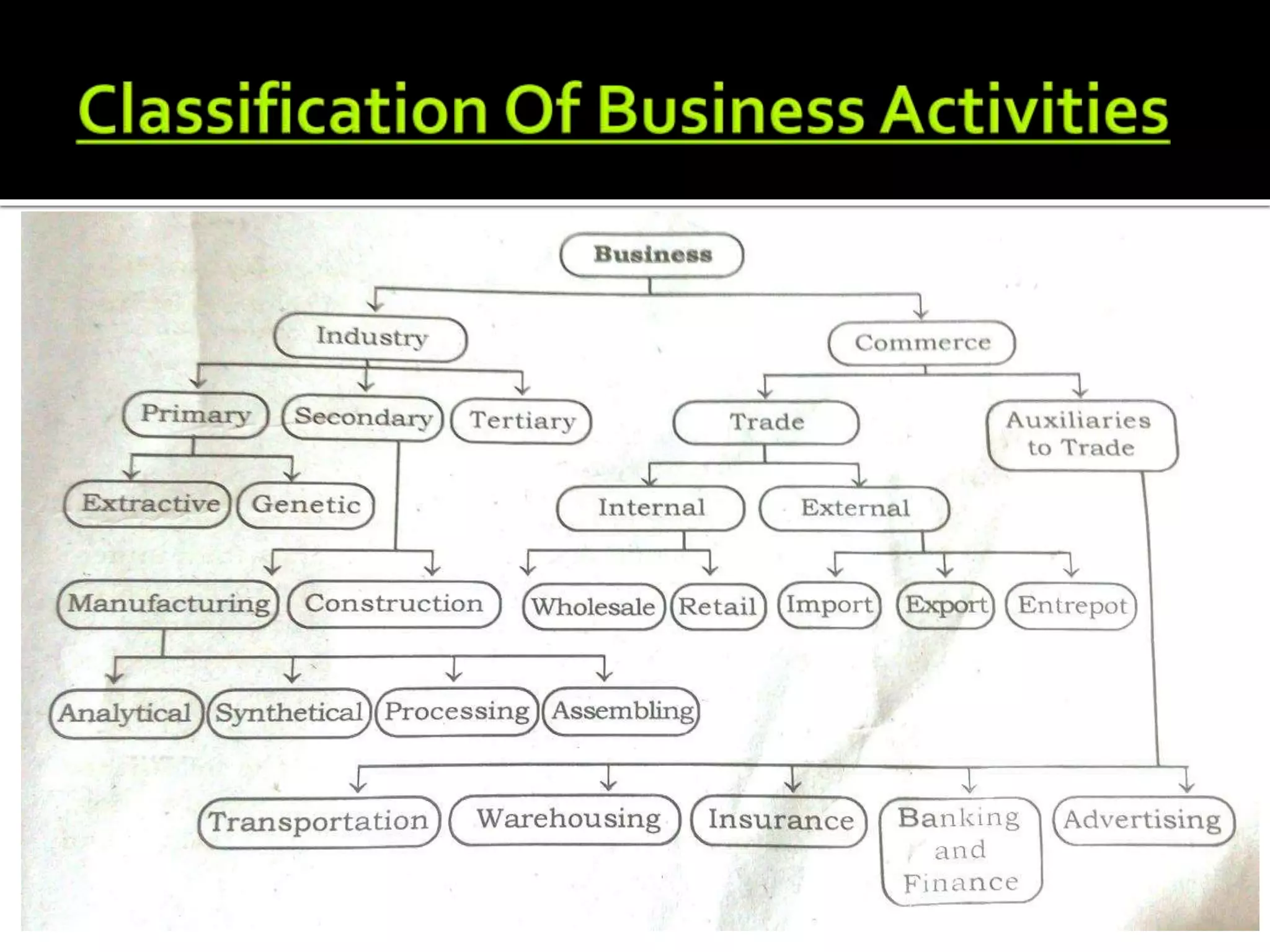
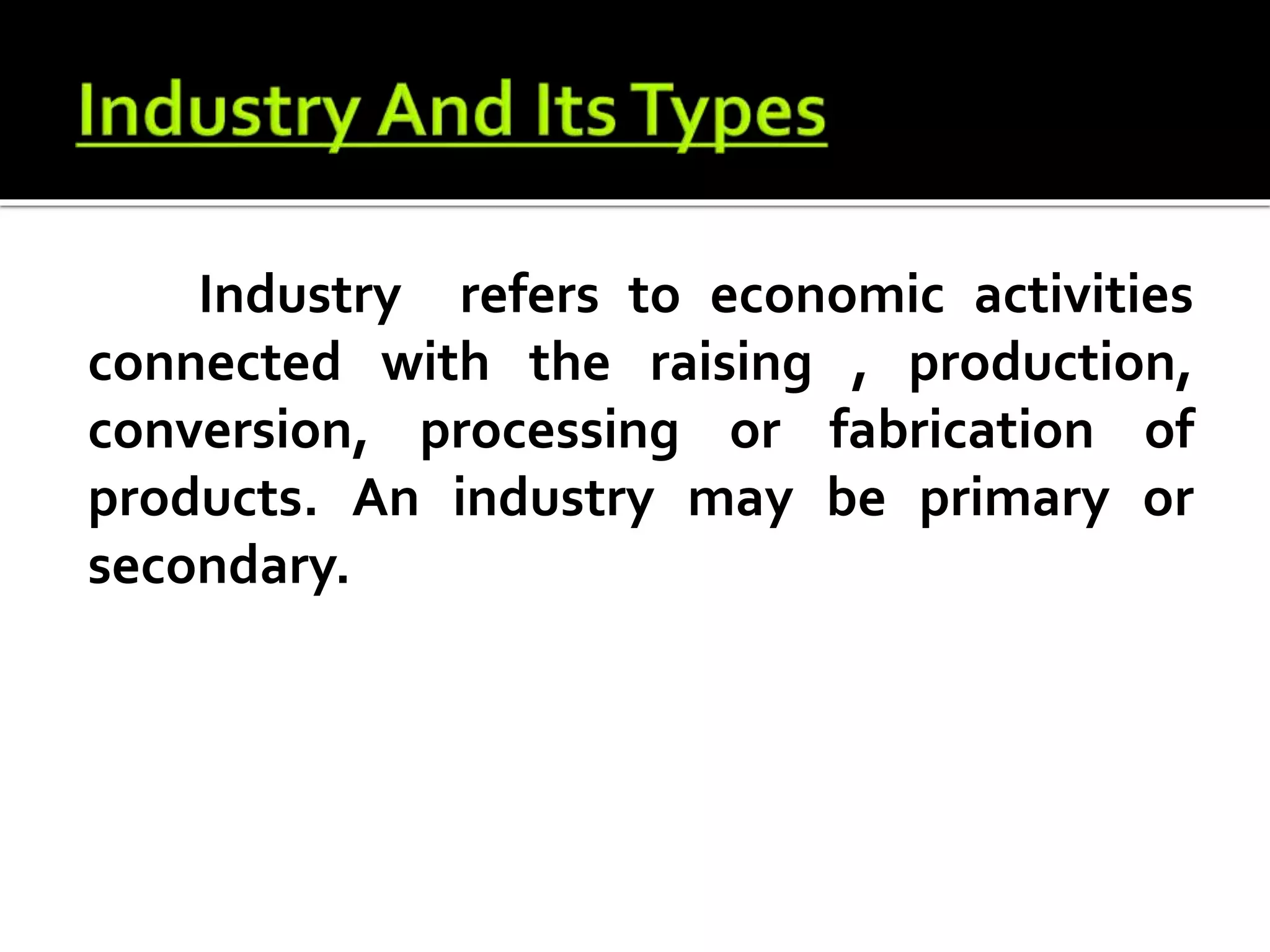
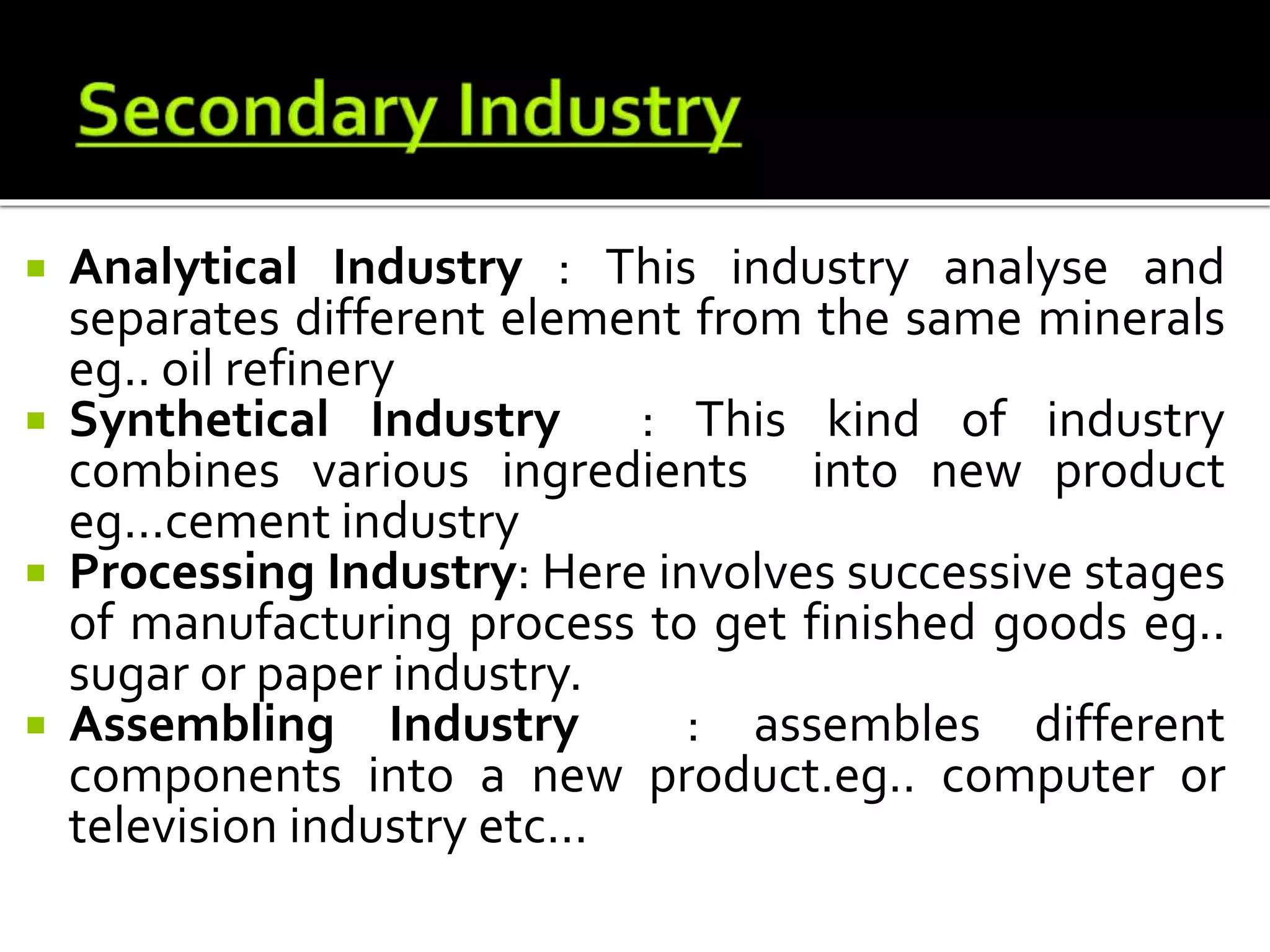
The document discusses different types of occupations and economic activities. It classifies occupations into business, profession, and employment. It also discusses the distinctions between these categories based on factors like nature of work, investment required, risk involved, and code of conduct. The document further explains different types of industries like primary industries involved in extracting and producing natural resources, and secondary industries including manufacturing and construction. It also discusses the role of commerce in facilitating trade through activities like transportation, banking, insurance, and warehousing.