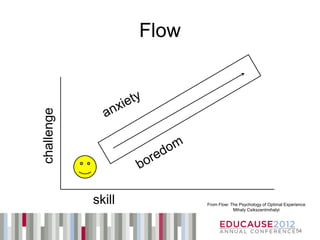
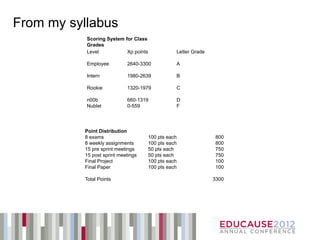
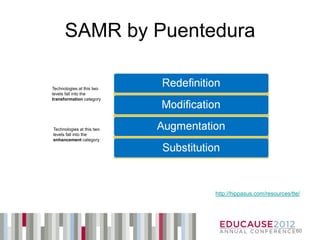
The document discusses how educators can learn from principles of game design used in the video game industry, identifying 15 instructional design principles found in video games and examples of how those principles have been implemented in educational settings through gamification techniques and technologies. It also outlines Bryan Fendley's workshop on this topic, which incorporated various game elements and mechanics to engage participants.