Embed presentation
Downloaded 175 times


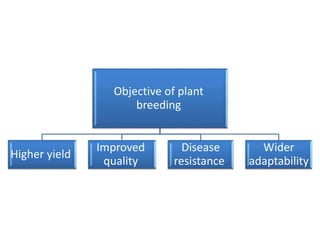
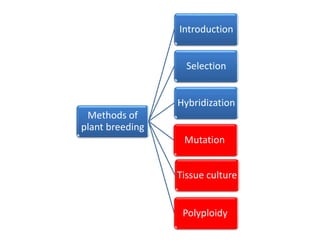
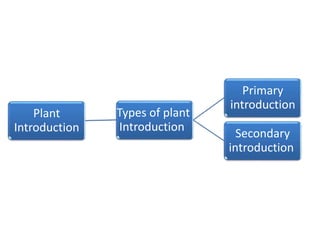

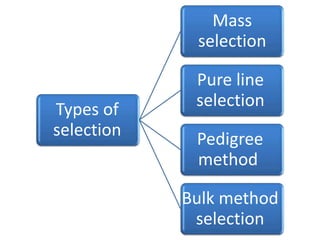
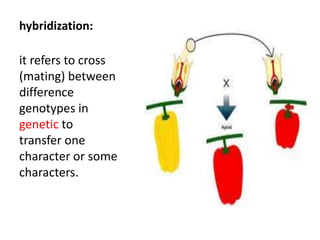
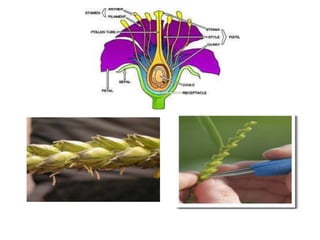
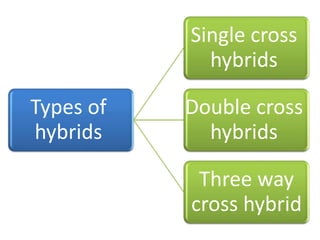


This document discusses plant breeding and outlines its objectives and methods. Plant breeding is defined as improving the genetic makeup of plants for economic uses. The objectives of plant breeding include higher yields, improved quality, disease resistance, and wider adaptability. The main methods covered are introduction, selection, and hybridization. Selection involves choosing plants with desirable traits from a population, and there are different types of selection. Hybridization is crossing different genotypes to transfer traits. There are also different types of hybrids that can be produced.












