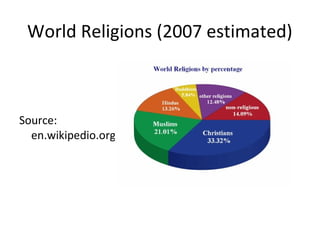
This document provides an introduction to ethics. It defines ethics as a set of principles that govern behavior and determine what is good and bad or right and wrong. Ethics comes from the Greek word for character. It covers moral bases, rights and responsibilities, and guides how to live a good life. Sources of ethics include religion, tradition, cultures and philosophies. Business ethics deals with right and wrong in business contexts. Work ethics applies morals and ethics to work situations. Factors influencing work ethics include personal values, social values, organizational/industry norms, and government rules and regulations. Values are important principles that influence behavior, while norms are expectations for proper behavior. Attitudes represent people's approaches and can be positive or negative.