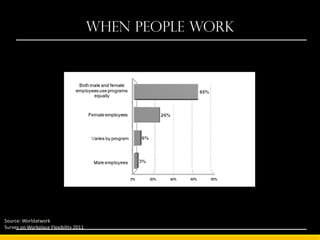
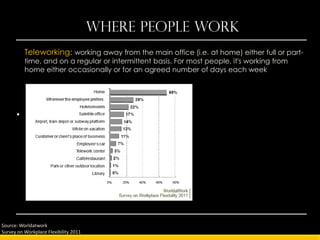
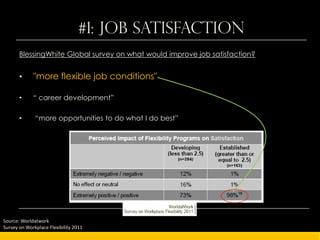
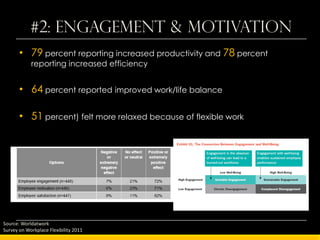
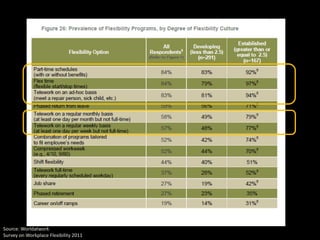
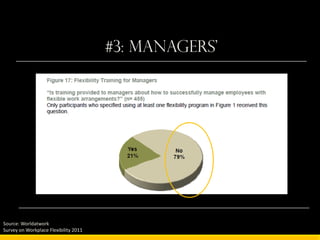
The document outlines the concept of workplace flexibility, emphasizing changes in when, where, and how people work to meet both individual and organizational needs. Various flexible work arrangements like telecommuting, job-sharing, and compressed work schedules are discussed, alongside the benefits such as increased job satisfaction, productivity, and work-life balance. It also highlights the importance of management training and addressing obstacles to effectively implement flexibility in the workplace.