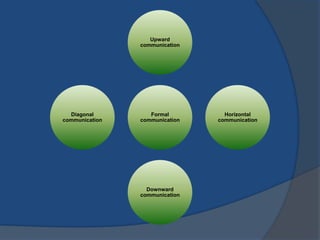
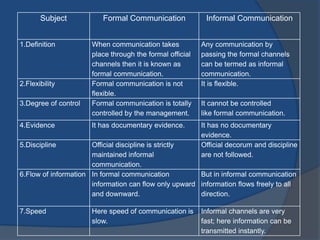
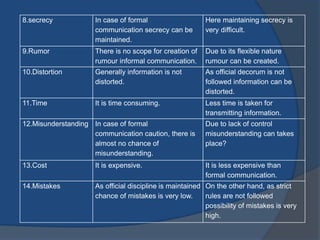
This document discusses formal and informal communication in organizations. Formal communication follows regulated channels and is recorded, including downward communication from superiors to subordinates and upward communication from subordinates to superiors. Informal communication occurs through unofficial grapevines and does not follow authority lines. While informal communication can distort information and lead to rumors, it also provides alternative information flow and emotional relief. The document also provides tips for improving communication effectiveness such as clarifying ideas before communicating and ensuring proper feedback.