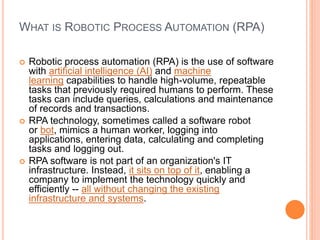
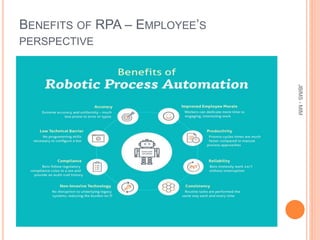
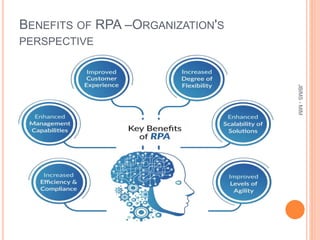
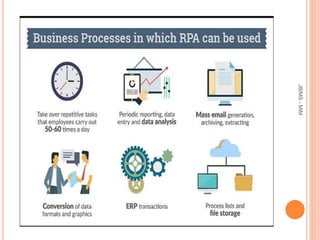
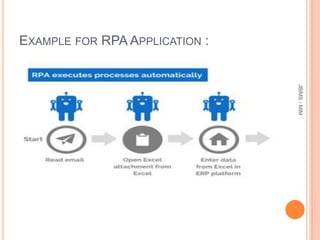
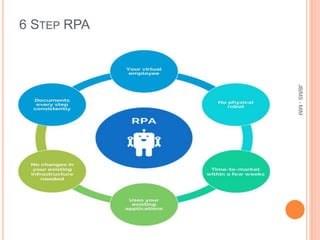
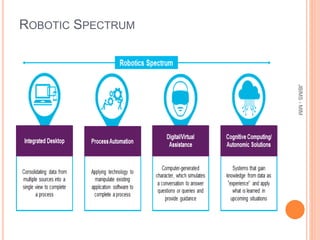
This document provides an overview of robotic process automation (RPA). It defines RPA as using software robots to automate repetitive tasks previously done by humans. The document discusses the evolution and benefits of RPA, including improved efficiency, cost savings, and employee productivity. It also outlines common RPA applications, implementation steps, top vendors, and considerations for C-level executives when adopting an RPA strategy. The market for RPA is expected to reach $5 billion by 2024 due to increased adoption by organizations seeking to enhance capabilities and reduce costs through automation.