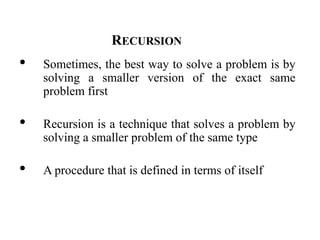
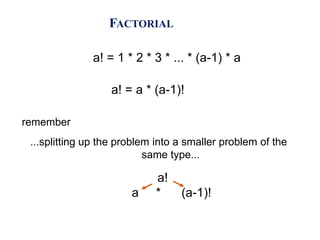
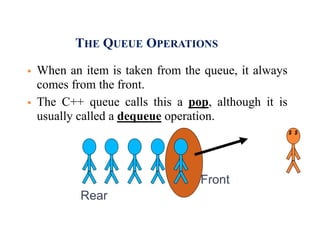
The document discusses different data structures including stacks, queues, linked lists, and their implementations. It defines stacks as LIFO structures that can add and remove items from one end only. Queues are FIFO structures that add to one end and remove from the other. Linked lists store data in nodes that point to the next node. Stacks, queues and linked lists can all be implemented using arrays or by linking nodes. Priority queues and deques are also discussed.














![ARRAY IMPLEMENTATION
A queue can be implemented with an array, as shown here.
For example, this queue contains the integers 4 (at the
front), 8 and 6 (at the rear).
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . . .
An array of integers
to implement a
queue of integers
4 8 6
We don't care what's in
this part of the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-18-320.jpg)
![ARRAY IMPLEMENTATION
The easiest implementation also keeps track
of the number of items in the queue and the
index of the first element (at the front of the
queue), the last element (at the rear).
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . . .
4 8 6
size3
first0
last2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-19-320.jpg)
![AN ENQUEUE OPERATION
When an element enters the queue, size is
incremented, and last changes, too.
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . . .
28 6
size3
first1
last3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-20-320.jpg)
![AT THE END OF THE ARRAY
There is special behaviour at the end of the
array.
For example, suppose we want to add a new
element to this queue, where the last index is
[5]:
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ]
2 16
size3
first3
last5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-21-320.jpg)
![AT THE END OF THE ARRAY
The new element goes at the front of the
array (if that spot isn’t already used):
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ]
2 16
size4
first3
last0
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-22-320.jpg)
![ARRAY IMPLEMENTATION
Easy to implement
But it has a limited capacity with a fixed array
Or you must use a dynamic array for an
unbounded capacity
Special behavior is needed when the rear reaches
the end of the array.
[ 0 ] [1] [ 2 ] [ 3 ] [ 4 ] [ 5 ] . . .
4 8 6
size3
first0
last2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-23-320.jpg)




![Ucommuting pipes
DEQUE (DOUBLE-ENDED QUEUE)[1]
Implemented by the class Arraydeque in Java 6 seen as a
doubly linked list with a head (right) and a tail (left) and
insert and remove at either ends.
head
tail
..... 43 1 625
5
1 2
4
6
headtail
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-28-320.jpg)

![LINKED LIST IMPLEMENTATION[2]
10
15
7
null
13
A queue can also be implemented with a linked
list with both a head and a tail pointer.
head_ptr
tail_ptr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-30-320.jpg)
![LINKED LIST IMPLEMENTATION[3]
10
15
7
null
13
Which end do you think is the front of the queue?
Why?
head_ptr
tail_ptr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-31-320.jpg)
![LINKED LIST IMPLEMENTATION[4]
10
15
7
null
head_ptr
13
The head_ptr points to the front of the list.
Because it is harder to remove items from the tail of the list.
tail_ptr
Front
Rear](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-32-320.jpg)

![Node[5]
Nodes : the elements in a linked list.
The nodes in a linked list are called self-referential records.
Each instance of the record contains a pointer to another
instance of the same structural type.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-34-320.jpg)

![36
header trailer
Empty Doubly-Linked List:[6]
Using sentinels, we have no null-
links; instead, we have:
head.next = tail
tail.prev = head
Singl Node List:
Size = 1
This single node is the first node,
and also is the last node:
first node is head.next
last node is tail.prev
trailerheader
first last](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bsccs-iidfsu-2linkliststackqueue-150317031642-conversion-gate01/85/Bsc-cs-ii-dfs-u-2-linklist-stack-queue-36-320.jpg)


