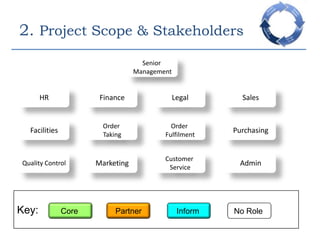
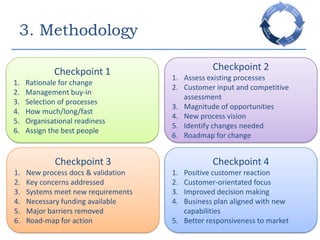
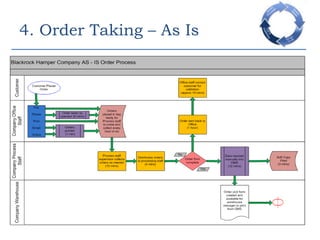
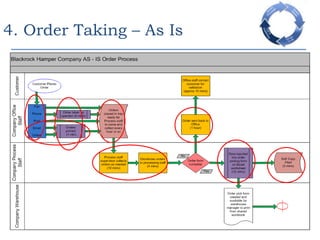
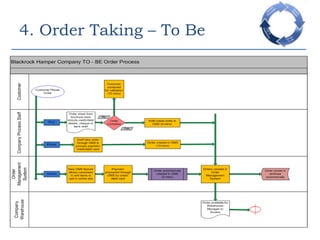
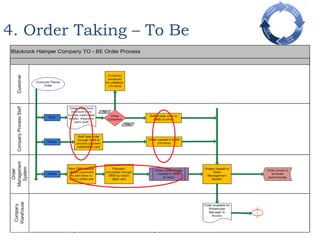
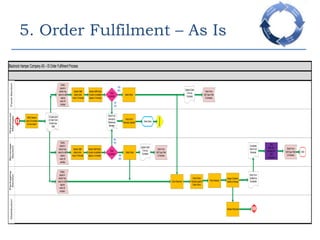
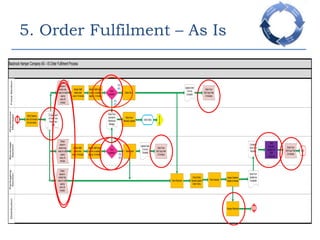
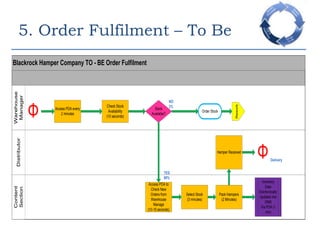
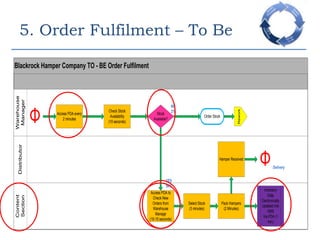
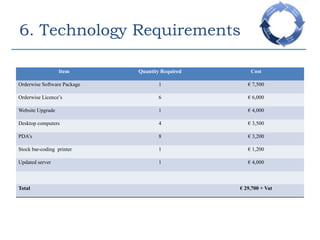
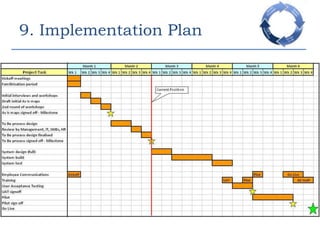
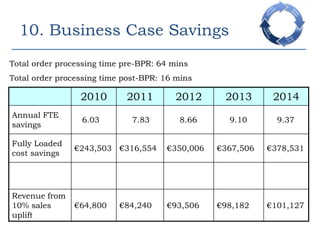
This document provides an overview of a business process reengineering (BPR) project for Blackrock Hamper Company. The project aims to address inefficiencies from legacy systems and manual processes that have hindered the company's growth. Key aspects of the BPR project include redesigning the order taking and order fulfillment processes, implementing a new order management system, reallocating staff to more value-added roles, and realizing an estimated 48 minute reduction in order processing time to generate cost savings. Risks and an implementation plan are also outlined. The methodology follows a three-stage process of preparation, transformation, and consolidation to properly manage the organizational change.