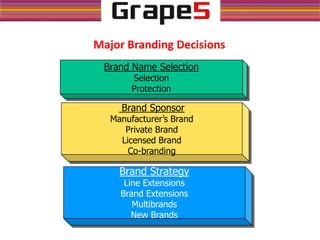
Brand management involves maintaining and improving a brand's value by associating it with positive consumer perceptions and benefits. Key aspects include cost, customer satisfaction, and competition, with a strong focus on marketing strategies that support brand identity and recognition. Successful brands invest in promotion, develop effective brand names, and navigate global marketing strategies to adapt to cultural differences while maximizing cost savings and brand synergy.