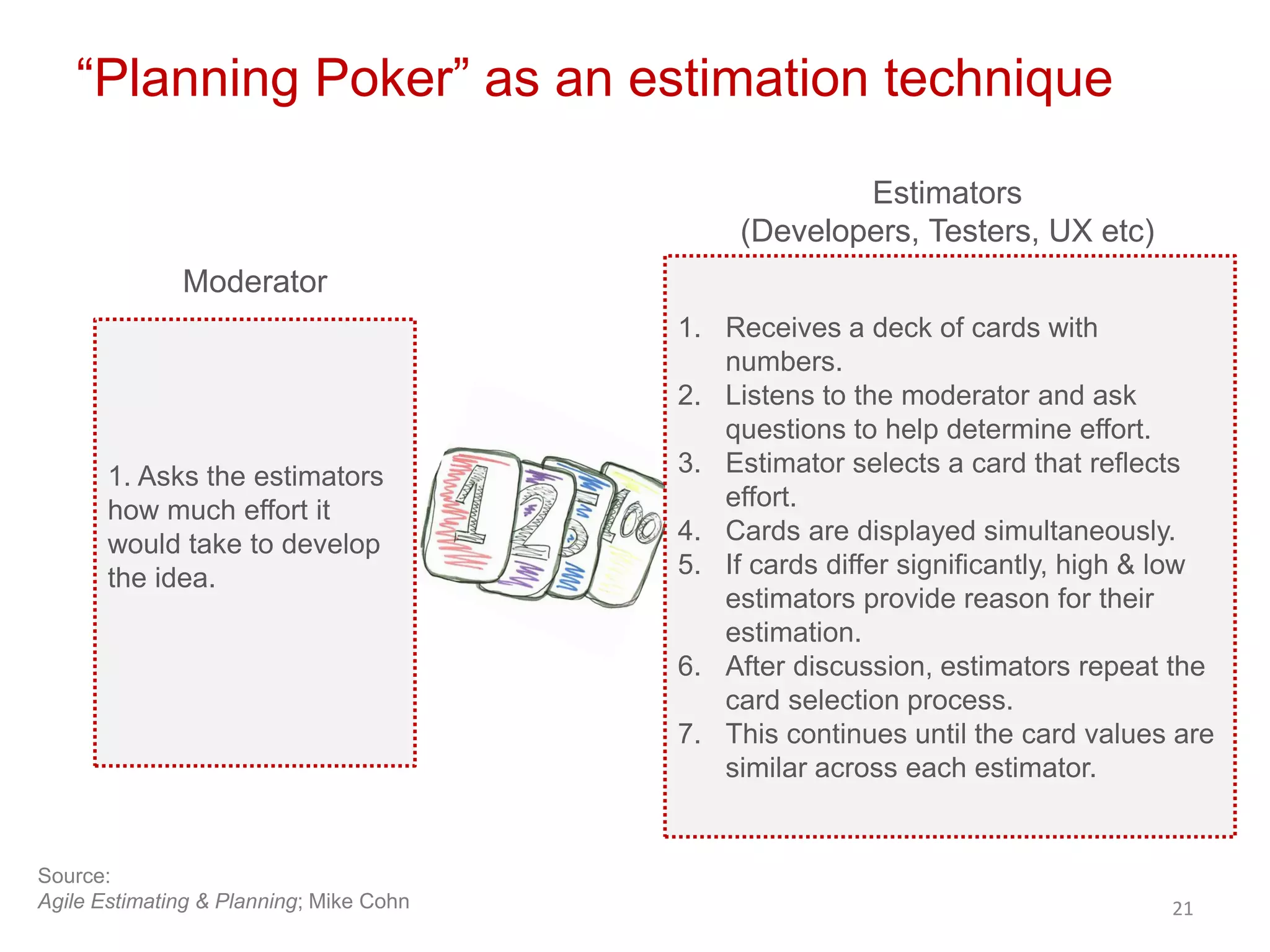
The document explains the concept of roadmapping as a crucial planning activity for product teams, emphasizing that a roadmap is a visual plan to guide an organization towards its goals. It outlines different types of roadmaps, their importance in aligning teams and prioritizing valuable activities, and provides a step-by-step guide on creating a roadmap, from idea collection to approval and communication. Key considerations include scoring ideas based on business goals and estimating the effort required for each idea.