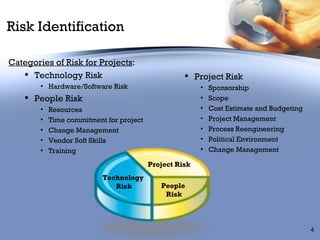
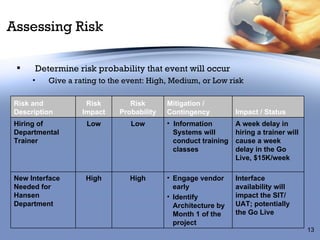
The document discusses identifying and analyzing risks for business process reengineering projects. It outlines categories of risks like technology, people, and project risks. It then discusses DeKalb County's implementation of a 311 call center as a case study, noting the project initially had too limited a scope and overlooked dependencies, representing a project risk. The document emphasizes developing a formal risk management plan to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks, with examples like contingencies for hardware delays or trainer hiring issues.