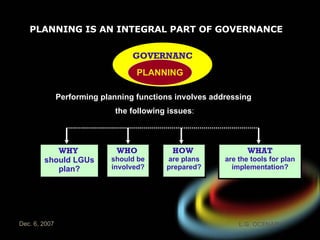
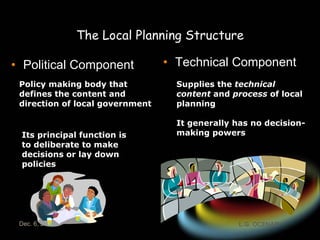
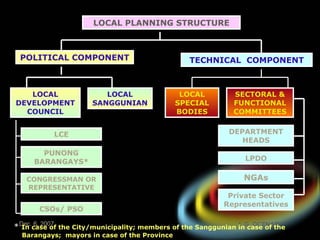
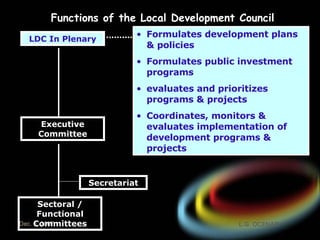
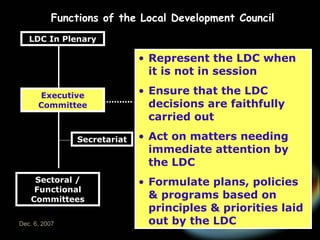
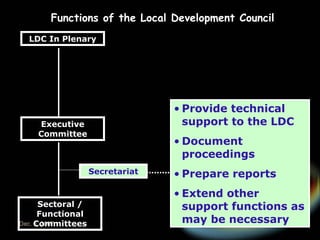
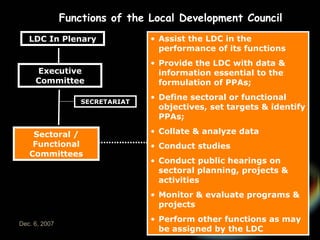
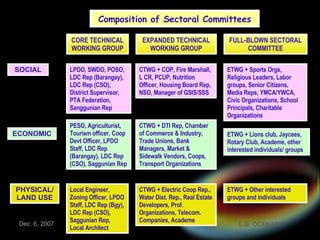
The document introduces the rationalized planning system for local governments in the Philippines. It describes the current state of planning as lacking vertical and horizontal linkages. It proposes establishing a local planning structure with political and technical components to address planning issues like who should plan, how plans are prepared, and how they can be implemented. The local development council would be the policy making body, with sectoral committees providing technical input. The planning and development office would formulate integrated development plans, conduct research, and monitor implementation.