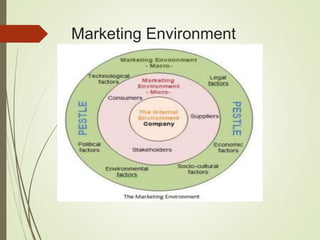
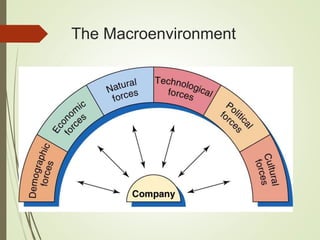
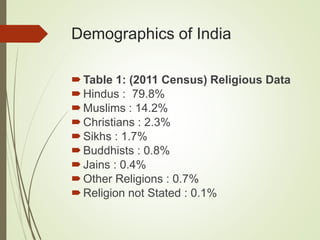
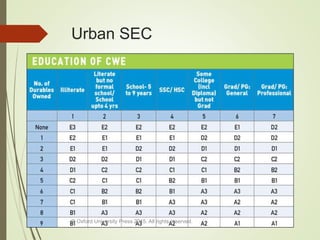
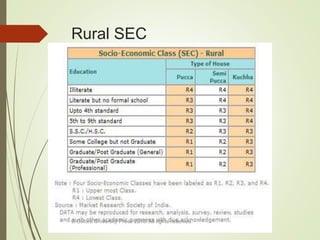
This document summarizes the key elements of a company's marketing environment including the microenvironment and macroenvironment. The microenvironment includes suppliers, customers, competitors, and publics. The macroenvironment includes the demographic, economic, technological, political/legal, and cultural forces. It provides details on India's demographic environment including population statistics, religious groups, languages, and geographic distribution. It also describes factors in India's economic environment like income distribution, urban/rural socioeconomic classes, and key economic indicators. The natural, technological, political, and cultural environments that influence marketing are also outlined.