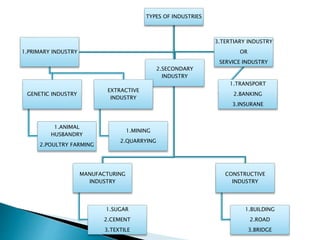
The document discusses business and industry. It defines business as an activity involving production and exchange of goods and services to earn profit. It also defines industry as the production aspect of business that uses natural resources and human labor to create useful goods. The key characteristics of business discussed are that it is an economic activity, involves buying and selling, is a continuous process, aims to earn profit while accepting risk, focuses on customer satisfaction, and is creative, dynamic, and subject to government controls. It also outlines different types of industries like primary, extractive, manufacturing, construction and more.