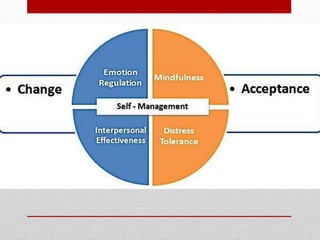
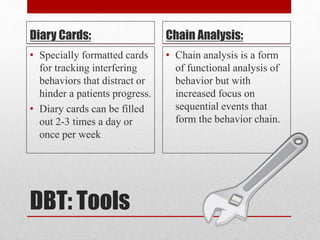
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) affects mood, emotions, and relationships, leading to self-harm and impulsive behaviors, with prevalence rates varying from 1.6% to as high as 20% among specific populations. Historically recognized since 1980, BPD is primarily diagnosed in women and is characterized by instability in relationships and self-image. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is highlighted as an effective treatment, focusing on mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.