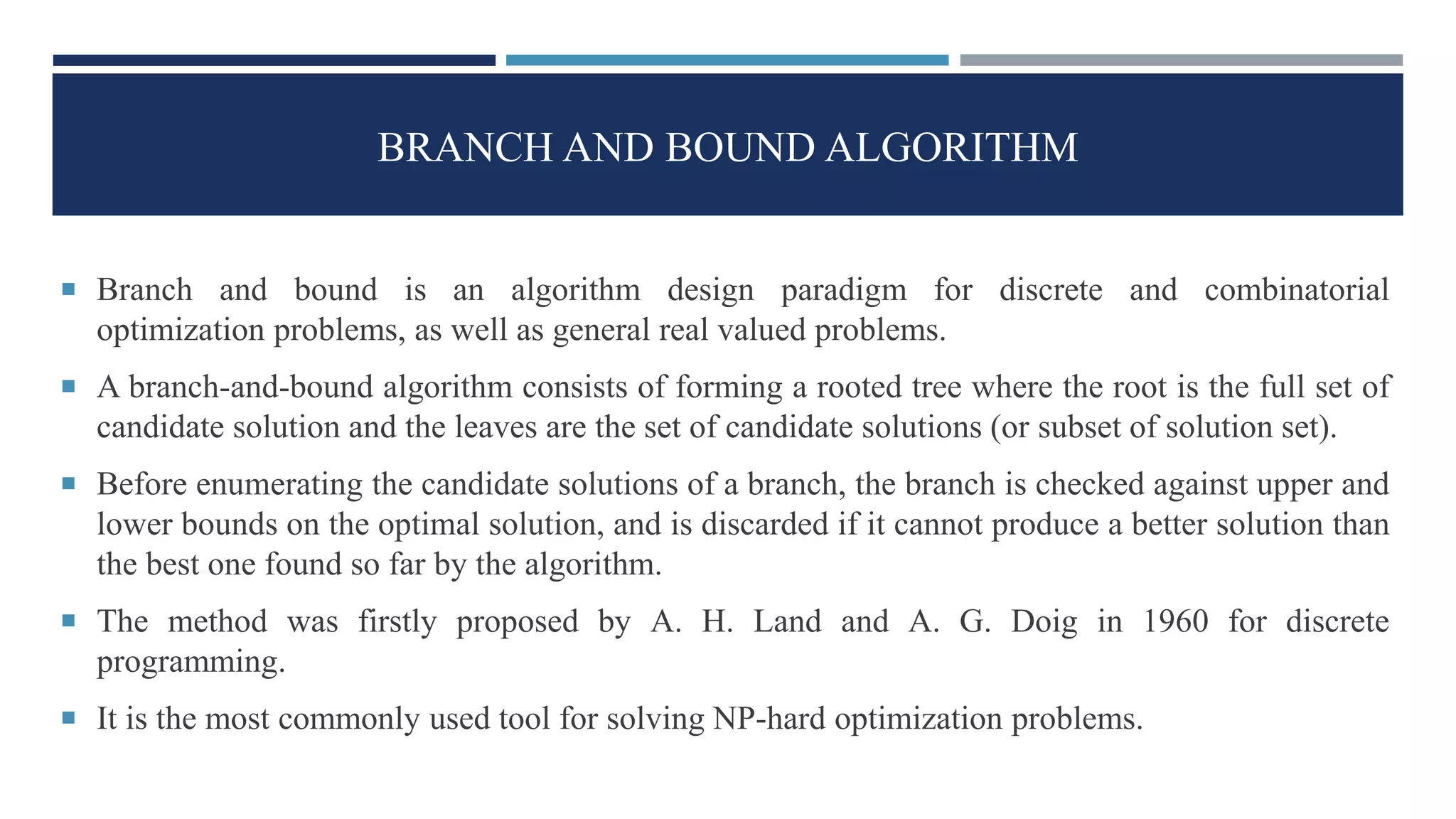
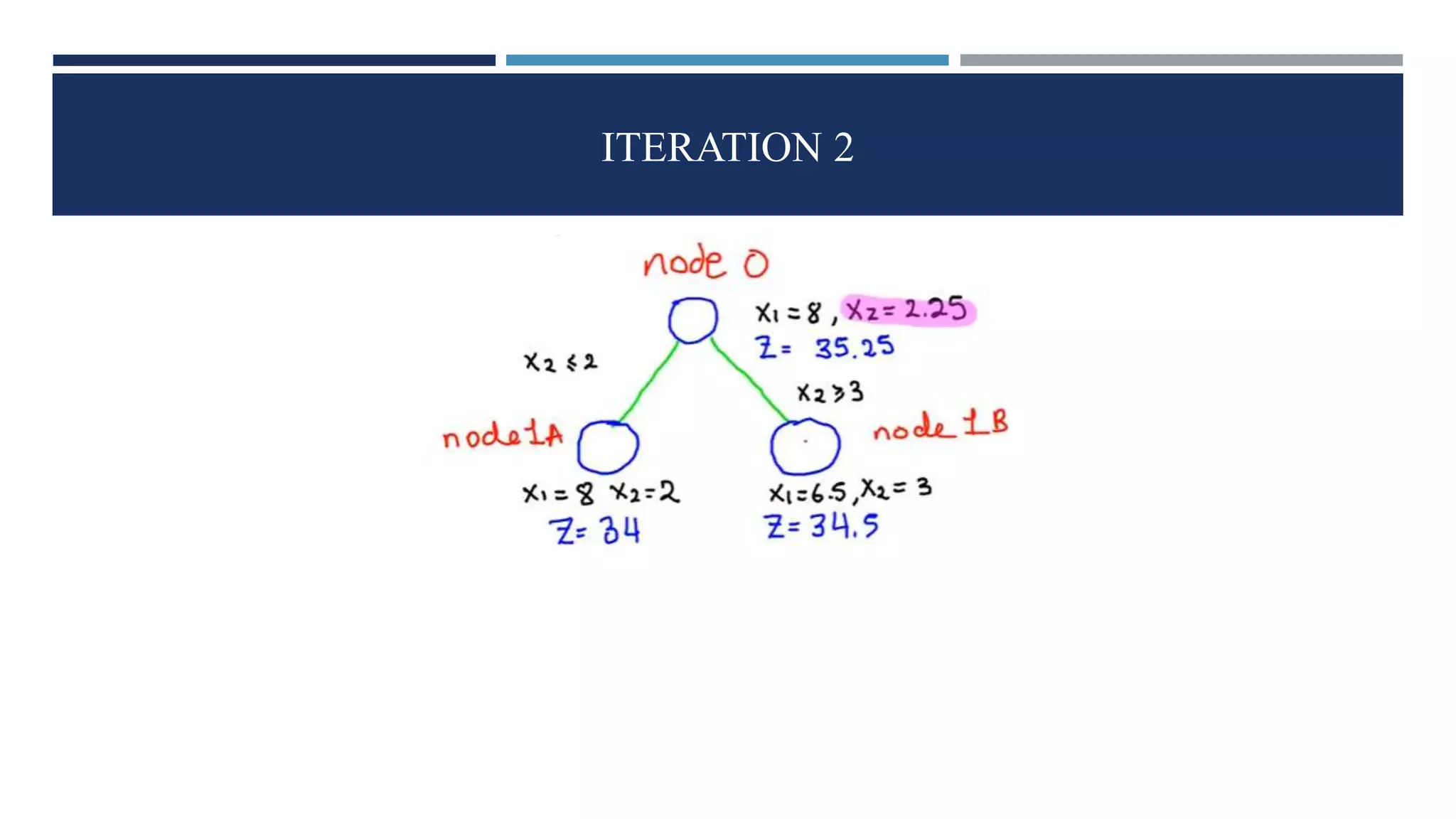
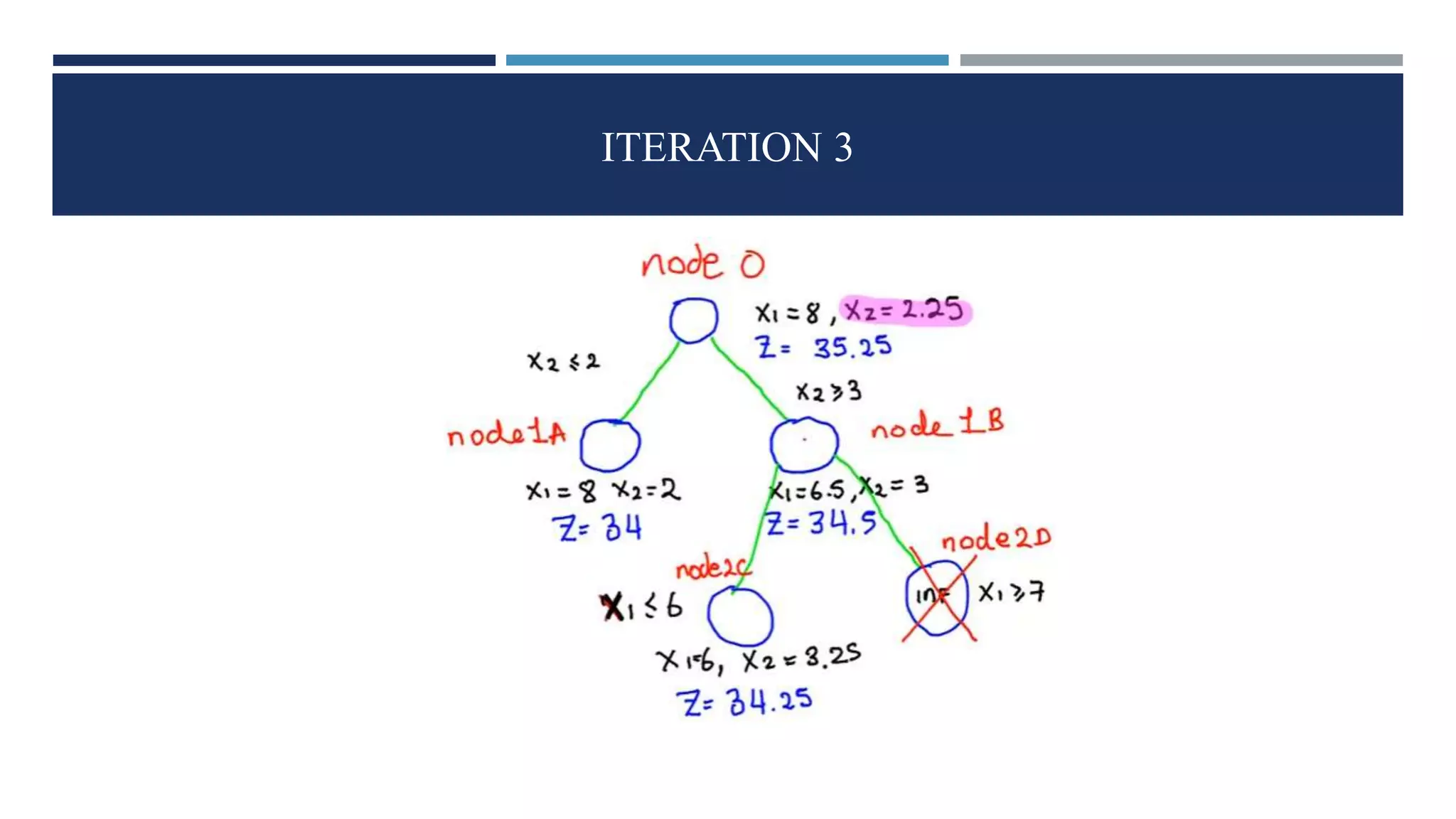
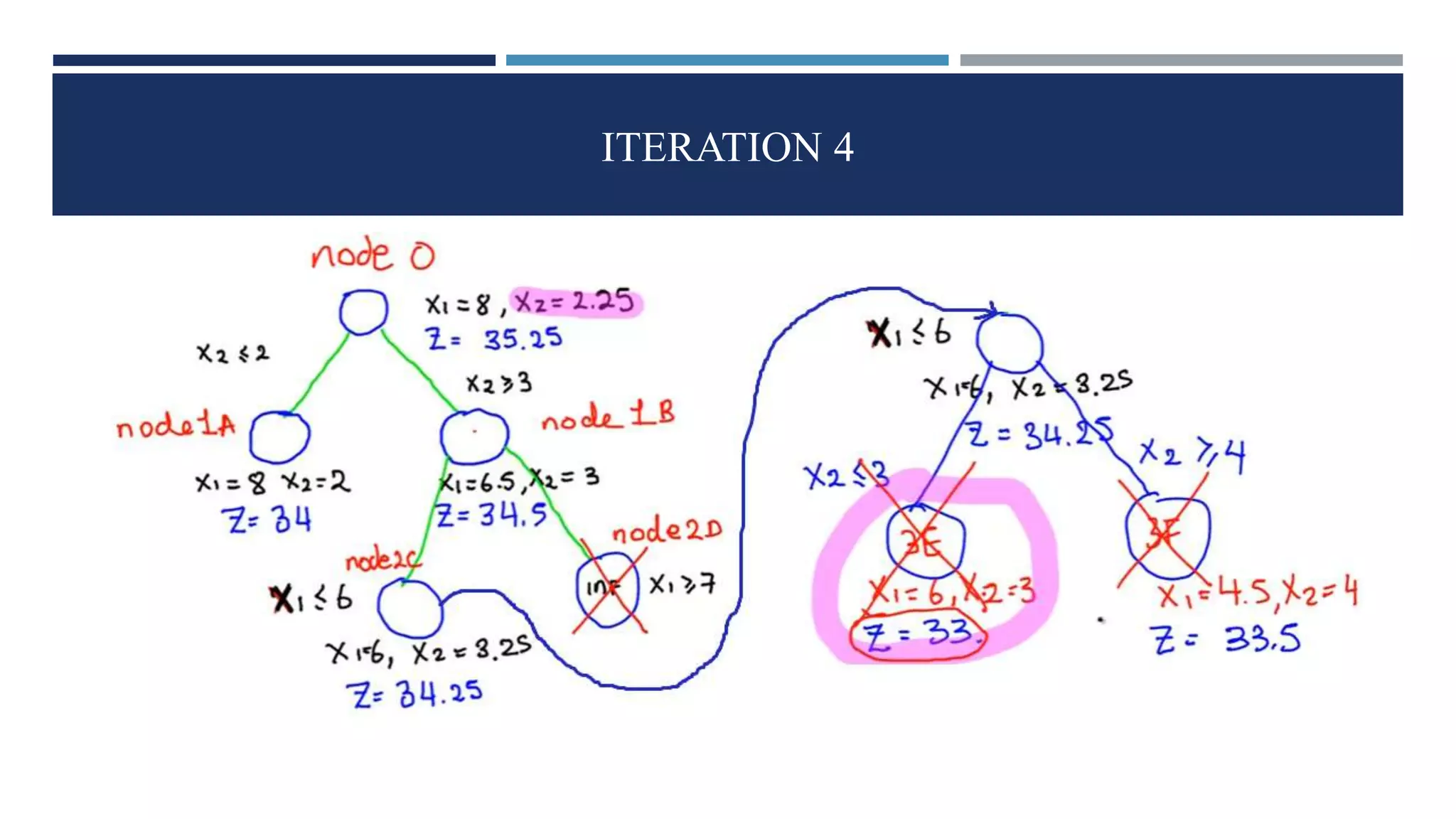
The document discusses integer linear programming (ILP) and its classification as a NP-hard problem, focusing on the branch and bound technique as a solution method. This involves dividing the problem into smaller sub-problems and estimating their solutions to find optimal outcomes. Examples of problems that can be formulated as ILPs are also provided, showcasing the practical application of these concepts.