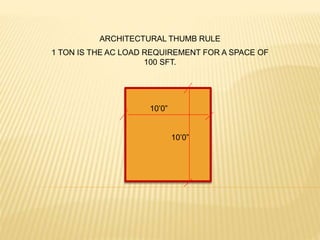
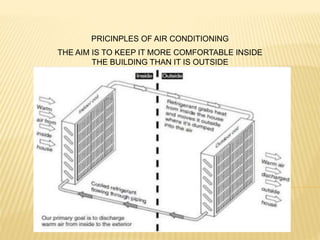
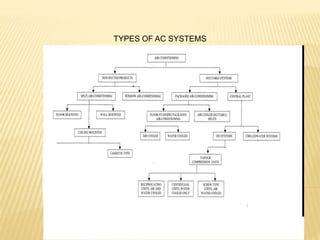
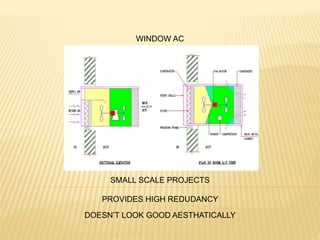
1. There are several types of HVAC systems an architect can choose from for a project, including window AC units, high wall AC units, cassette/ceiling mounted AC units, split systems, variable refrigerant volume (VRV) systems, and centralized AC systems.
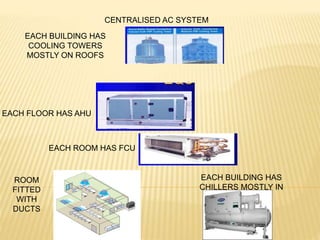
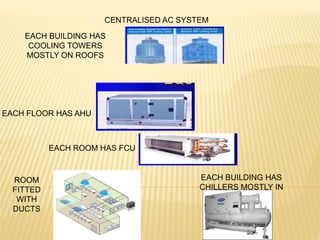
2. A centralized AC system has ducts in each room fitted with a fan coil unit (FCU). Each floor has an air handling unit (AHU) and each building has cooling towers mostly on the roof and chillers mostly in the basement to service the entire building.
3. When comparing air cooled split systems, water cooled split systems, air cooled VRV systems, air cooled screw chillers and water cooled screw chillers for









![SYSTEM COMPARISON FOR SERVICES APARTMENTS, RESTAURANTS AND FOOD COURT PROJECT: CONSCIENT ONE DATED: 15 JULY 2013
S No PARAMETER AIR COOLED SPLIT SYSTEM WATER COOLED SPLIT SYSTEM AIR COOLED VRV SYSTEM AIR COOLED SCREW CHILLER WATER COOLED SCREW CHILLER
1 COMPONENTS
Indoor unit. Indoor unit. Indoor unit. Aircooled screw chillers. Watercooled screw chillers.
Aircooled outdoor unit. Watercooled condensing unit. Aircooled outdoor unit. Chilled water pumps. Chilled water pumps.
Refrigerantpiping. Refrigerantpiping. Refrigerantpiping. Chilled water piping. Condenser water pumps.
Cooling towers. Electroniccontrols. Airhandlingunits / Fan coil units. Chilled water piping.
Condenser water pumps. Condenser water piping.
Condenser water piping. Cooling towers.
Air Handling units / Fan coil units.
2 PHASE WISE INSTALLATION Possible Possible Possible Not Possible Not Possible
3 CAPITAL COST L1 L2 H H L3
4
POWER CONSUMPTION HIGH LOW LOW Higher at full load LOW
IKW [Full Load] 1.35 kW/TR 1.1 kW/TR 1.2kW/TR 1.6 kW/TR 1.1 kW/TR
5 OPERATING COST
I
Cooling Requirement at 80%
diversity
382 Tons 382 Tons 382 Tons 382 Tons 382 Tons
IIPower consumption 516 420 459 611 420
6 SPACE REQUIREMENT
IOPEN SPACE for ODUs Required Not Required Required Not Required Not Required
IIOPEN SPACE for PLANT Not Required Not Required Not Required Required Not Required
III
OPEN SPACE for COOLING
TOWERS
Not Required
Required.[for condenser pumps
also]
Not Required Not Required Required
IVBASEMENT SPACE for PLANT Not Required Not Required Not Required Not Required Required
7 REFRIGERANT PIPING Length less than 15 m. Required Length 50m-100m. NA NA
8 BILLING Easiest
Easy, only cooling towers and
pumps are common.
Easy, in case of separate system for
each user.
Difficultdue to common plant Difficultdue to common plant
9 DERATION
High in peak ambient
conditions
Low in peak ambient conditionsHigh in peak ambient conditions High in peak ambient conditions Low in peak ambient conditions
10
SOFT WATER REQUIREMENT NA 8LPH/TR NA NA 8LPH/TR
TOTAL WATER
REQUIREMENT/DAY (12
HOURS)
NA 36710 LITRES/DAY NA NA 36710 LITRES/DAY
11 RECOMMENDATIONS
Not recommendeddue to non
availability of open spaces for
ODUs
Recommended for best
efficiencyand low capex if
water is not scarce.
Not recommendeddue to non
availability of open spaces for ODUs
Recommended due to water scarcity
and good performanceon part loads.
Recommended for best efficiency
and low capex if water is not scarce.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-150830095159-lva1-app6891/85/BS5-Lecture-2-HVAC-Systems-14-320.jpg)