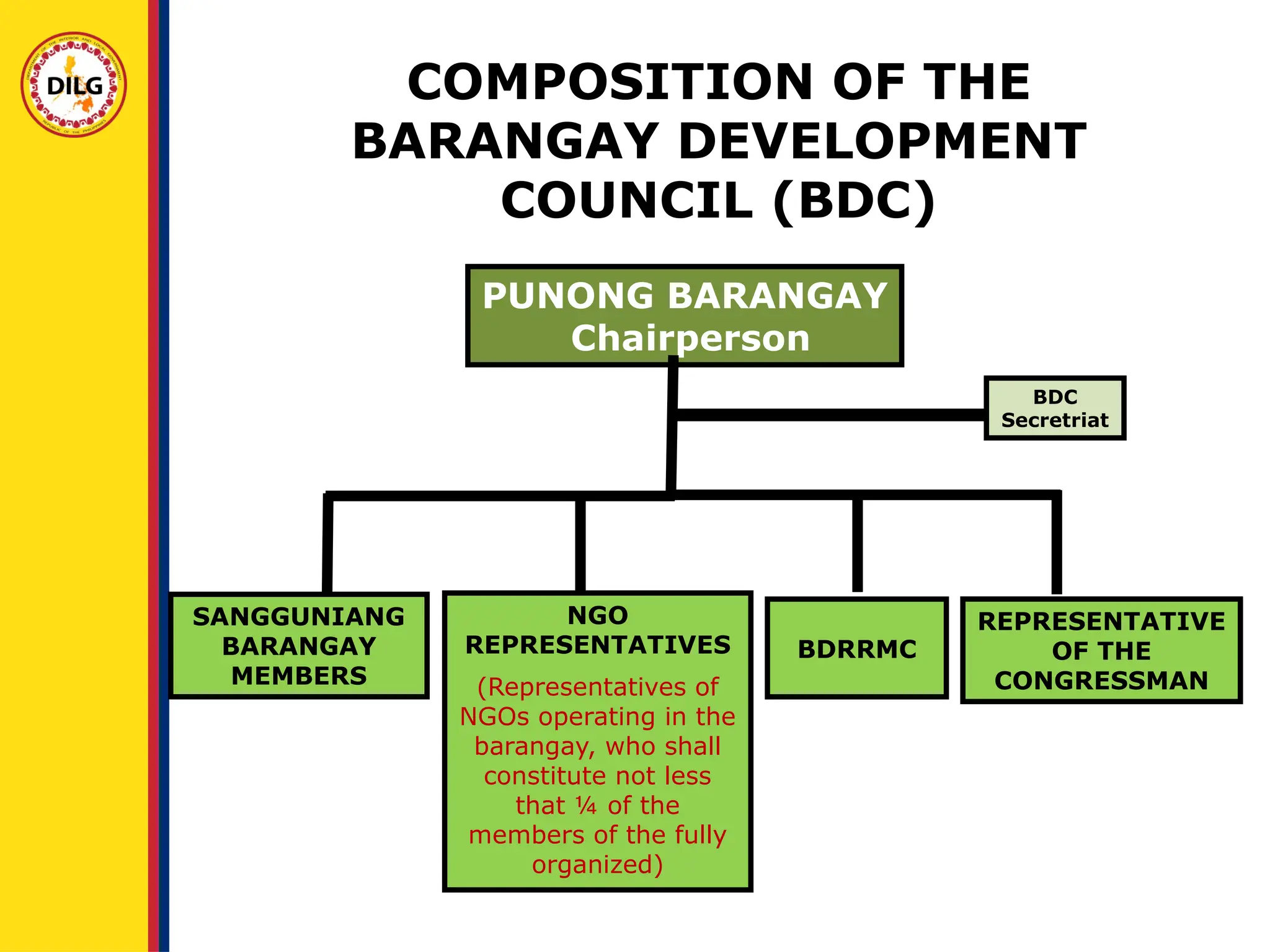
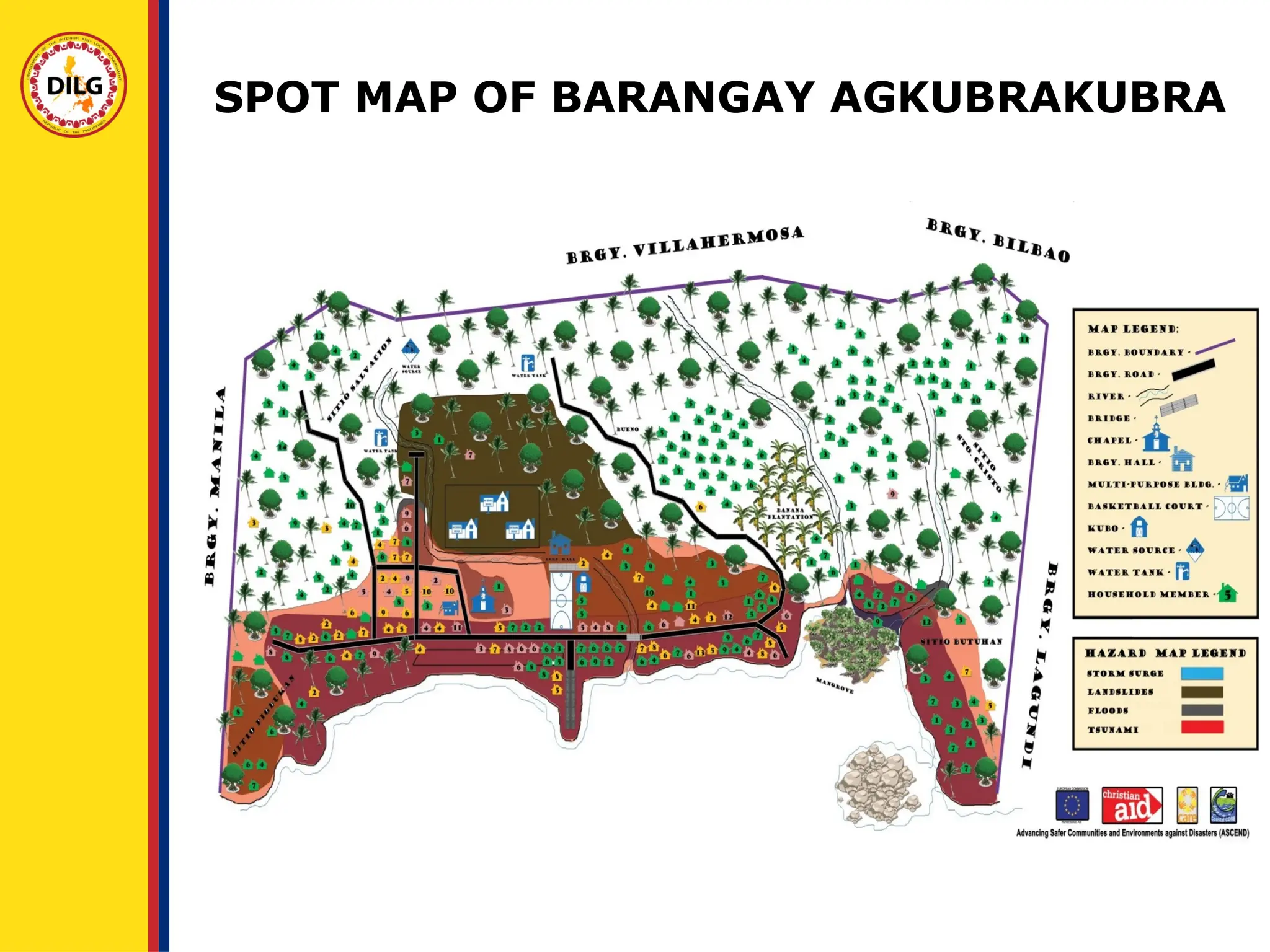
It serves as a guide in attaining the vision of the barangay;
It protects common good and promotes the general welfare of constituents;
It maximizes the utilization of limited resources; and
It serves as a basis for higher local development councils in integrating barangay priority projects