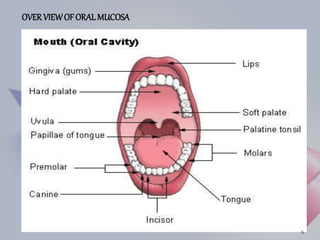
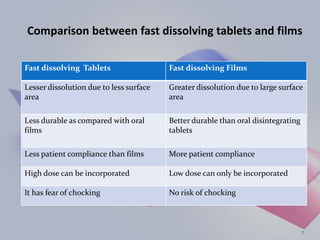
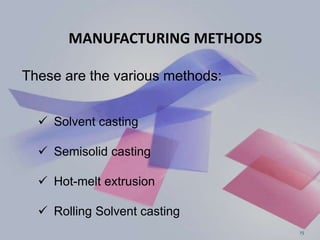
This document provides an overview of fast dissolving oral thin films (FDOTF). It begins with an introduction describing FDOTFs as thin polymeric strips that dissolve quickly in the mouth without water. The document then covers special features of FDOTFs, compares them to fast dissolving tablets, and describes their mechanism of action, classifications, properties, advantages, disadvantages, formulations, manufacturing methods, evaluation, and concludes with references.