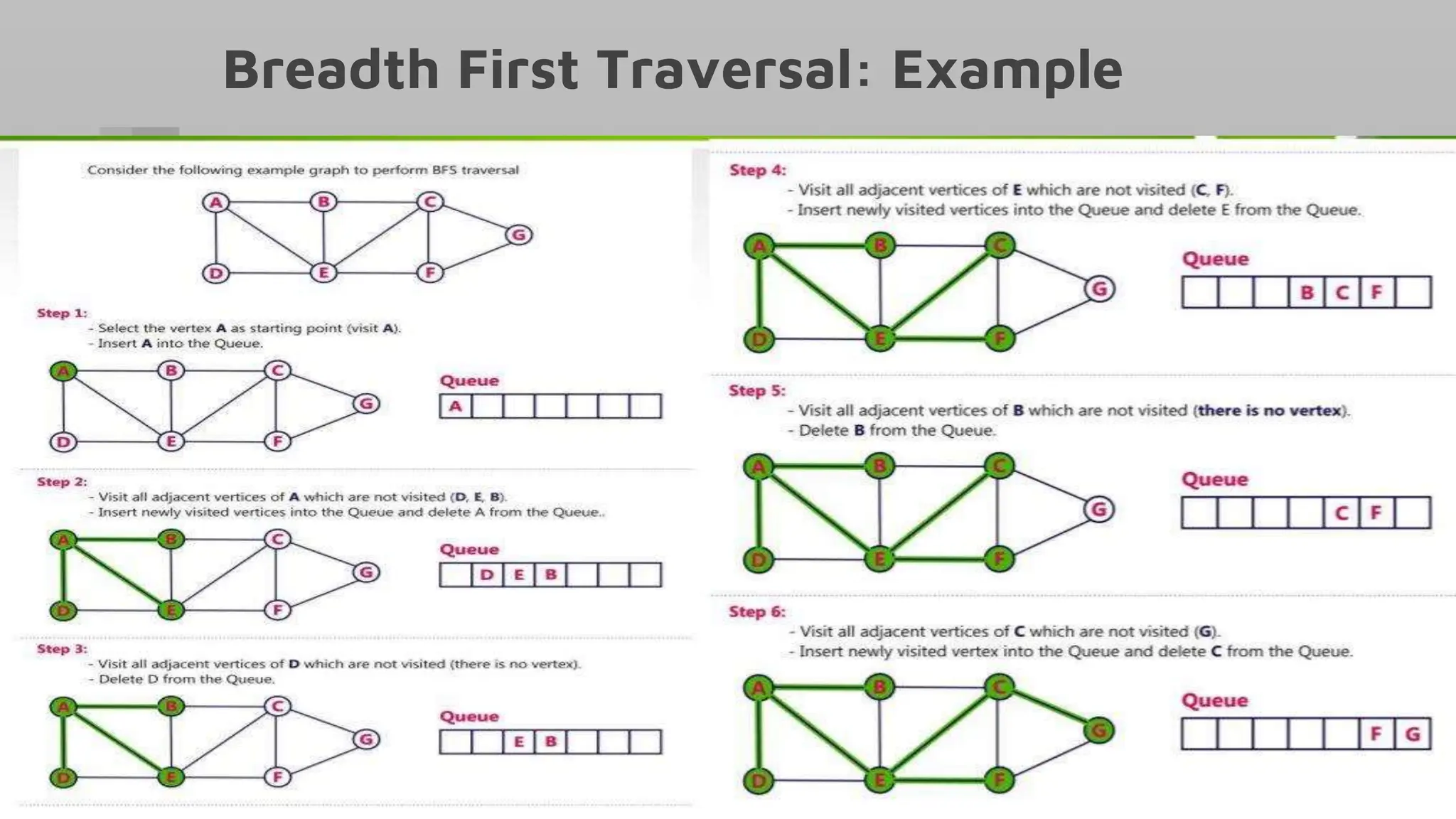
Breadth First Search (BFS) is a graph traversal algorithm that explores all vertices in a graph level-by-level starting from a specified starting vertex. It uses a queue data structure to keep track of vertices to be explored. The time complexity of BFS is O(V+E) where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges, as it visits all vertices and edges in the worst case. The space complexity is O(V) as all vertices may need to be stored in the queue.