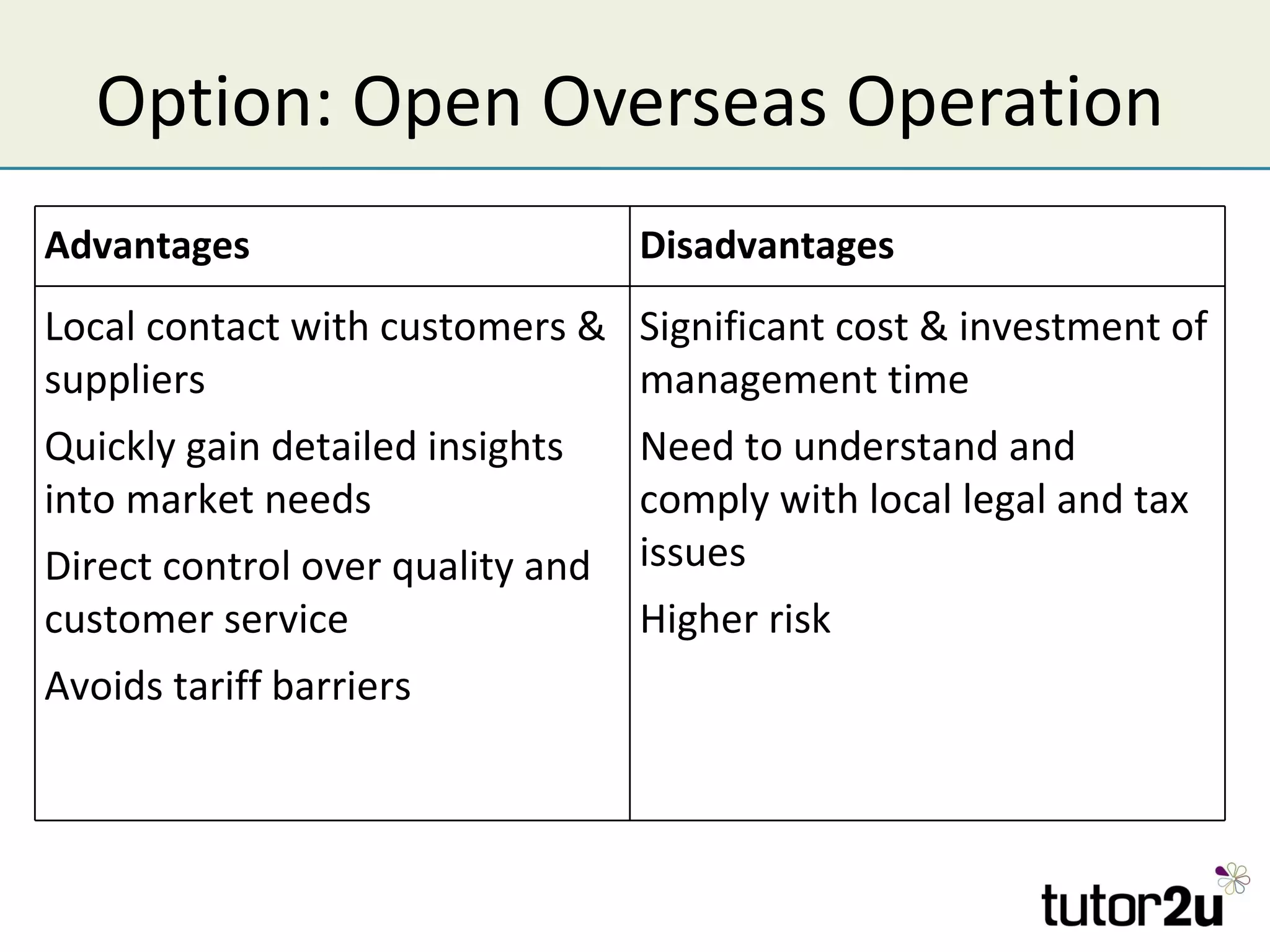
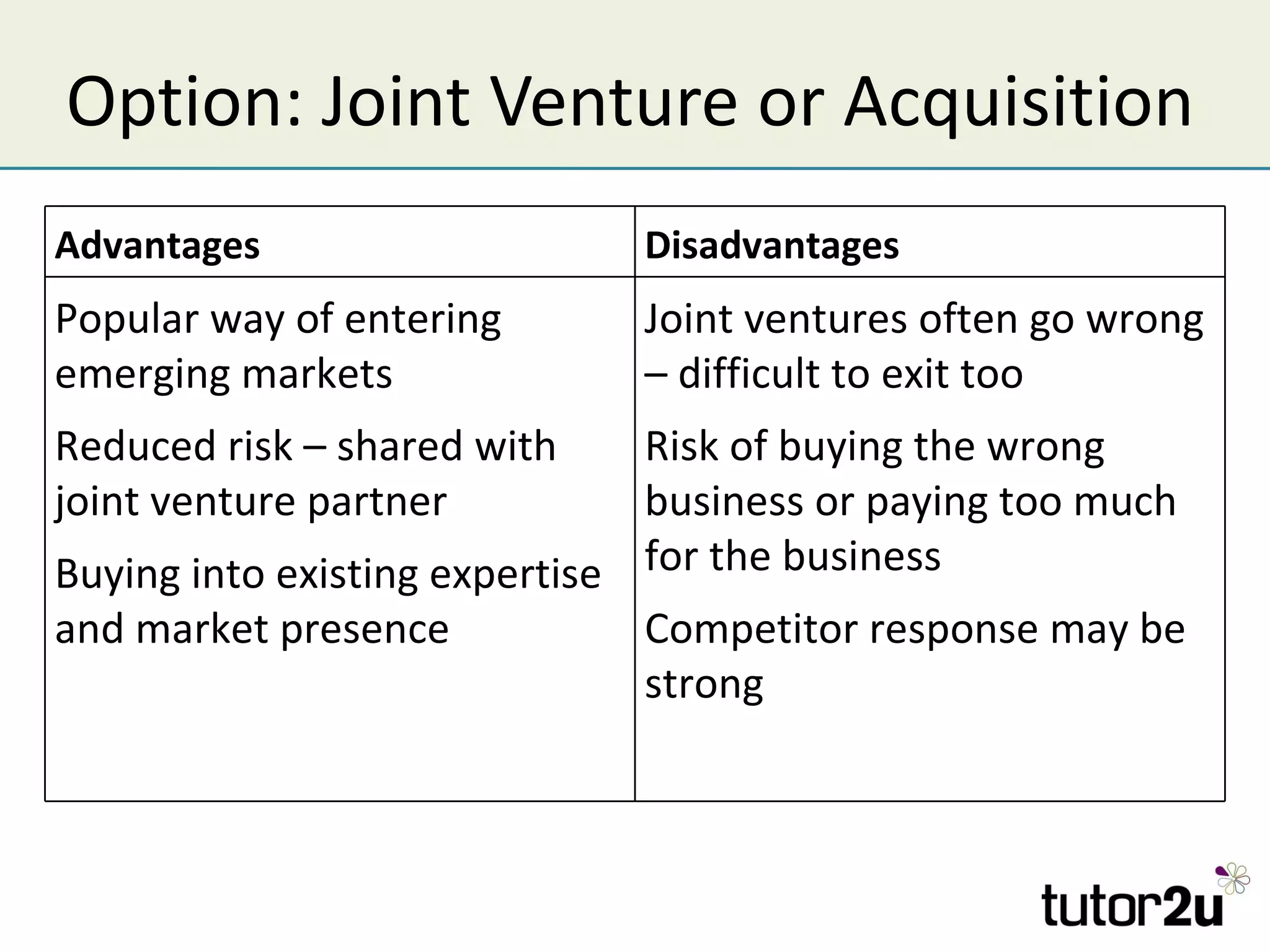
The document discusses various companies entering emerging markets, highlighting examples like Starbucks partnering with Tata in India, Jaguar Land Rover's assembly plant, and Heinz's expansion into Brazil and China. It outlines the definition, opportunities, and risks associated with emerging markets, including the potential for growth and challenges like political instability and cultural differences. The text also mentions strategies for international expansion, such as joint ventures, acquisitions, and market development, emphasizing the importance of understanding local markets and adapting business practices accordingly.