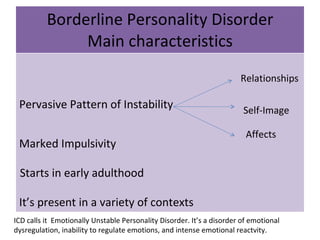
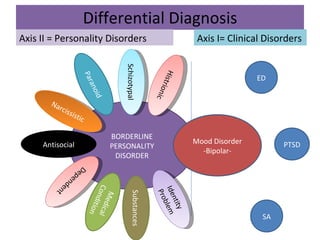
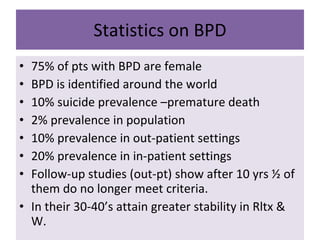
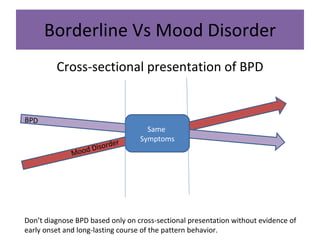
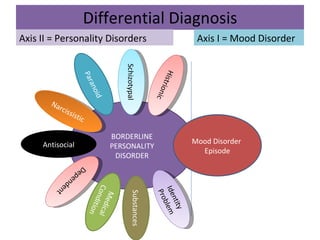
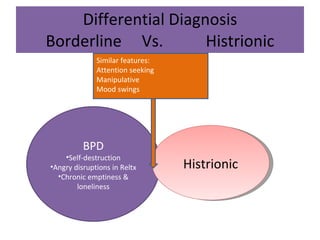
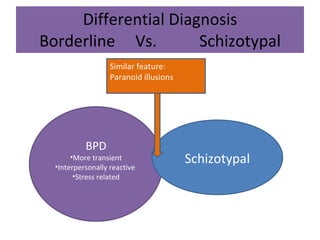
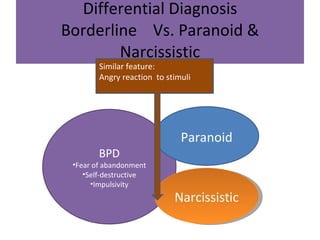
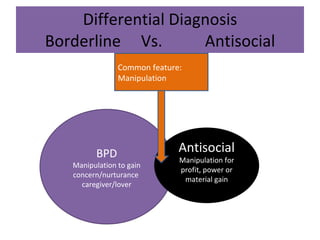
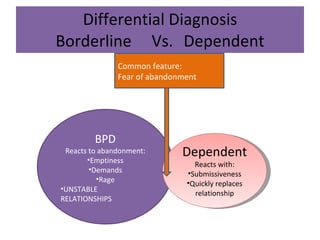
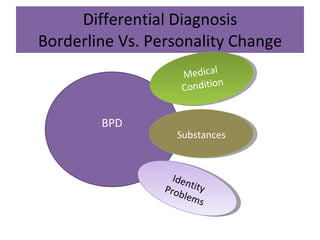
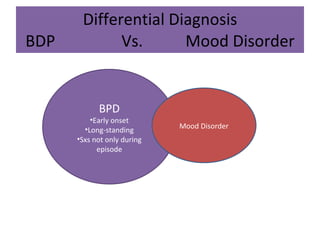
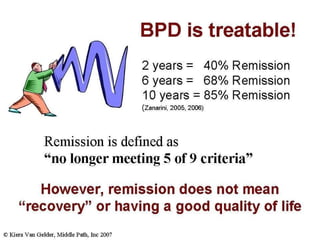
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is characterized by emotional instability, impulsivity, and instability in relationships and self-image, often beginning in early adulthood. Symptoms include fear of abandonment, intense relationships, self-damaging behavior, and suicidal tendencies. Treatment typically involves Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT), which focuses on mindfulness, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.