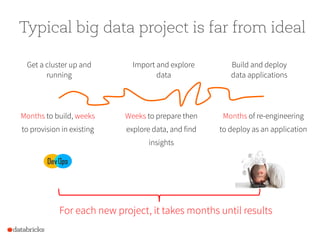
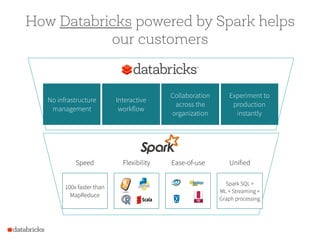
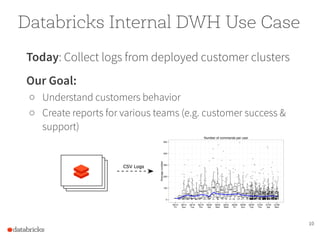
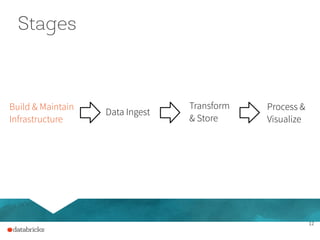
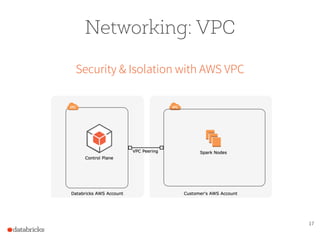
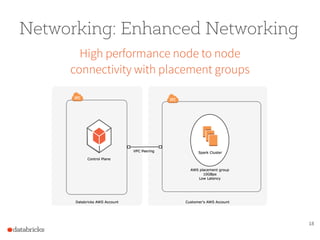
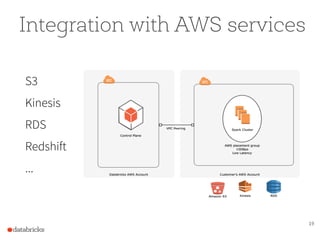
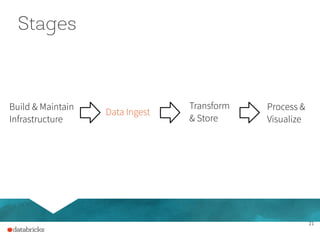
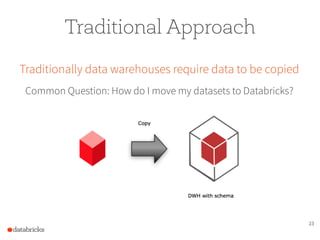
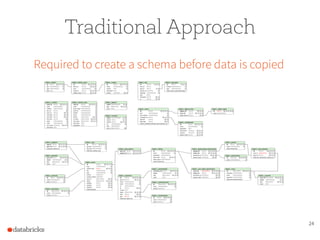
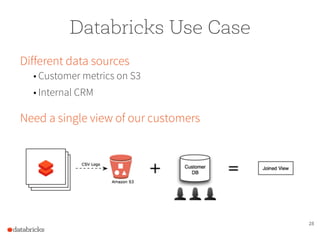
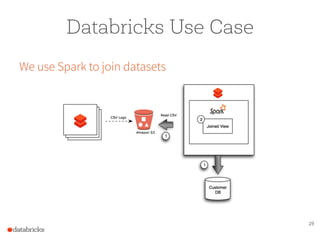
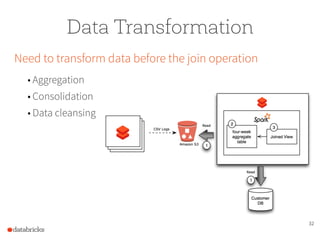
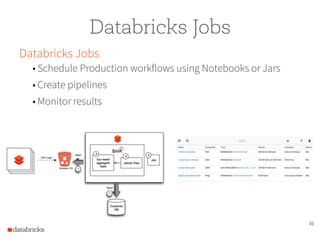
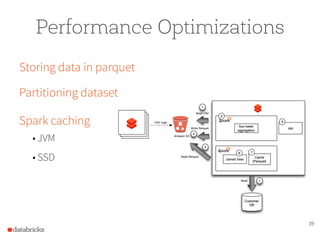
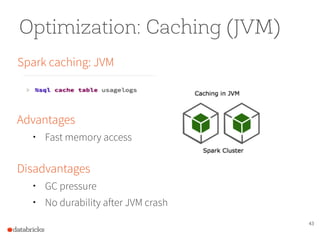
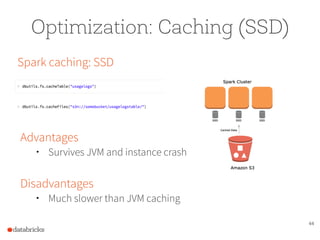
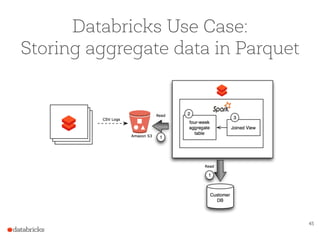
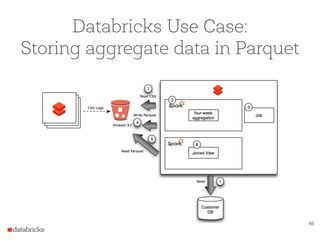
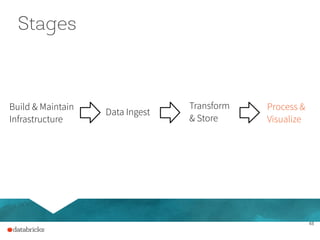
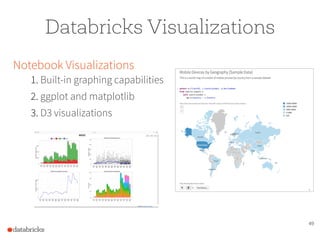
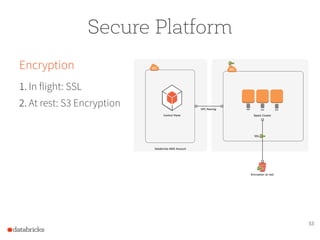
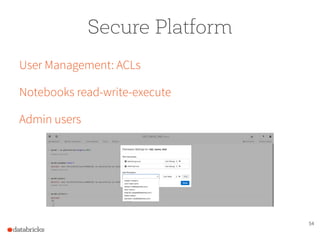
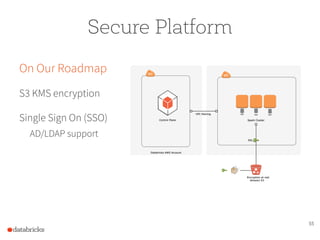
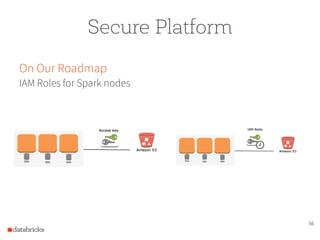
The document presents a comprehensive overview of building a high-performance data warehousing platform using Databricks, focusing on key aspects such as infrastructure, data ingestion, ETL processes, and performance optimizations. It highlights the advantages of Databricks over traditional data warehousing methods, emphasizing its speed, flexibility, and ease of use powered by Apache Spark. Additionally, the content addresses security measures, integration with AWS services, and real-world use cases of the platform.