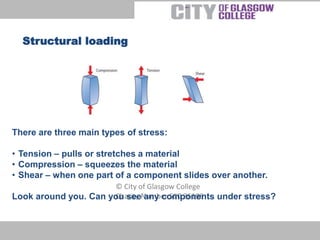
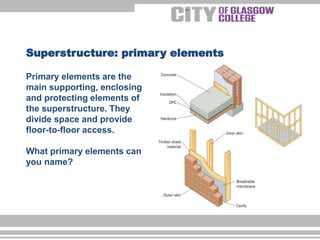
There are three main types of structural loading: tension, compression, and shear. Tension pulls or stretches material, compression squeezes material, and shear occurs when one part of a component slides over another. All buildings have a substructure below ground, including foundations, and a superstructure above ground. Primary elements of the superstructure are the main supporting, enclosing, and protecting elements like floors and walls that divide space and provide access between floors. Secondary elements are not essential for strength but provide specific functions like completing openings in walls. Finishing elements are the final surfaces of a building like flooring or wall finishes that can be functional or decorative.