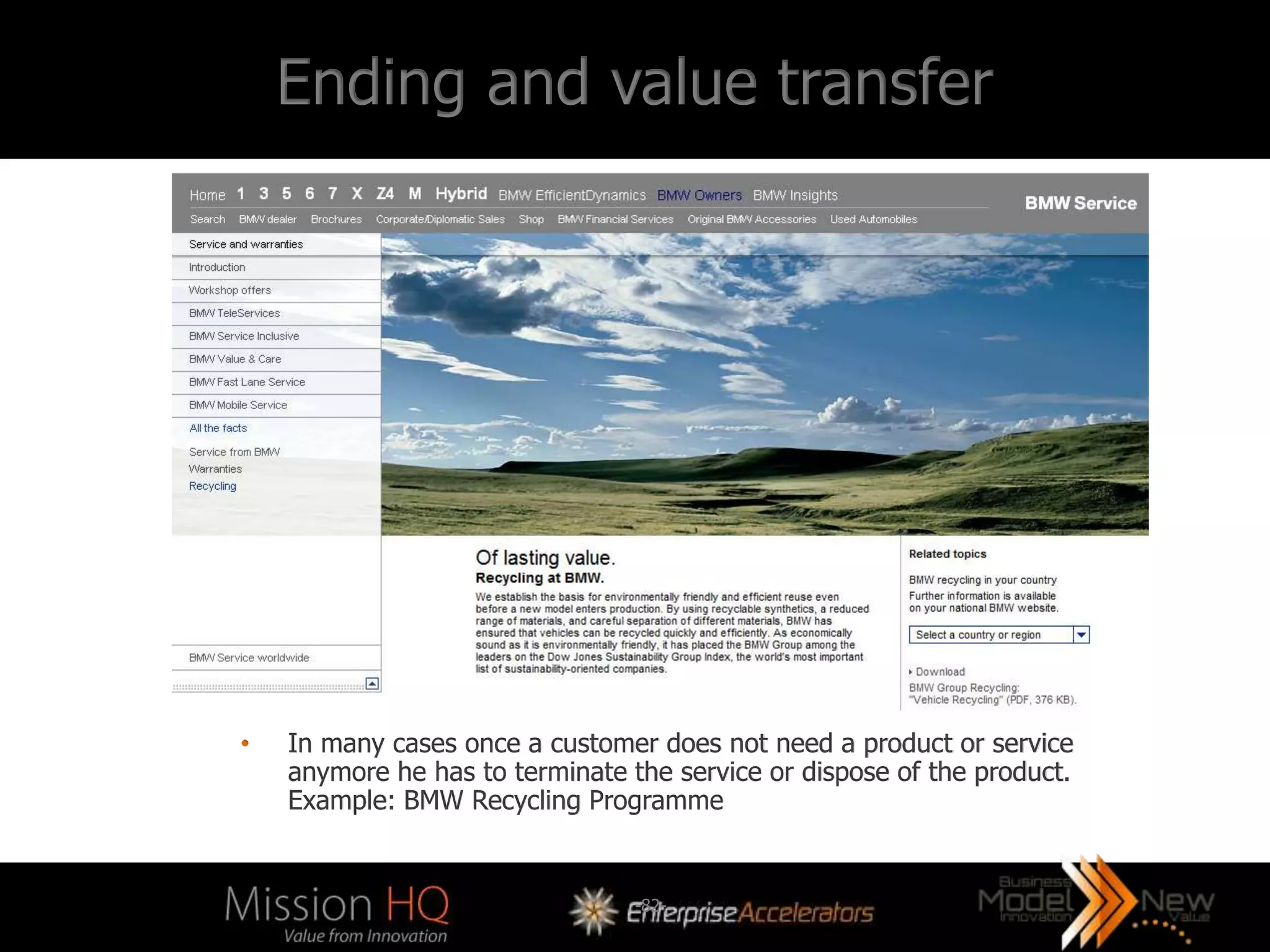
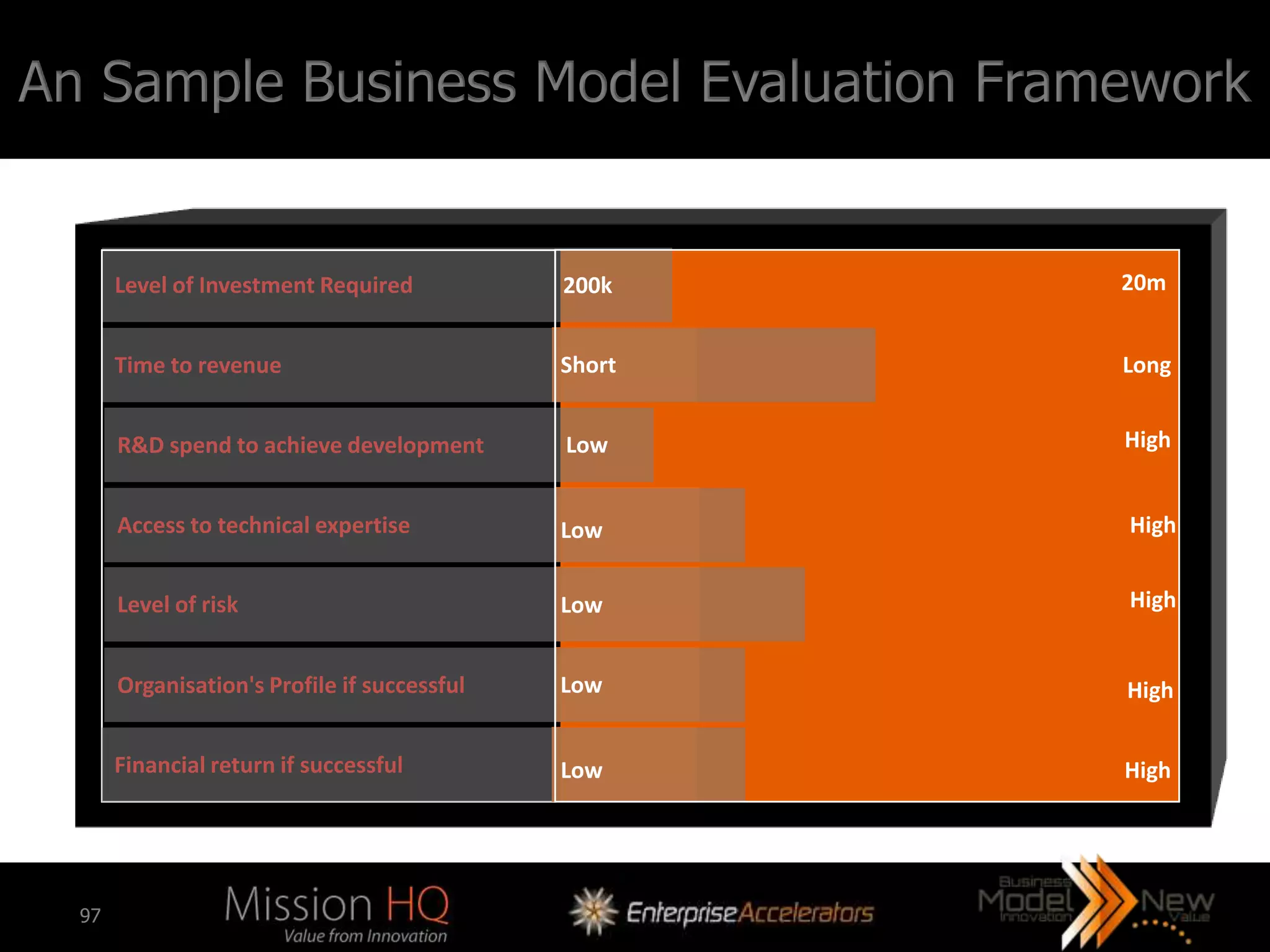
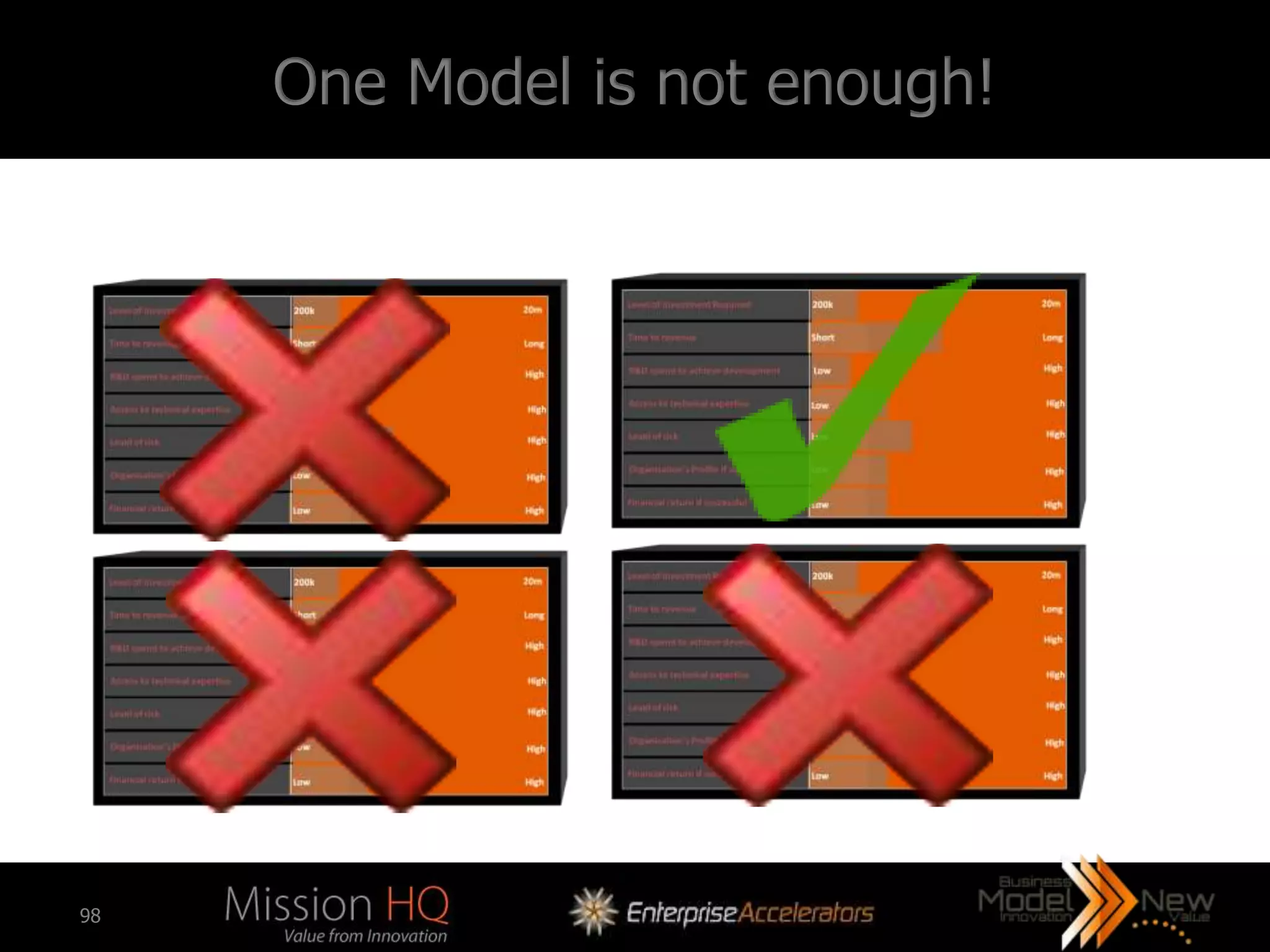
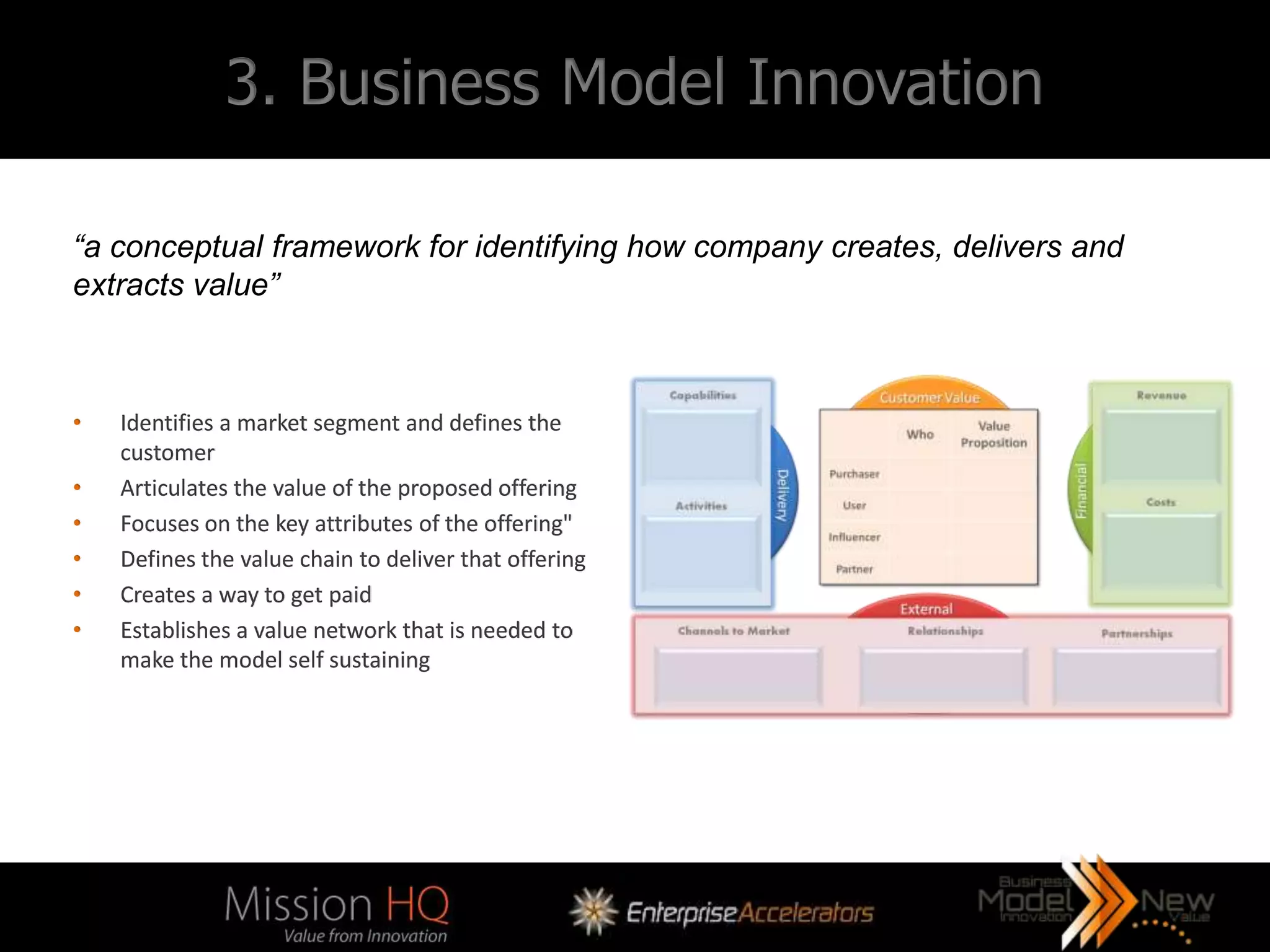
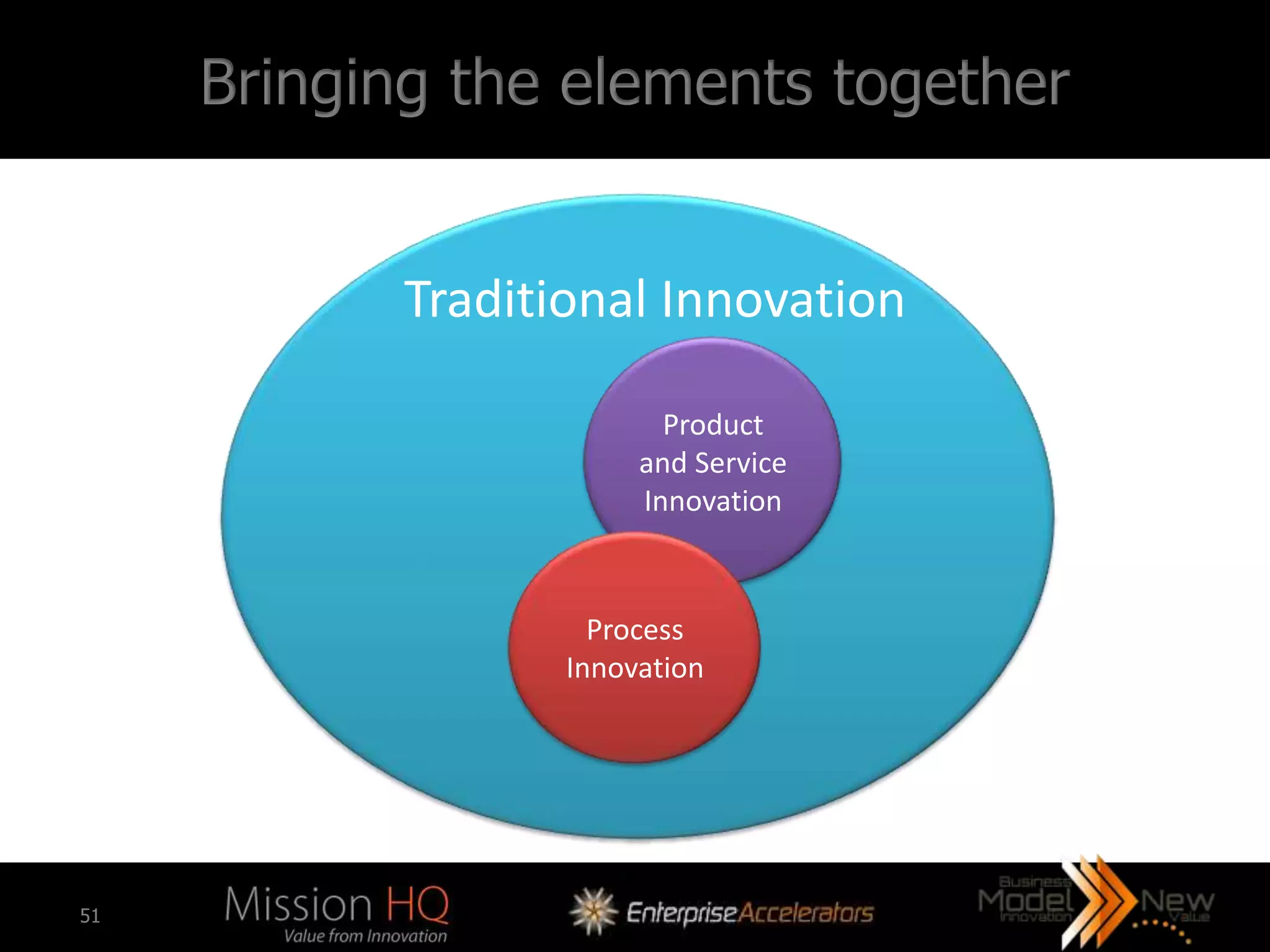
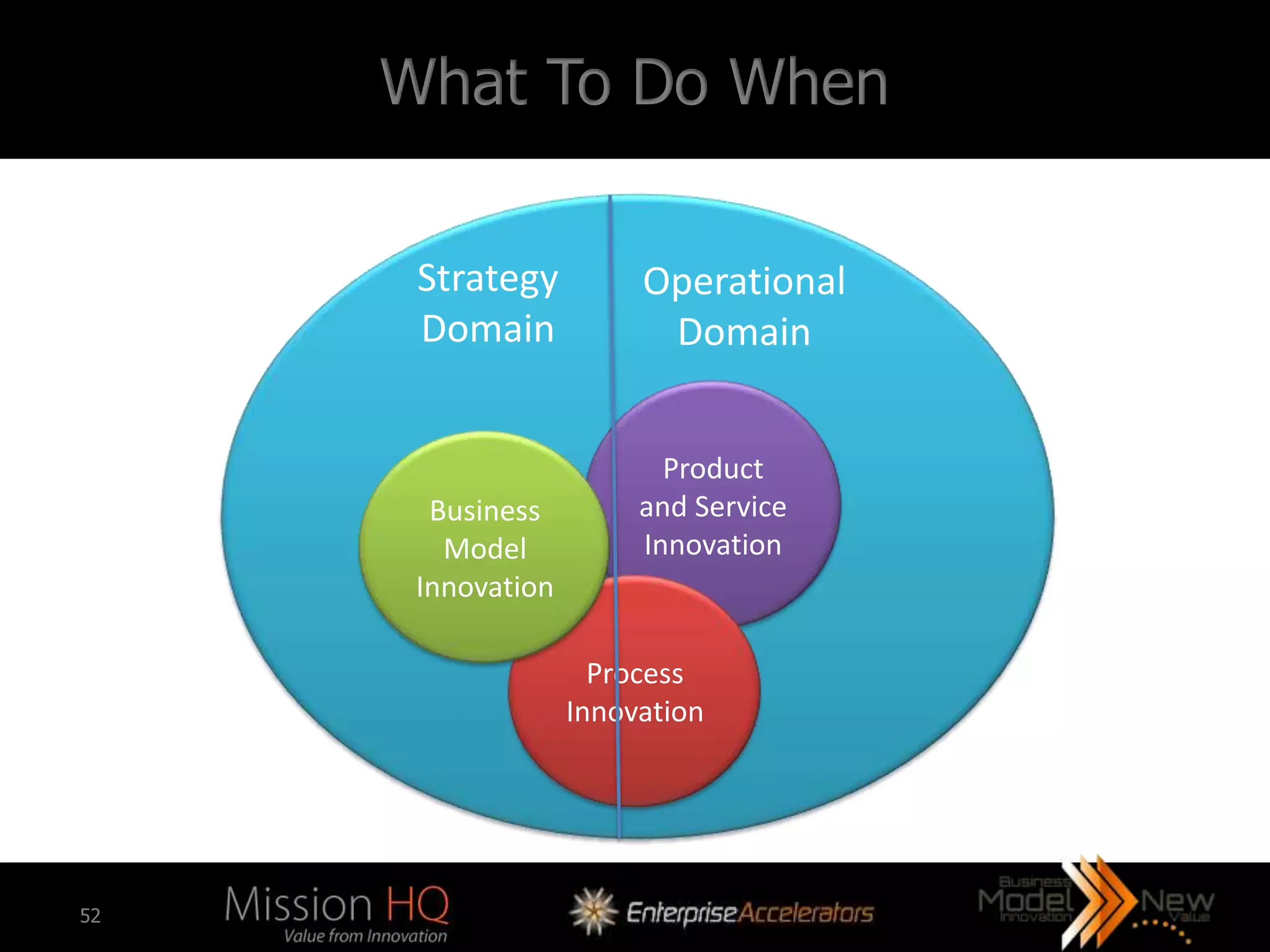
The workshop led by Marcus Tarrant focuses on business model innovation as a key competitive advantage in today's market, emphasizing that companies must not only innovate products but also their business models. The agenda includes discussions on defining business models, assessing innovation types, and implementing these innovations within organizations, supported by case studies such as Kodak and FujiFilm. Participants are encouraged to engage in exercises to explore practical applications of business model innovation tailored to their businesses.











































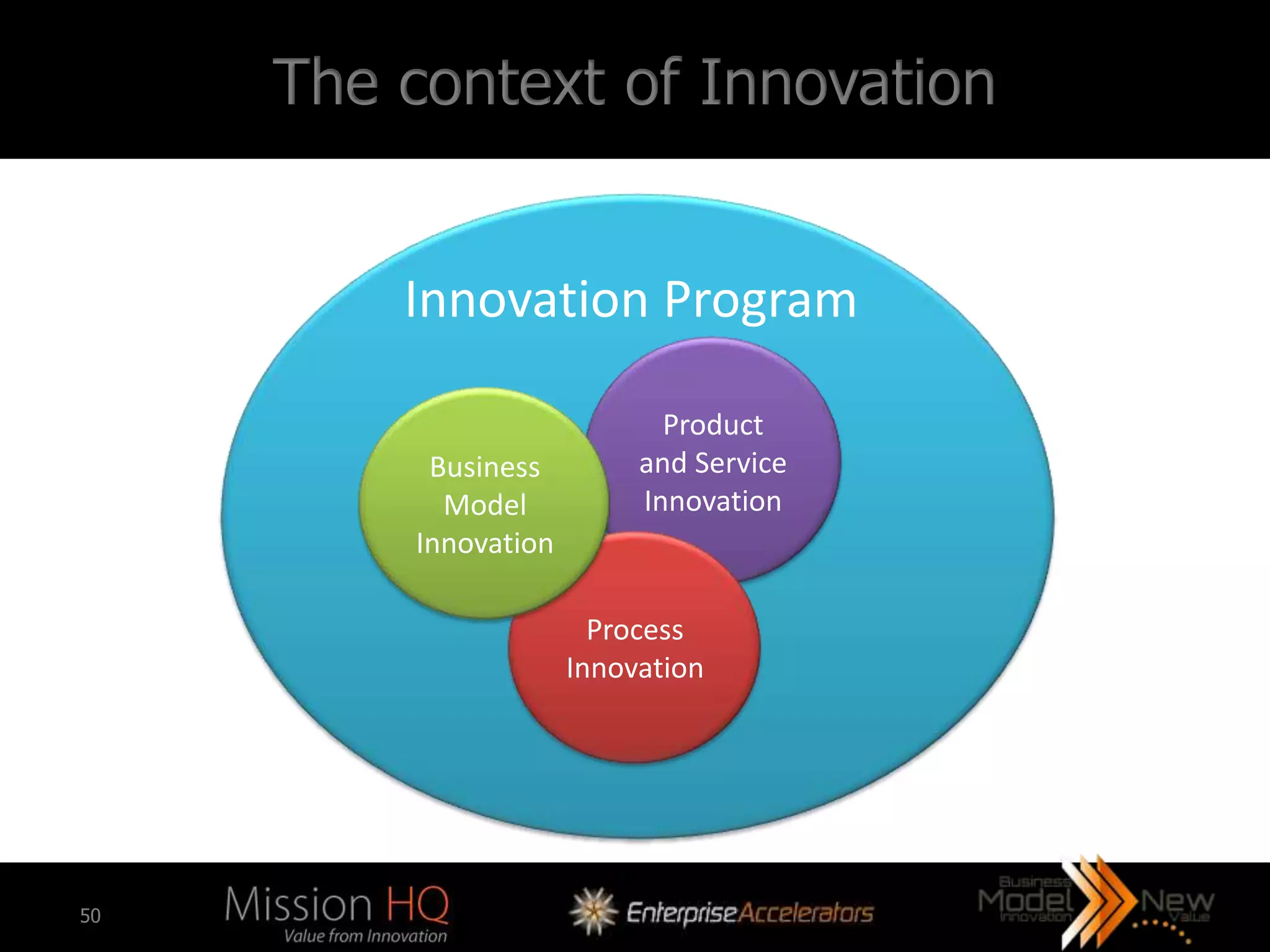
![So where does business model innovation fit
exactly?
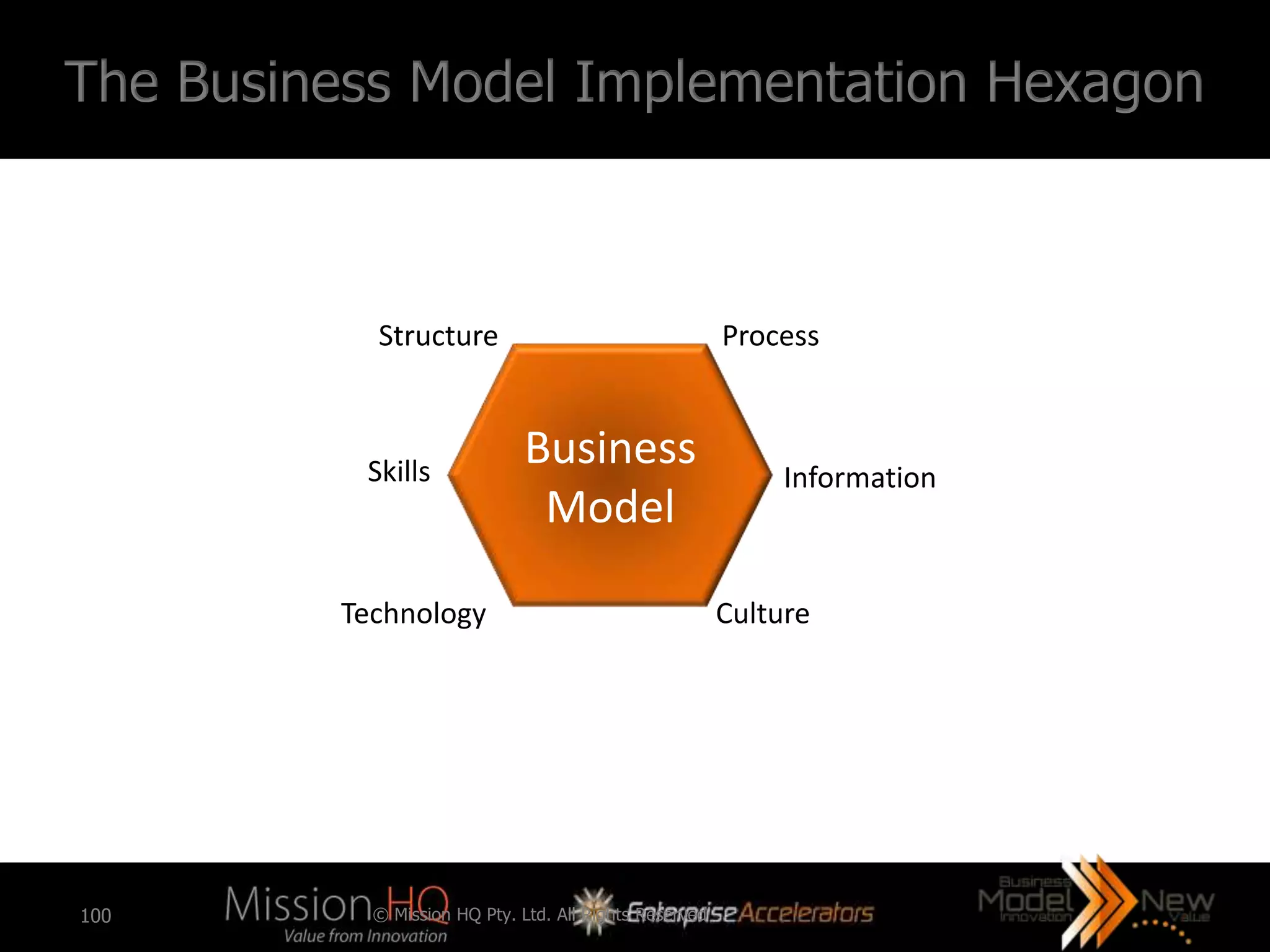
• Business Model Renovation
[BMR] is presented as the
highest level of a strategy for
managing change that usually
cannot be handled by
continuous improvement and re-
engineering methods or
organizational restructuring
(Kovacic, 2001).
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/businessmodelinnovation-newvalue-120305223813-phpapp01/75/Business-model-innovation-new-value-53-2048.jpg)