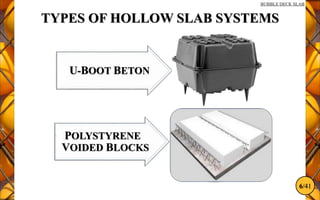
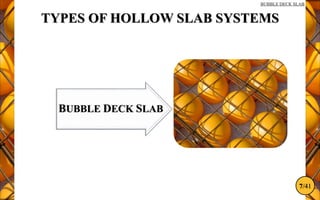
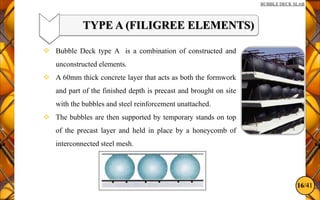
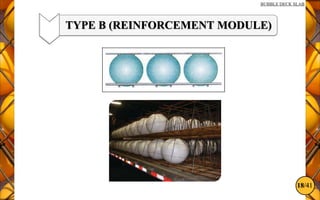
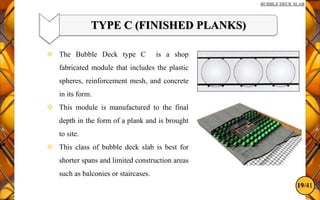
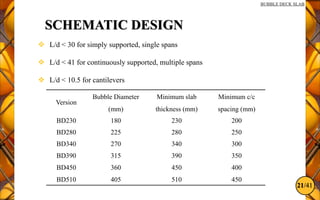
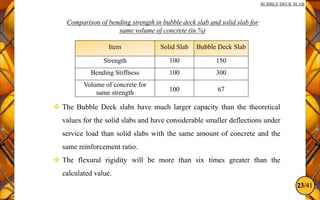
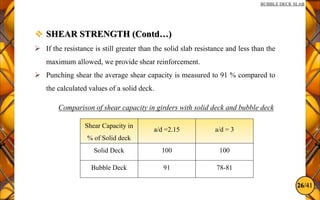
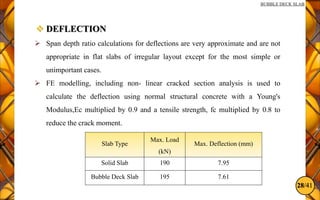
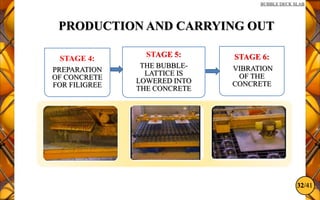
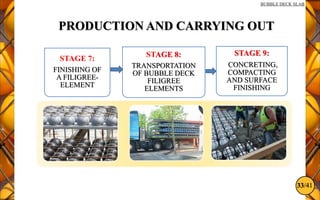
The document discusses the bubble deck slab, a biaxial hollow core slab that reduces weight and material consumption in construction by using hollow spheres made from recycled plastic. This innovative construction method allows for longer spans, lower costs, and supports environmental sustainability by decreasing concrete usage and related emissions. However, while bubble decks offer advantages in reducing dead weight and enhancing flexural strength, they have lower shear resistance compared to traditional solid slabs.