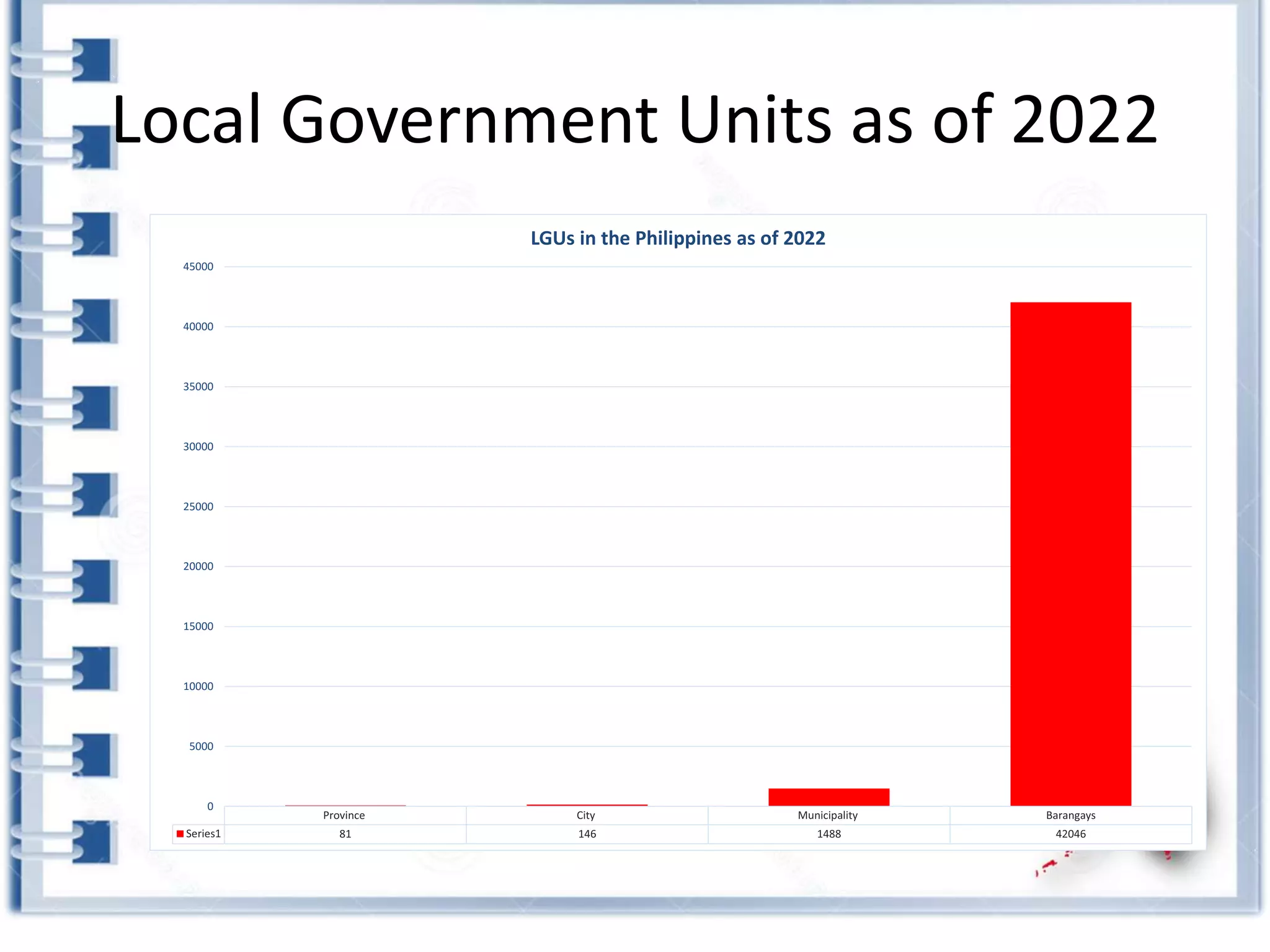
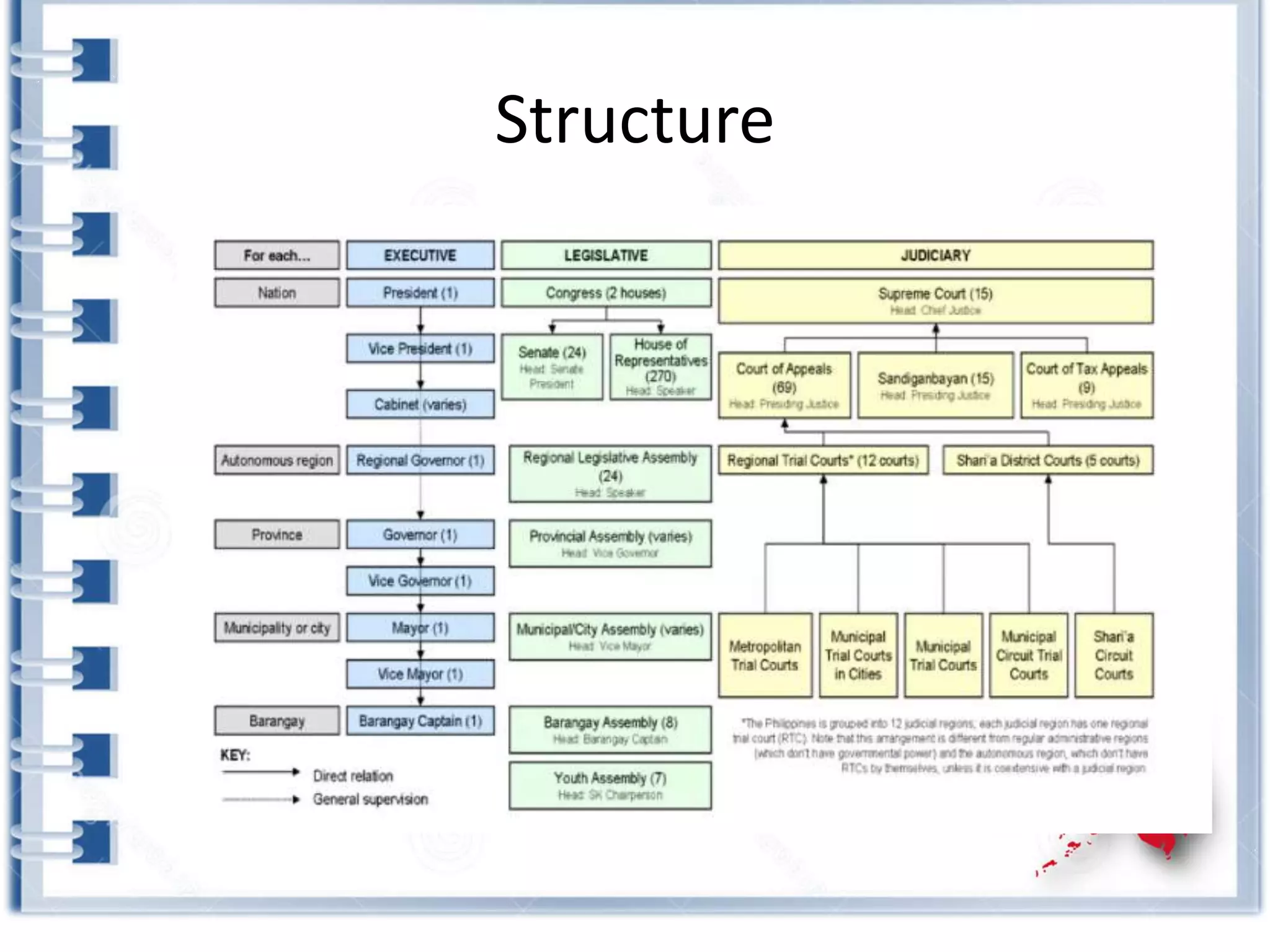
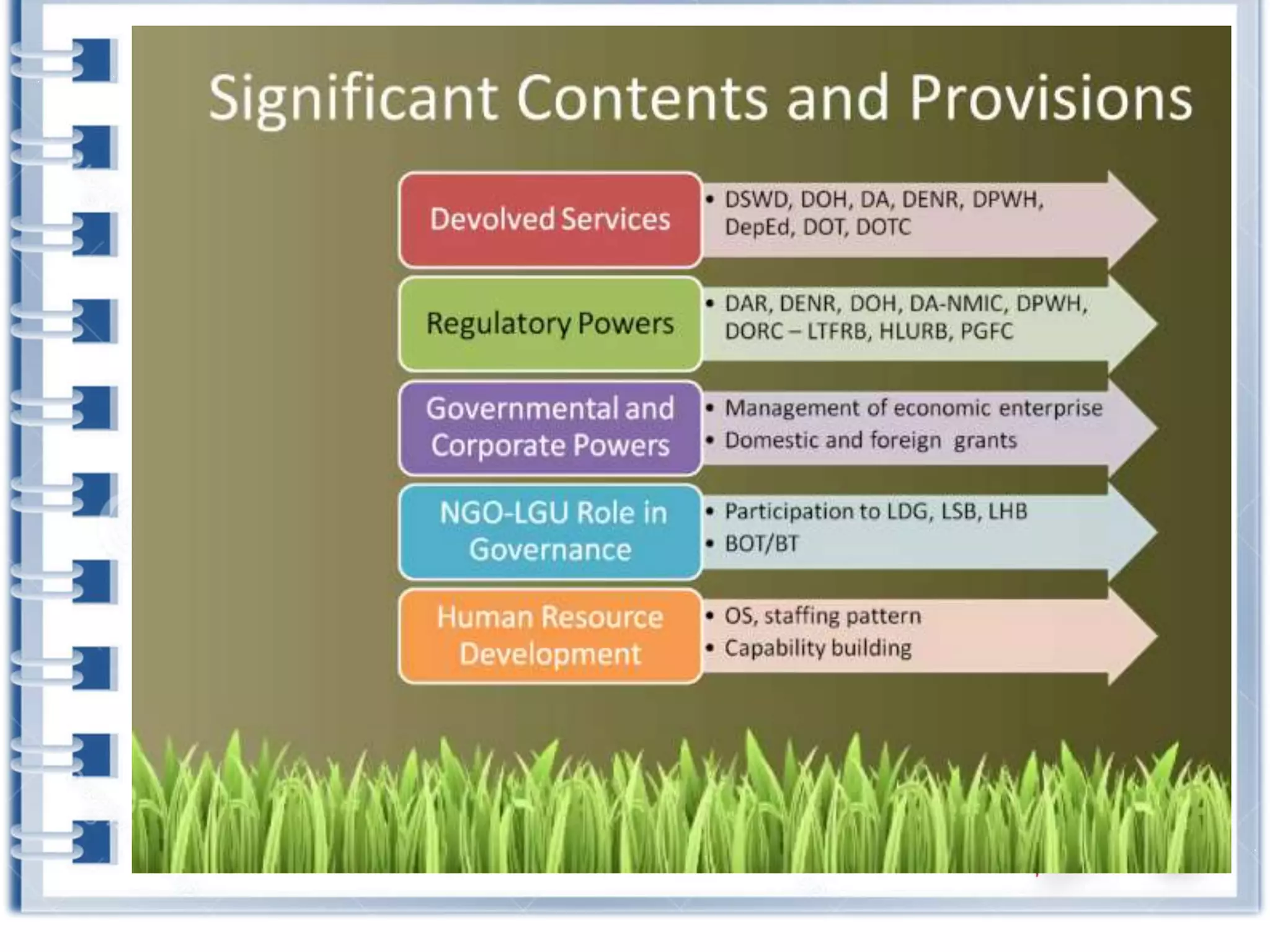
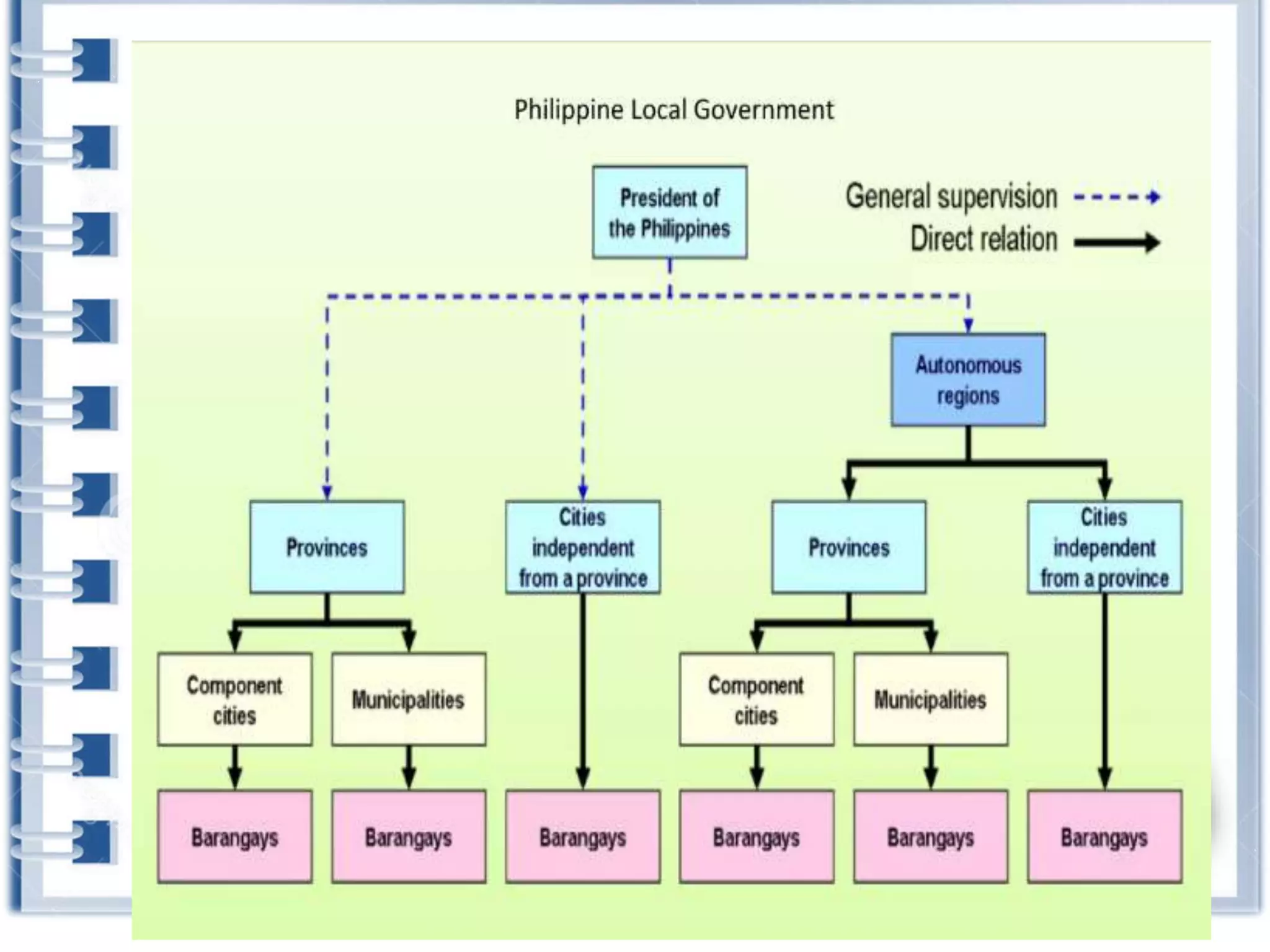
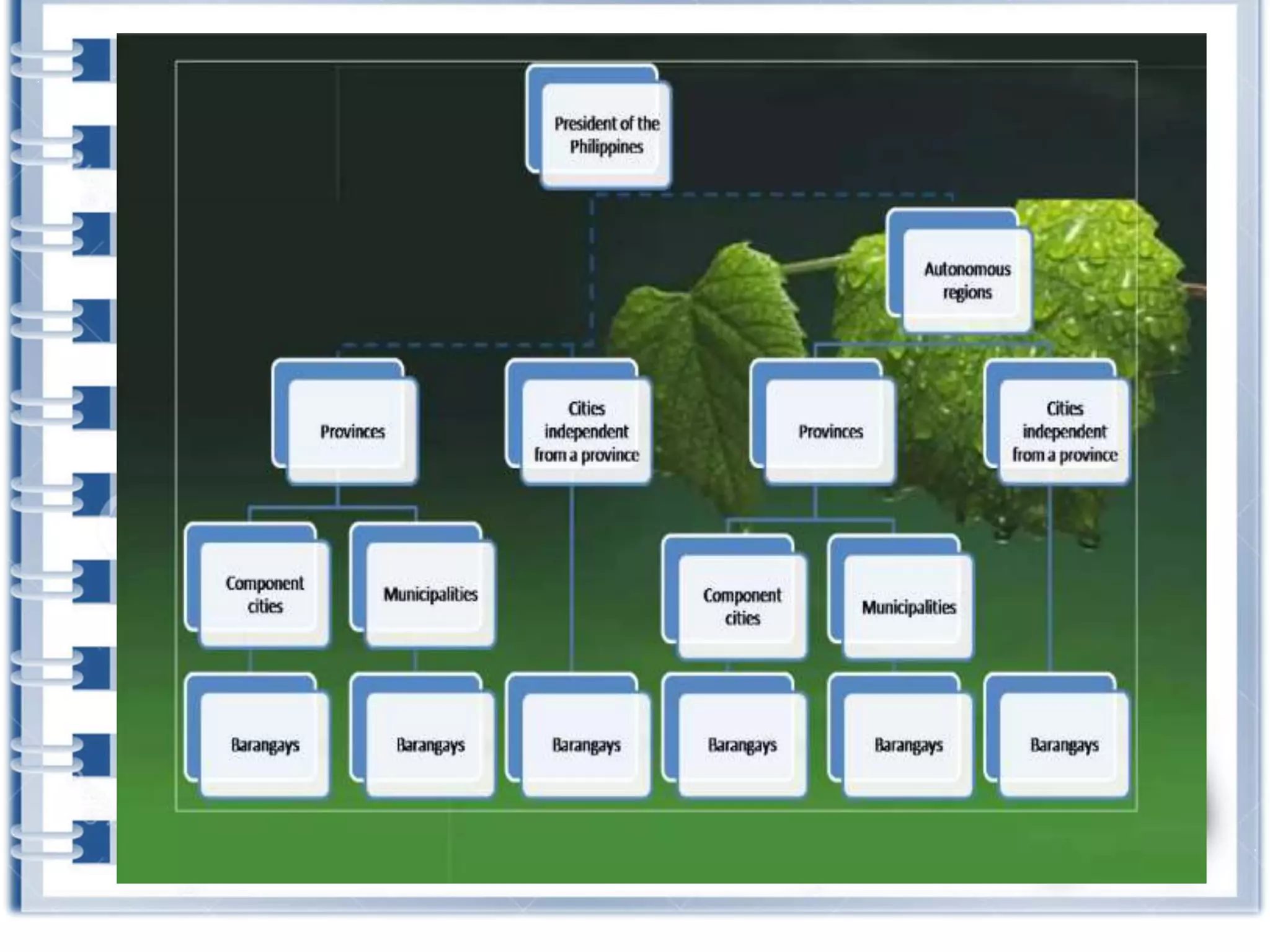
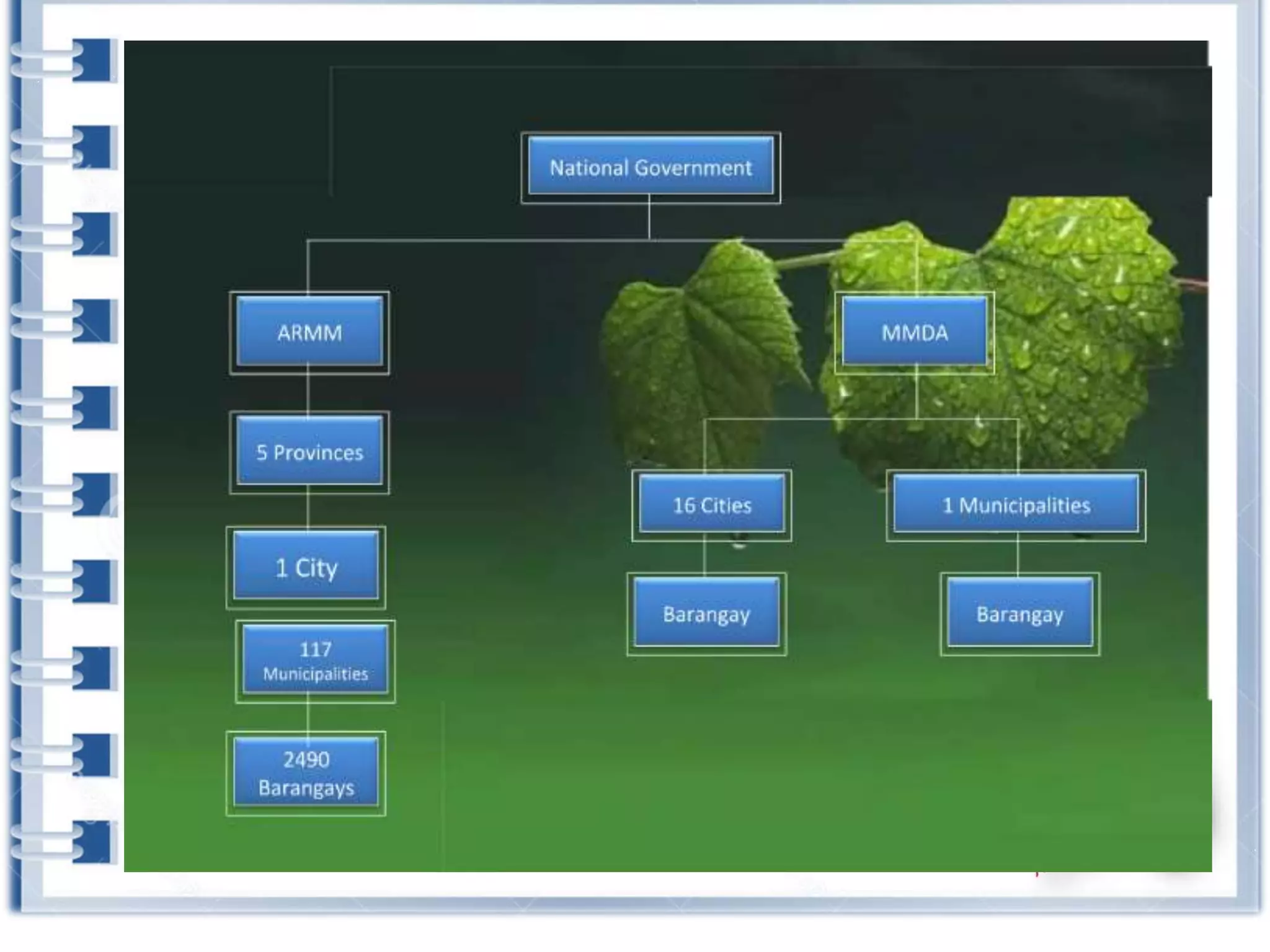
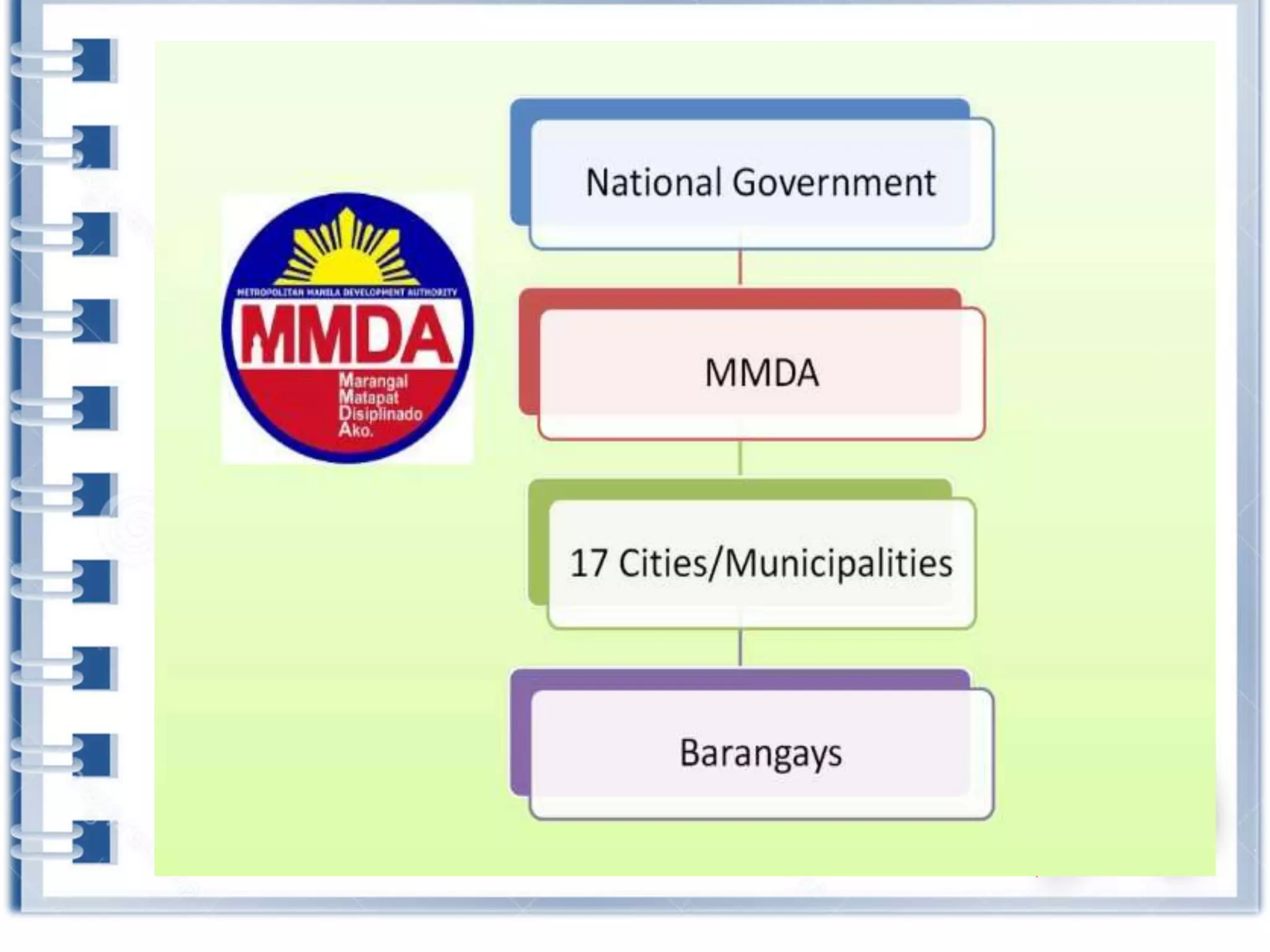
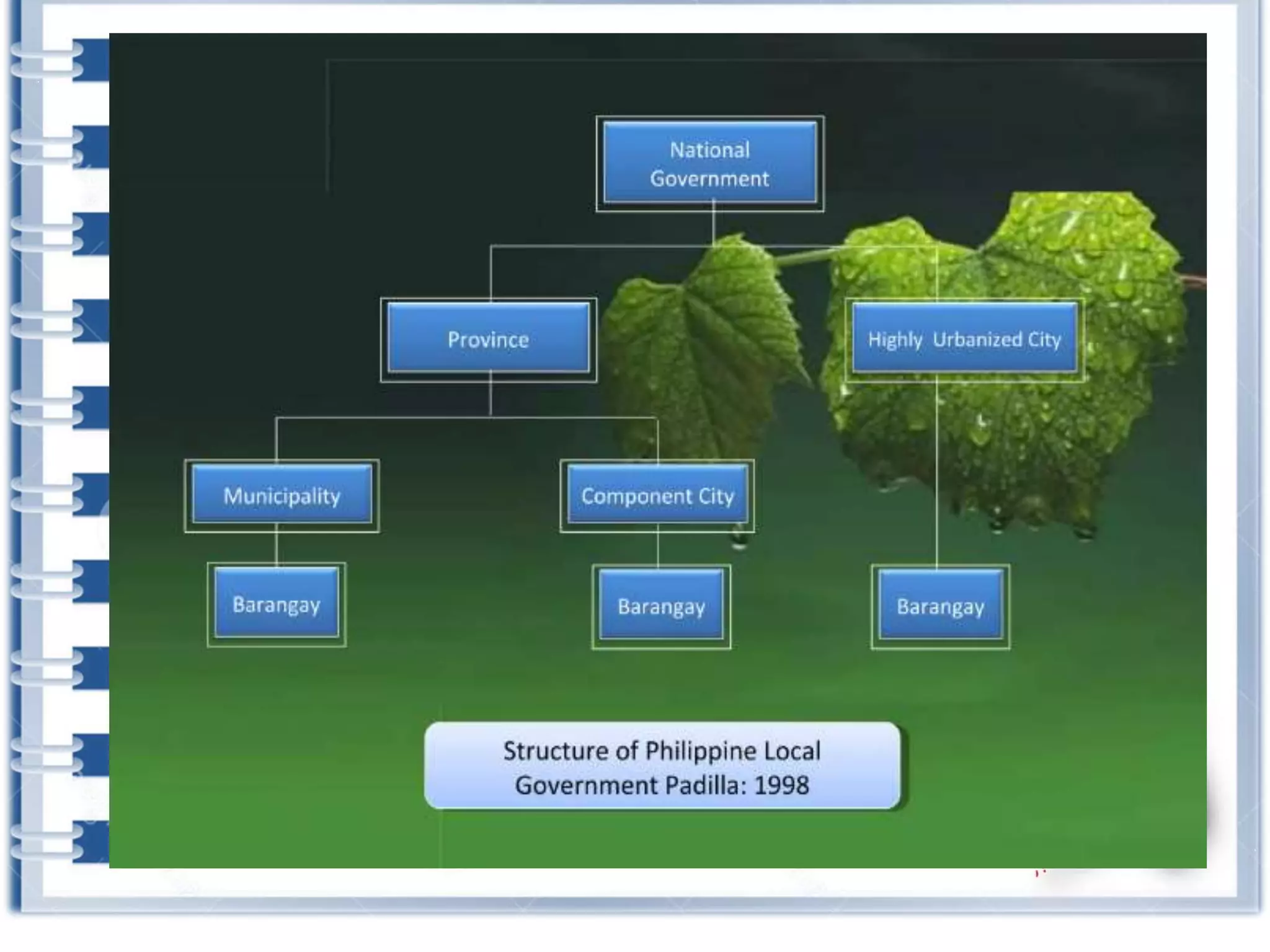
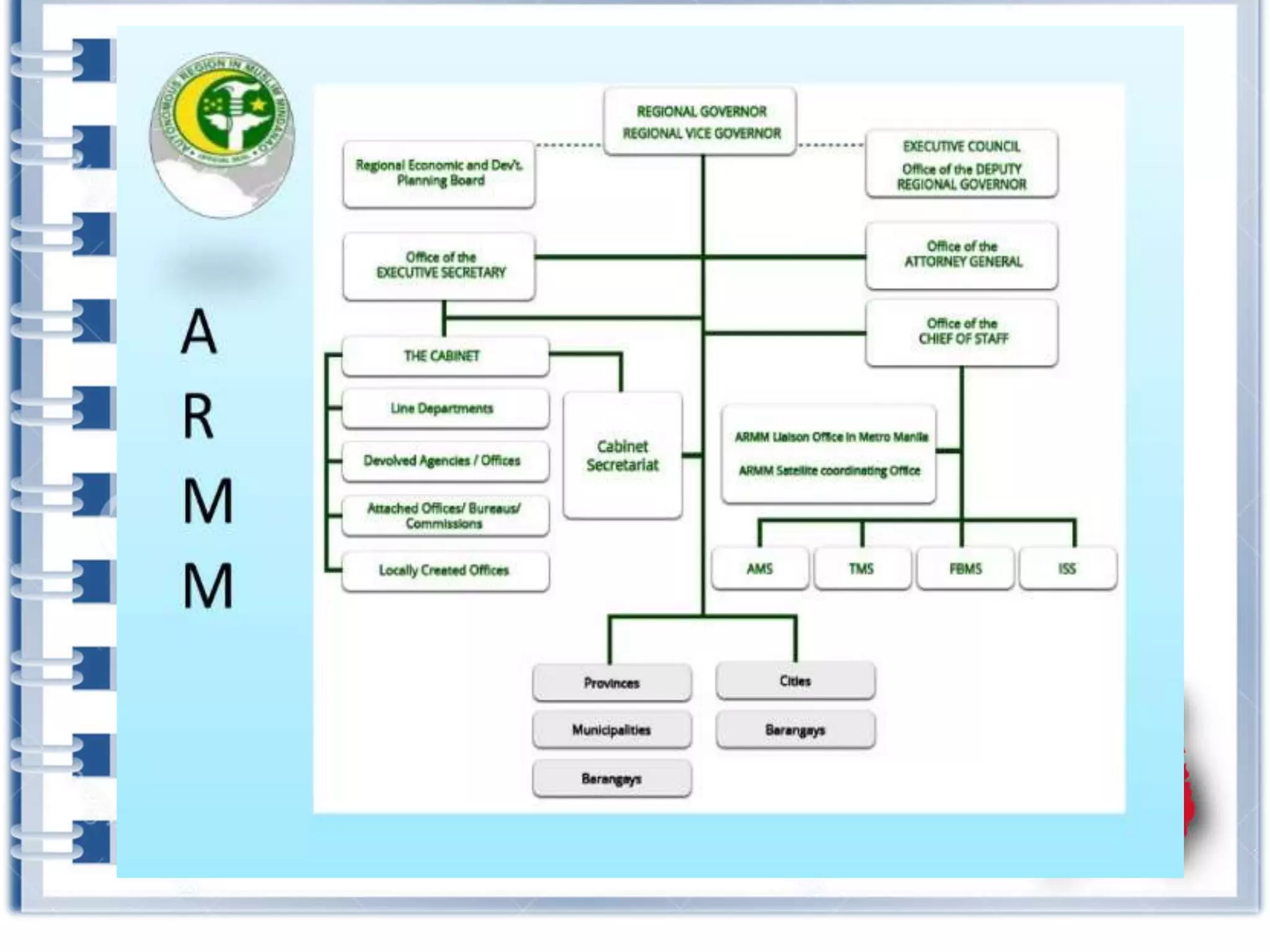
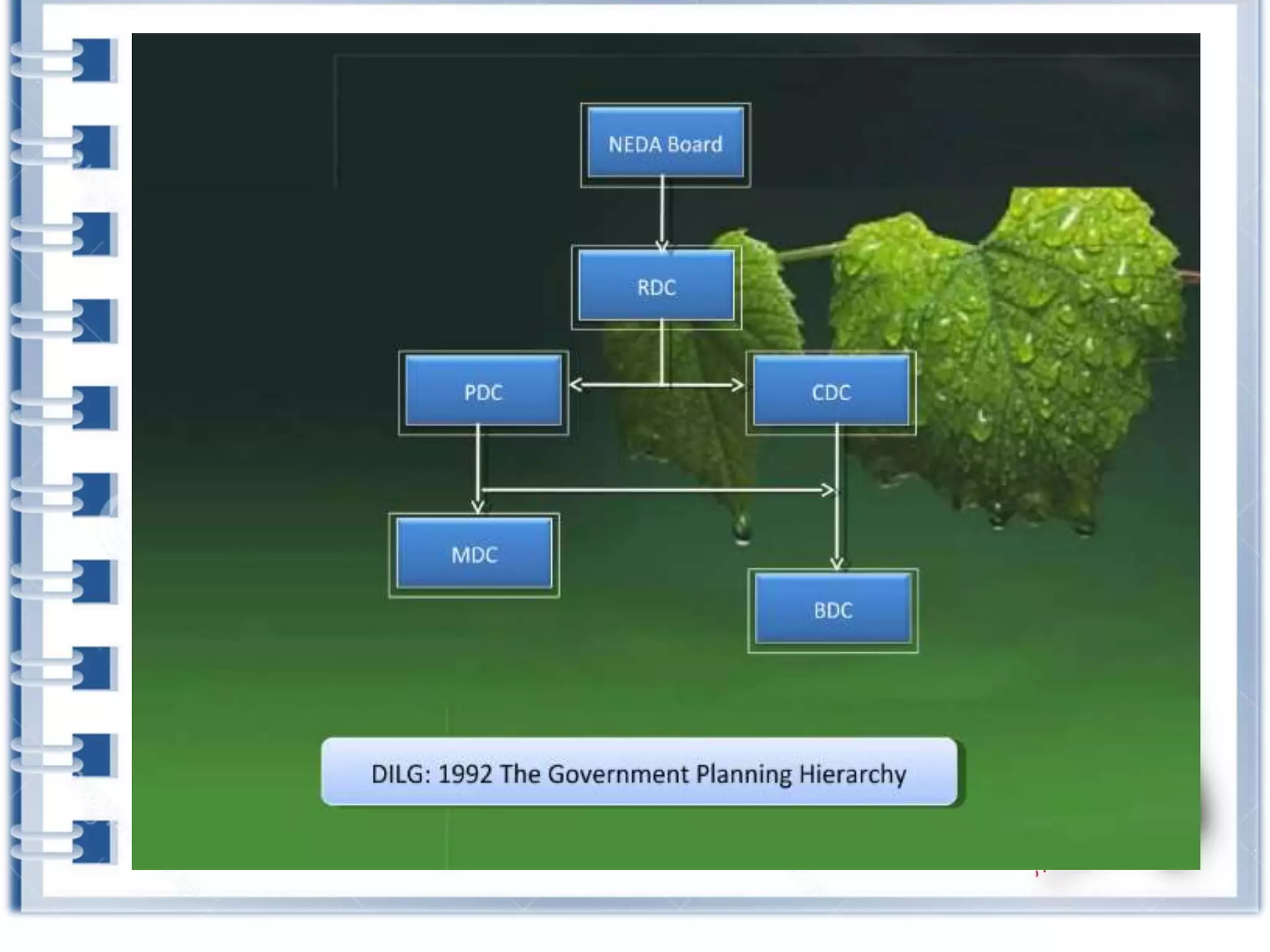
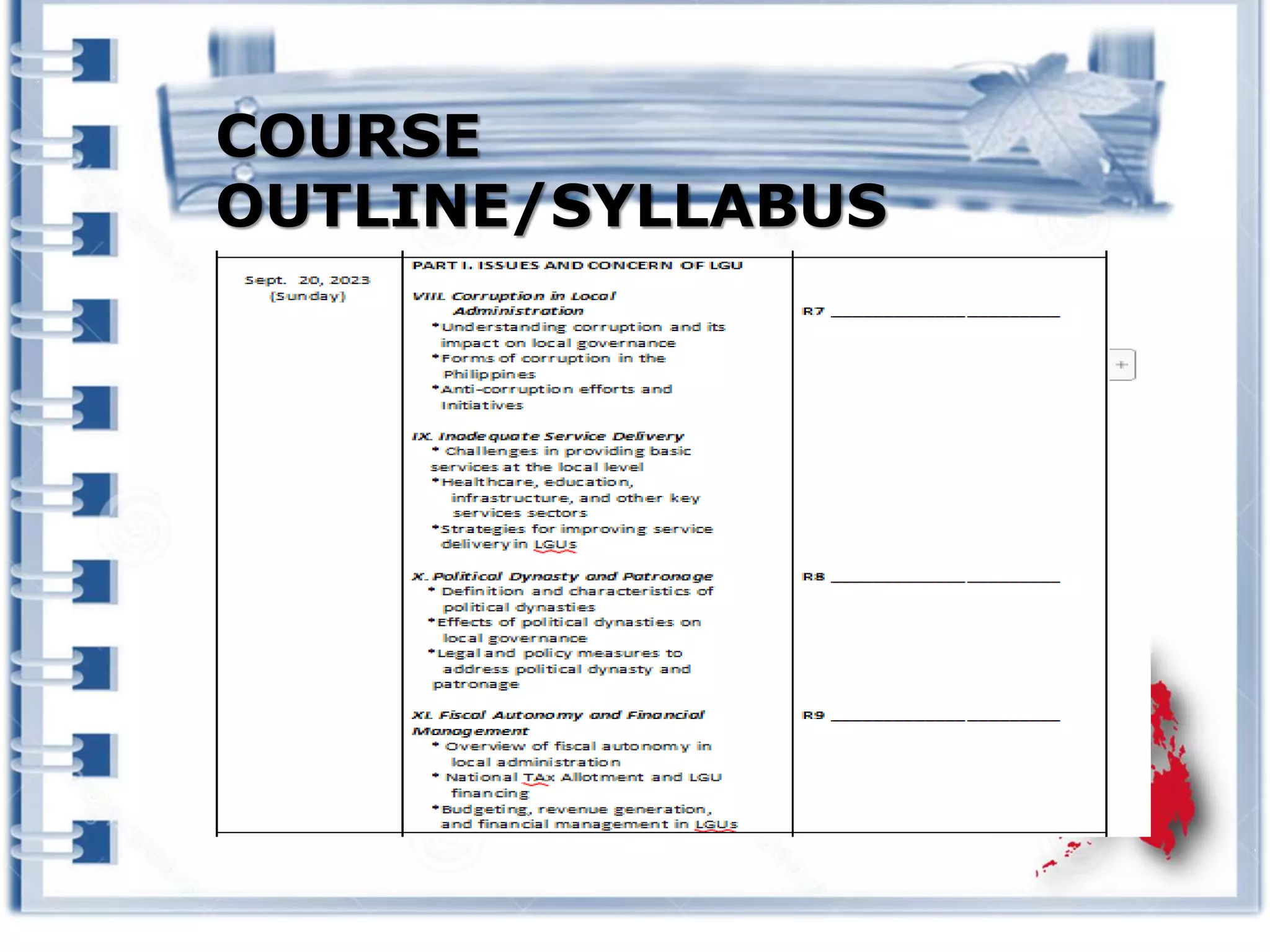
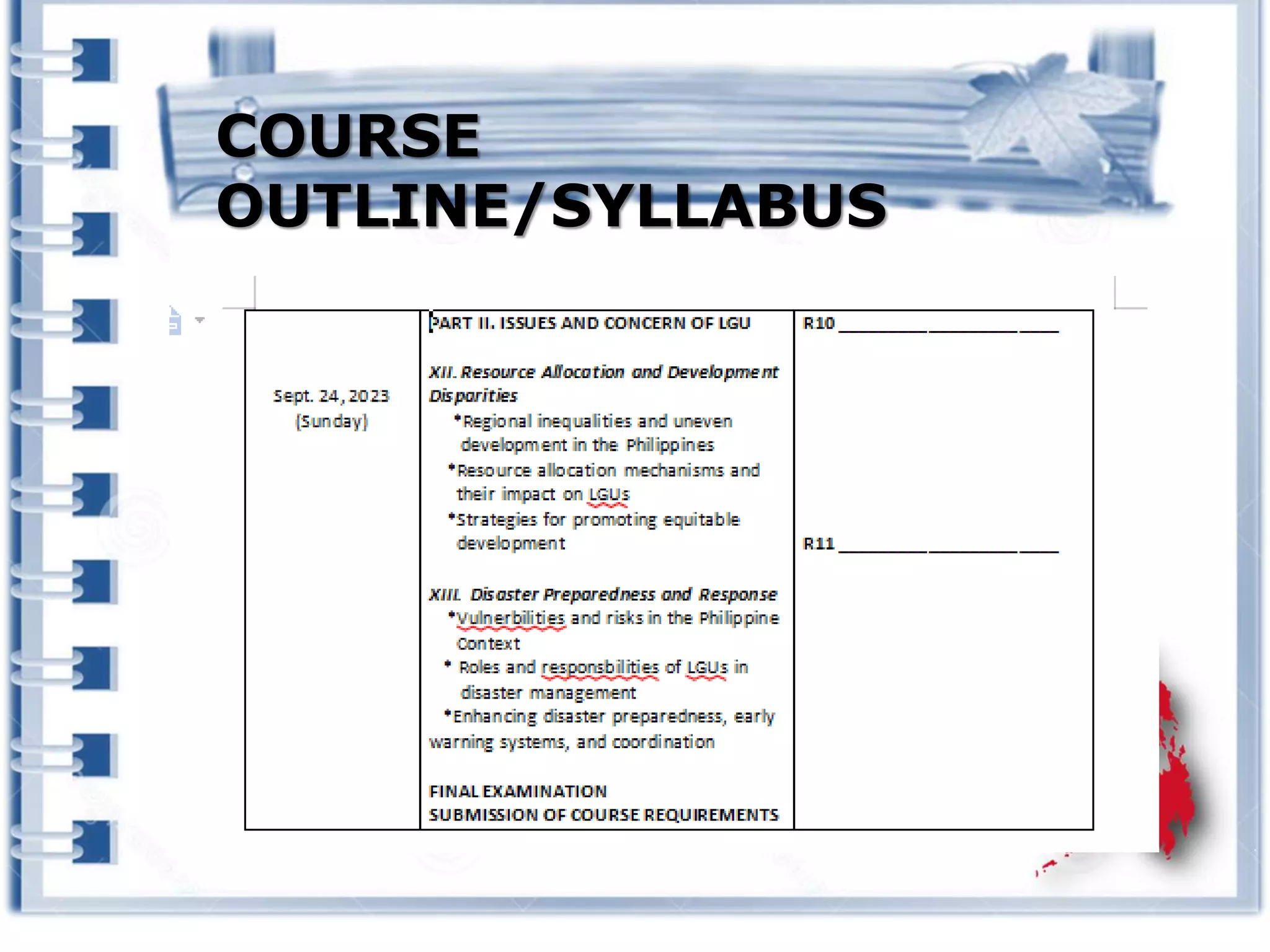
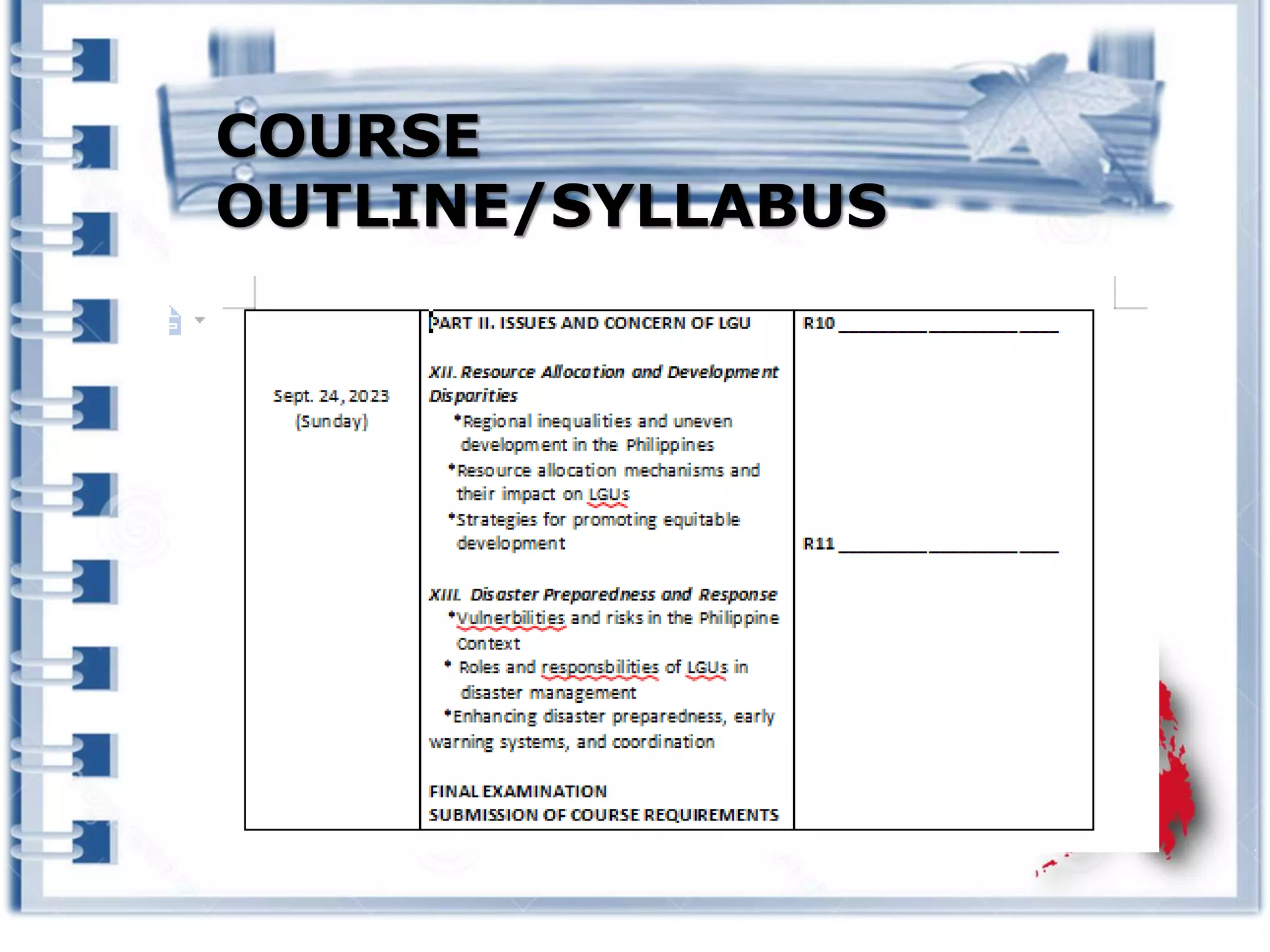
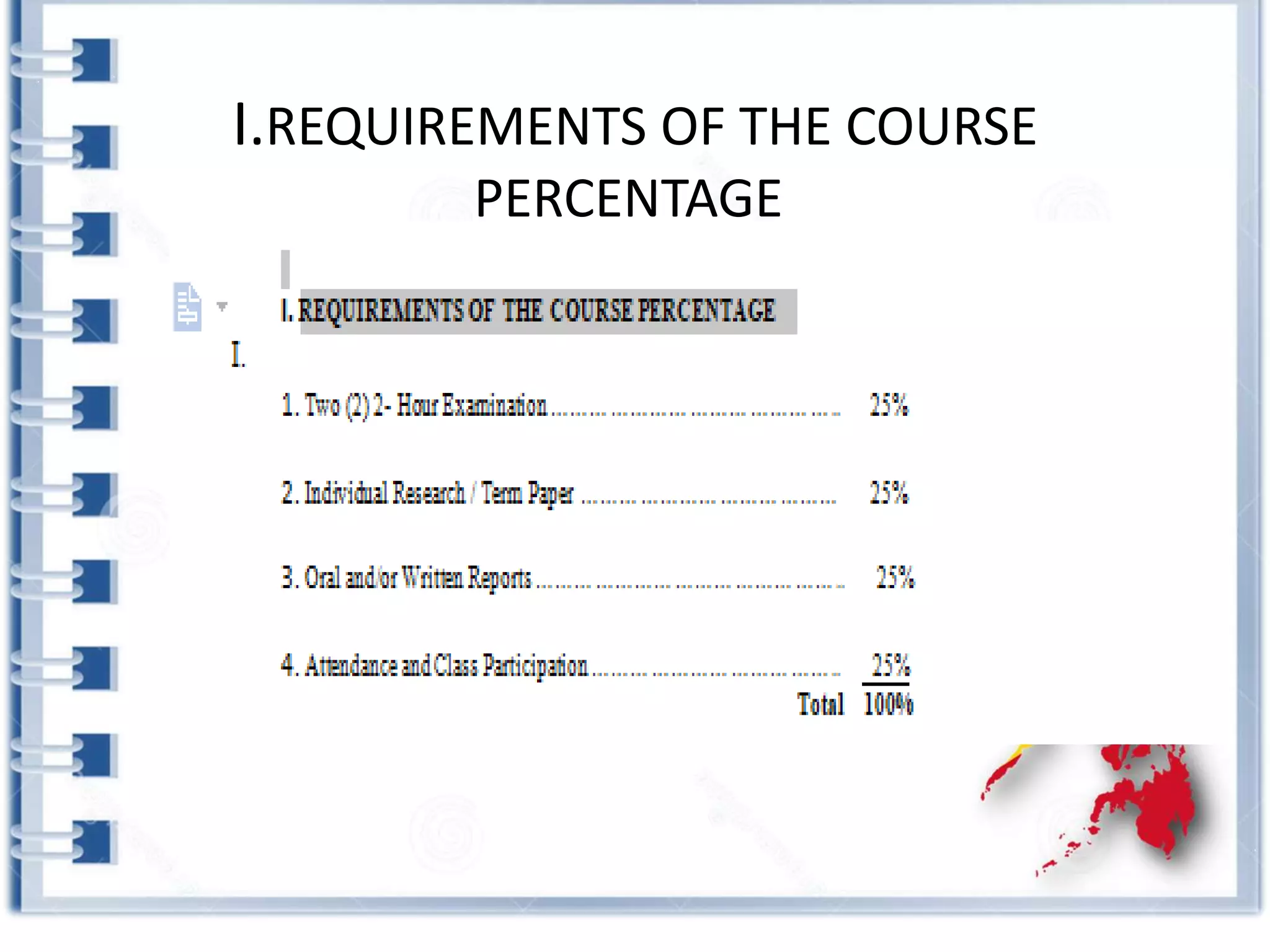
This course provides an exploration of current issues in local administration and government. It examines challenges, trends, and best practices. Topics covered include policy development, service delivery, fiscal management, community engagement, and ethics. Students will analyze case studies, participate in discussions, and complete exercises to develop a comprehensive understanding of the complexities of local administration.