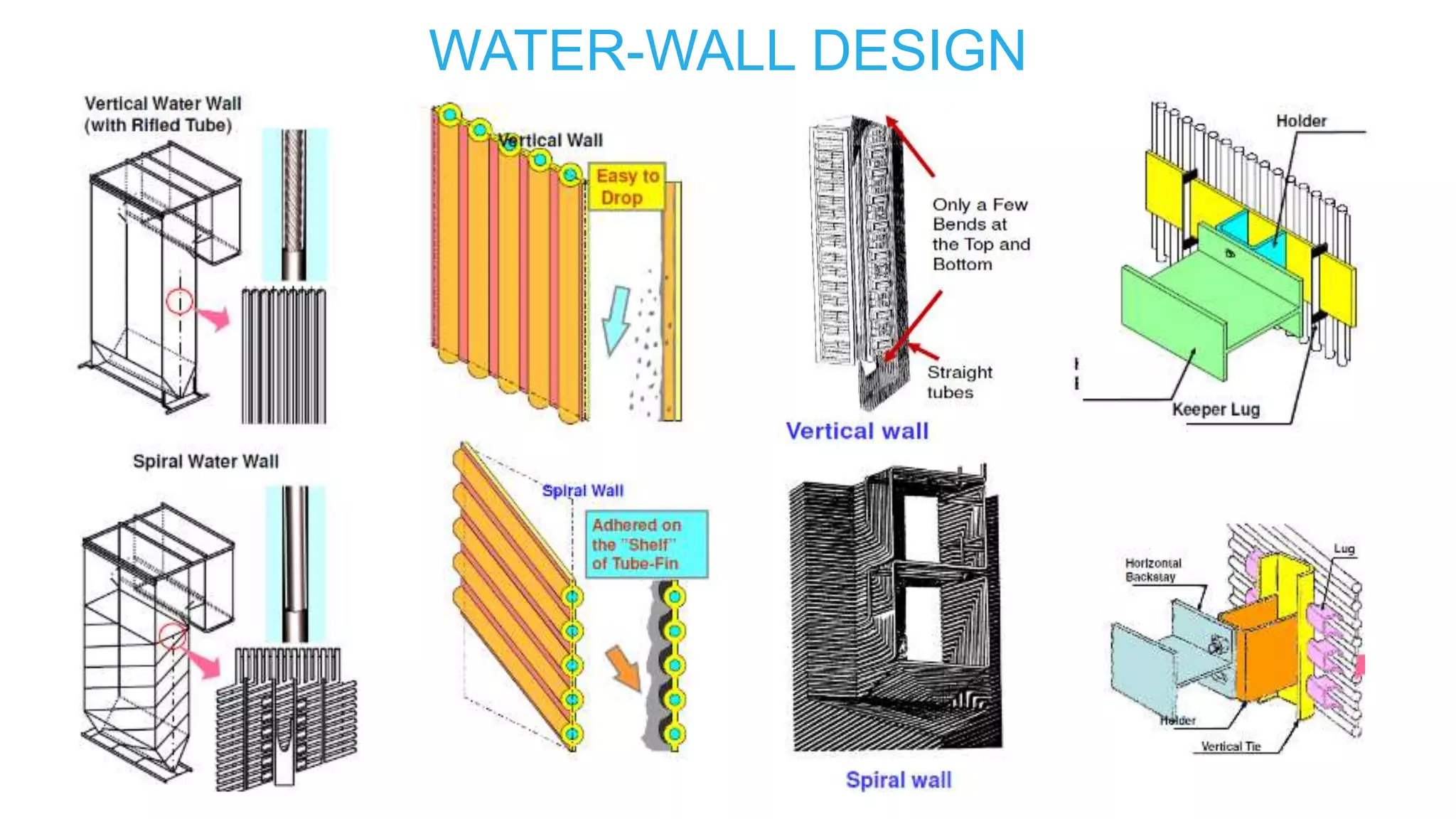
The document discusses boiler circulation systems and boiling phenomena. It covers:
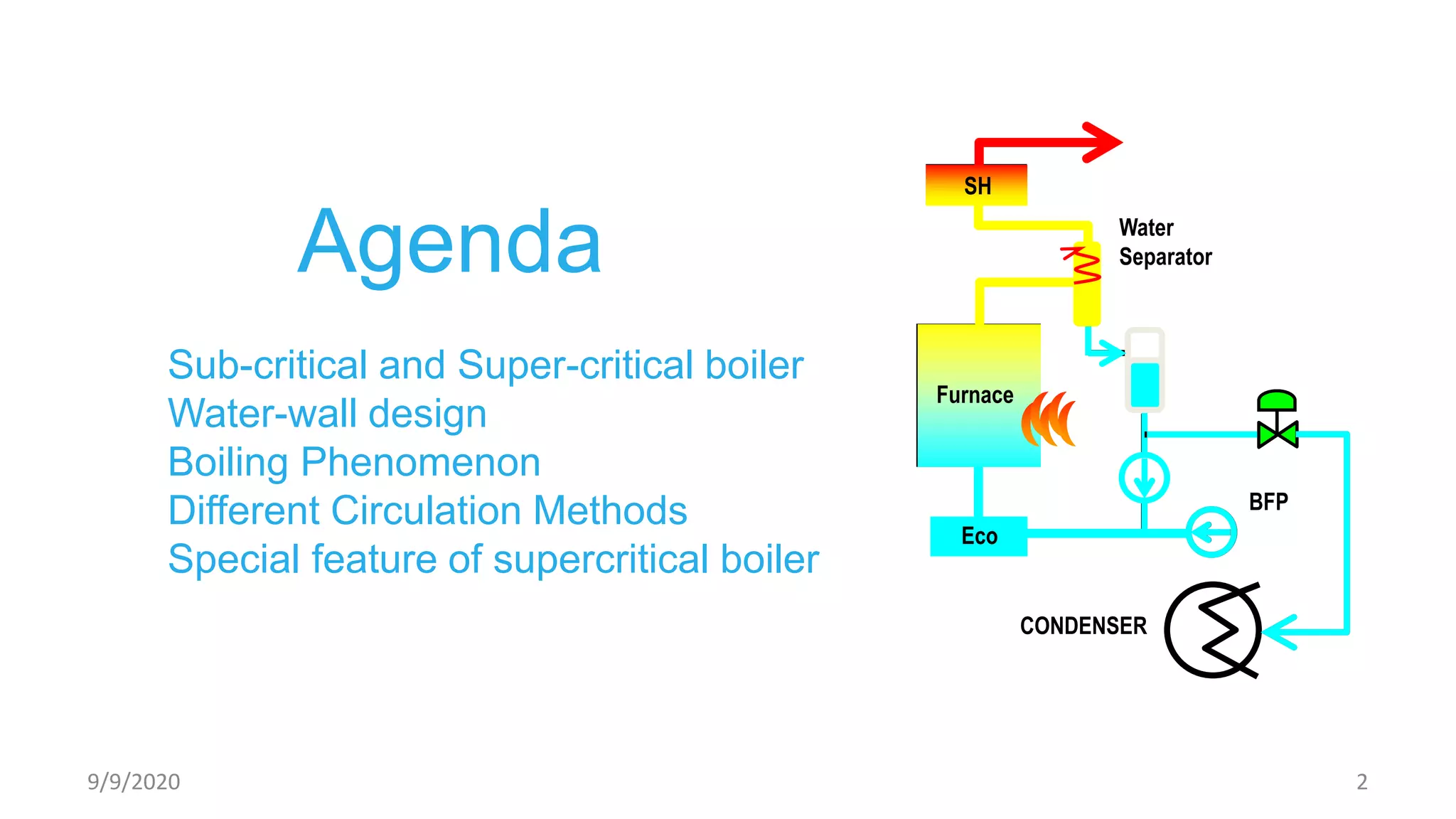
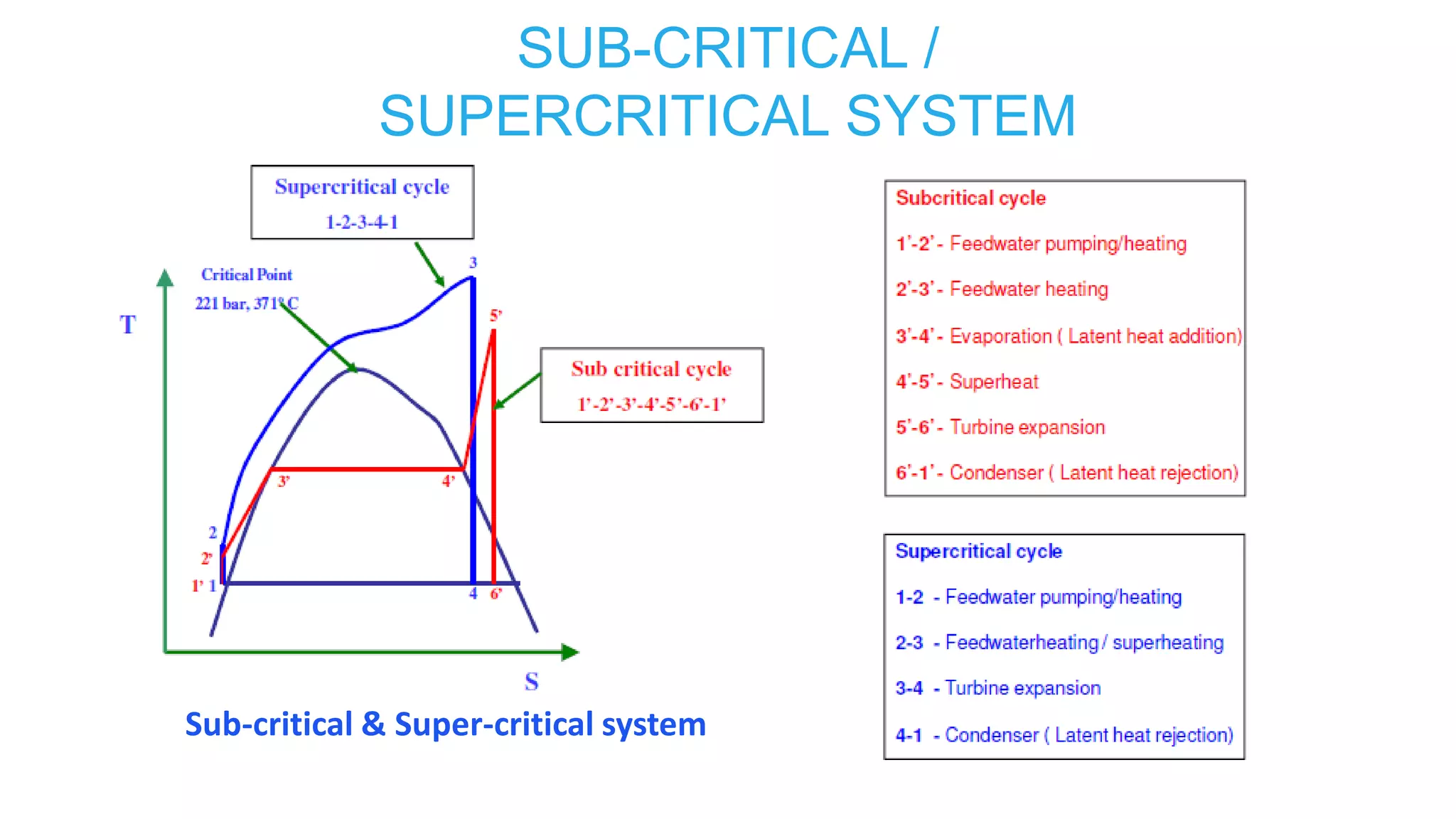
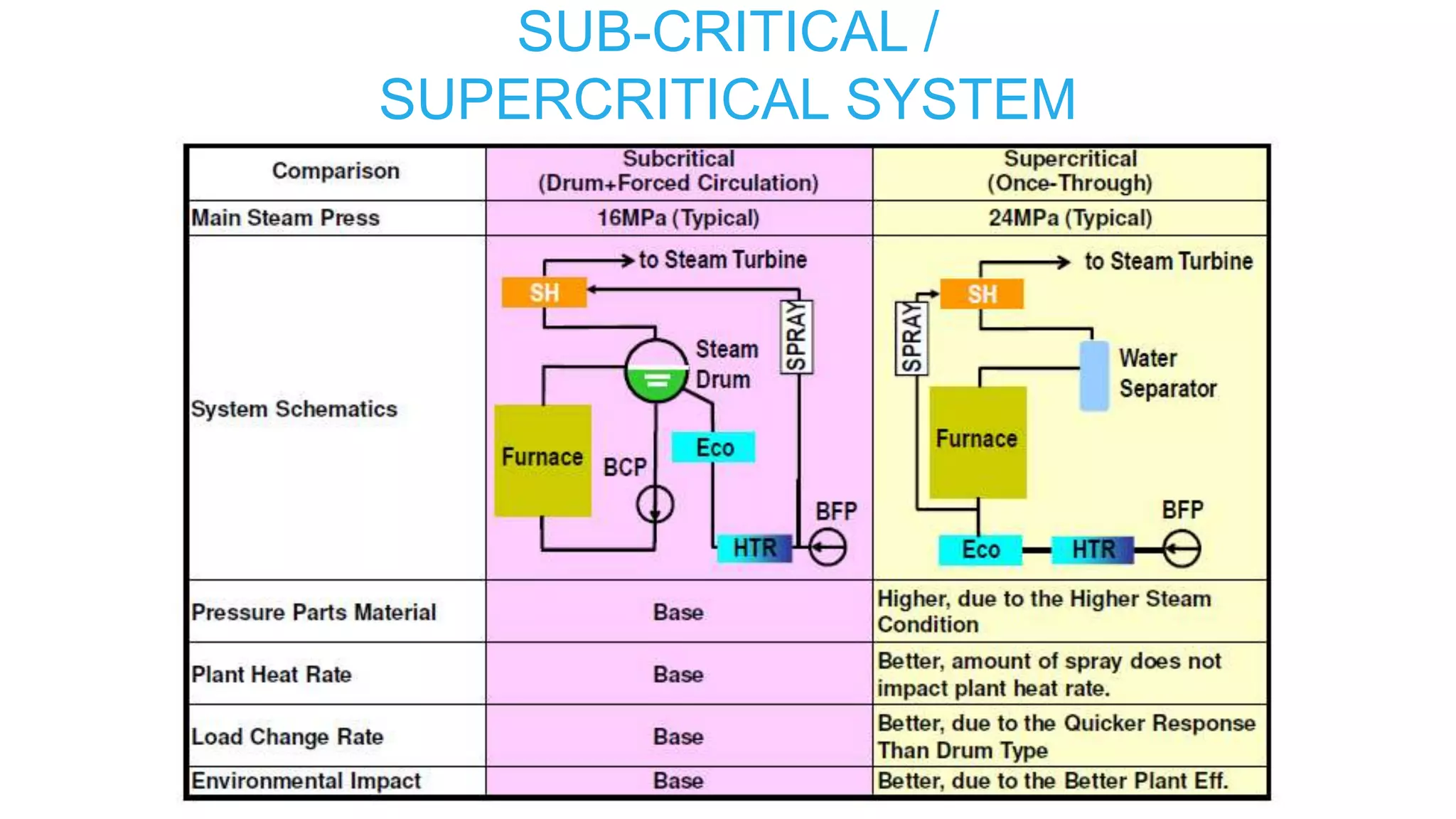
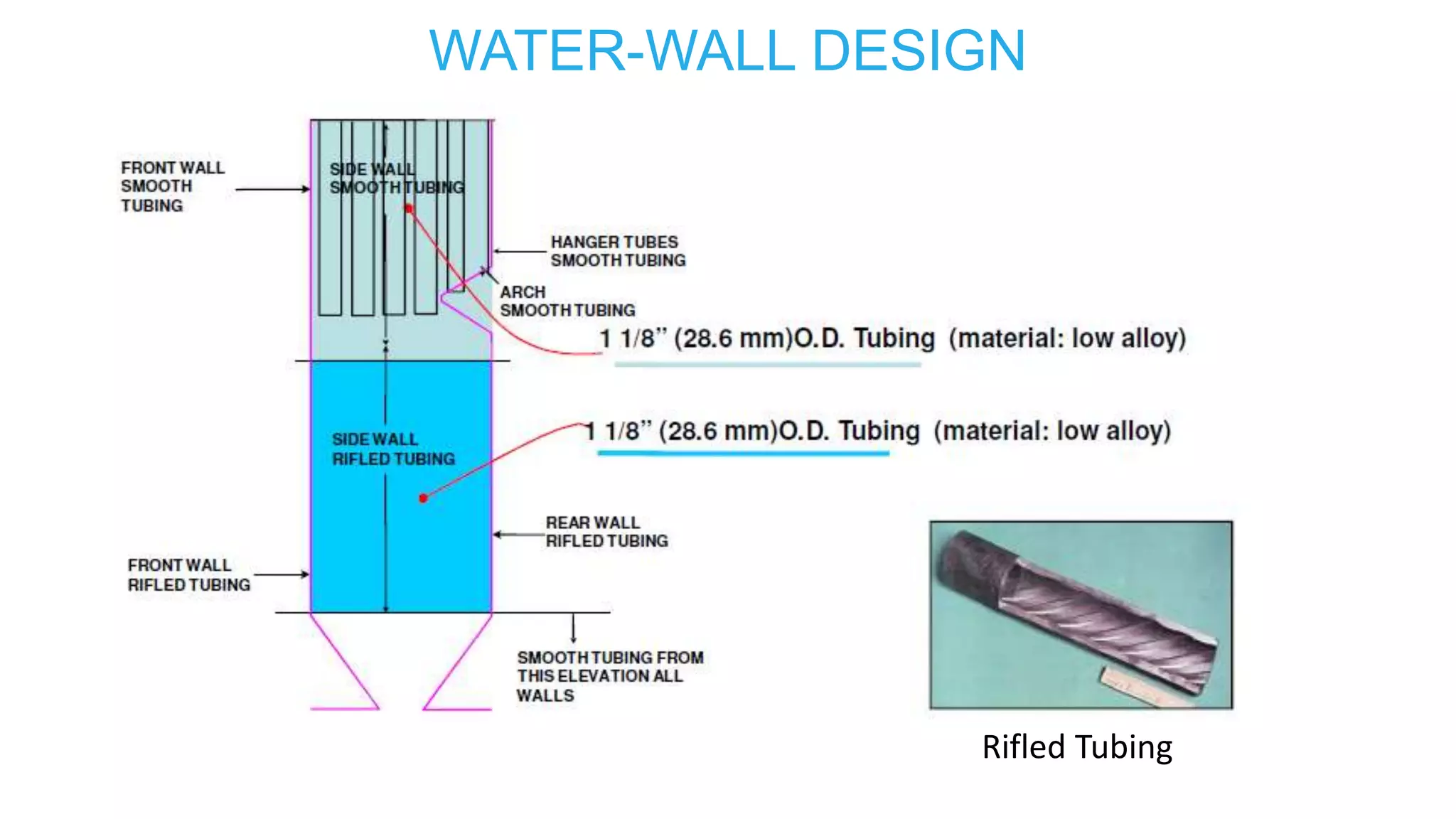
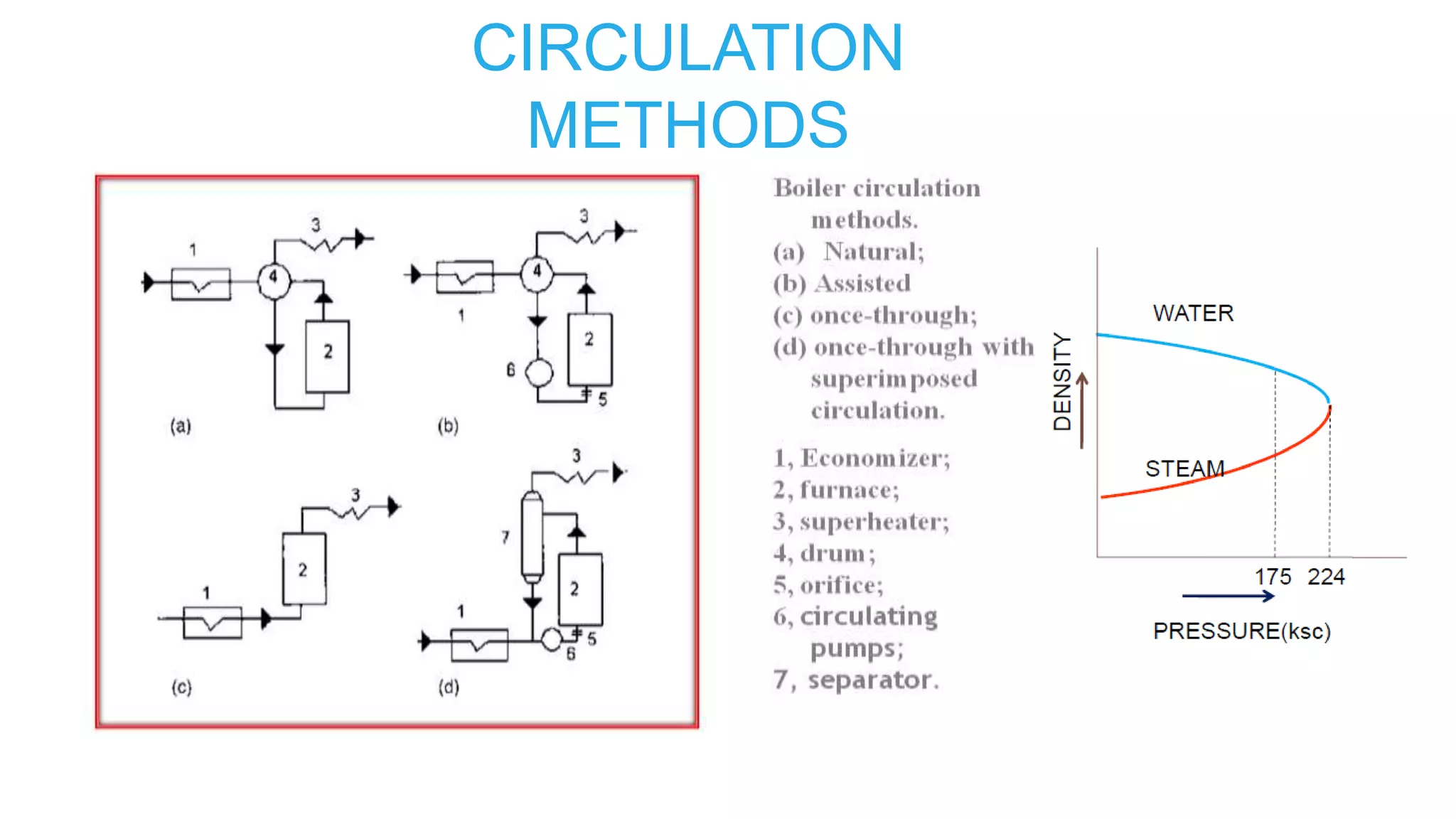
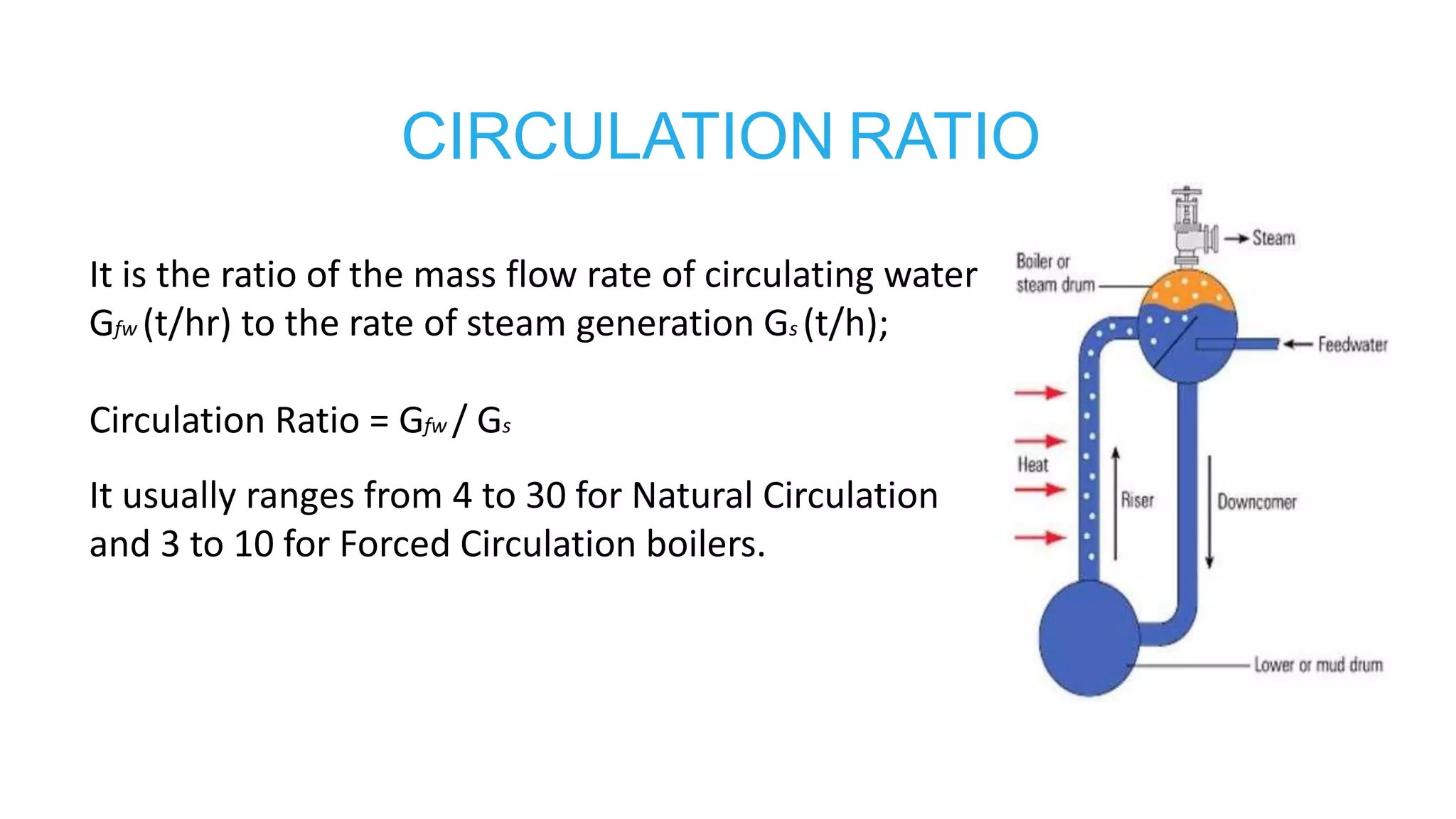
1) Sub-critical and super-critical boiler systems and different circulation methods like natural, forced, and assisted circulation.
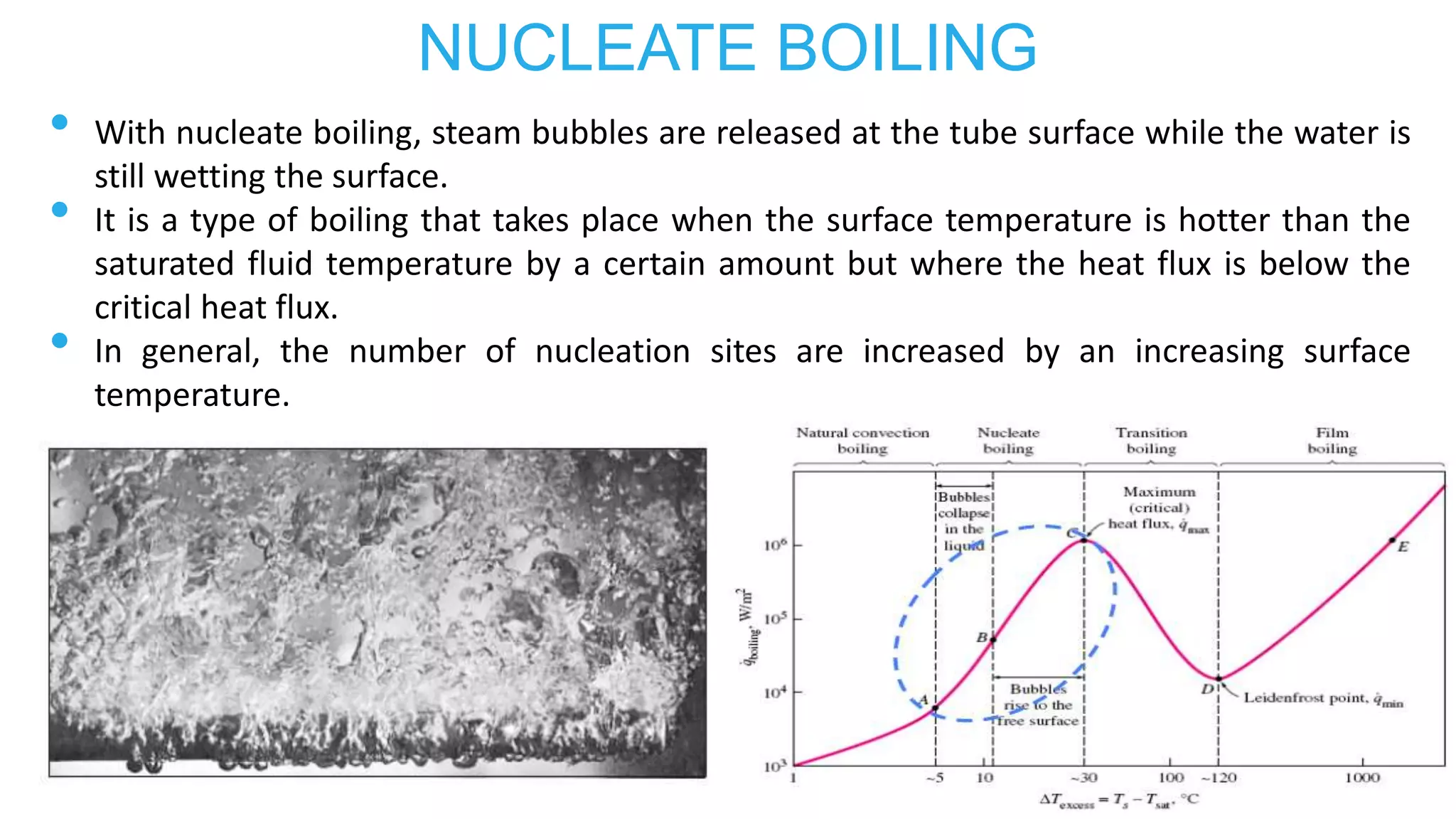
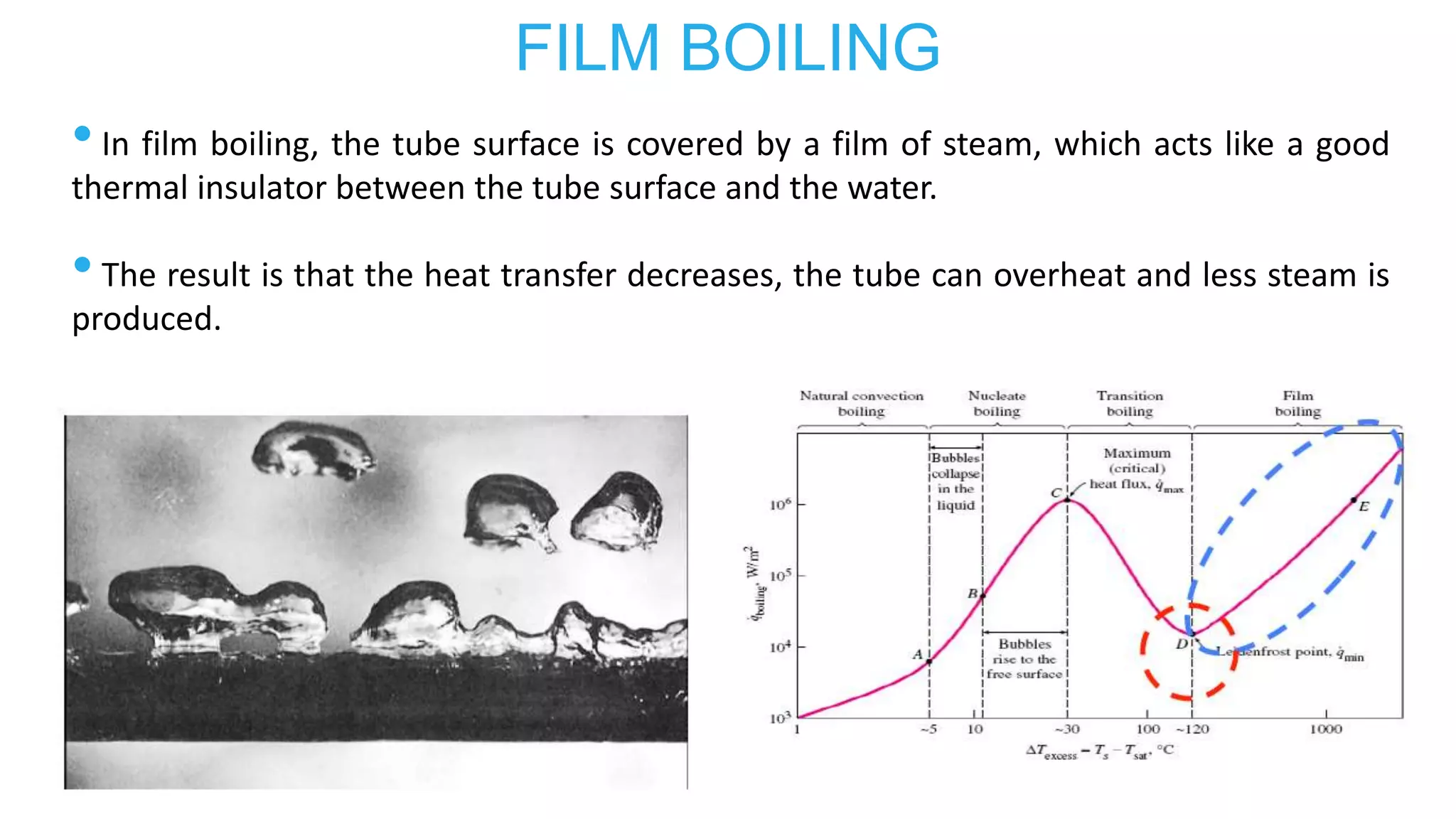
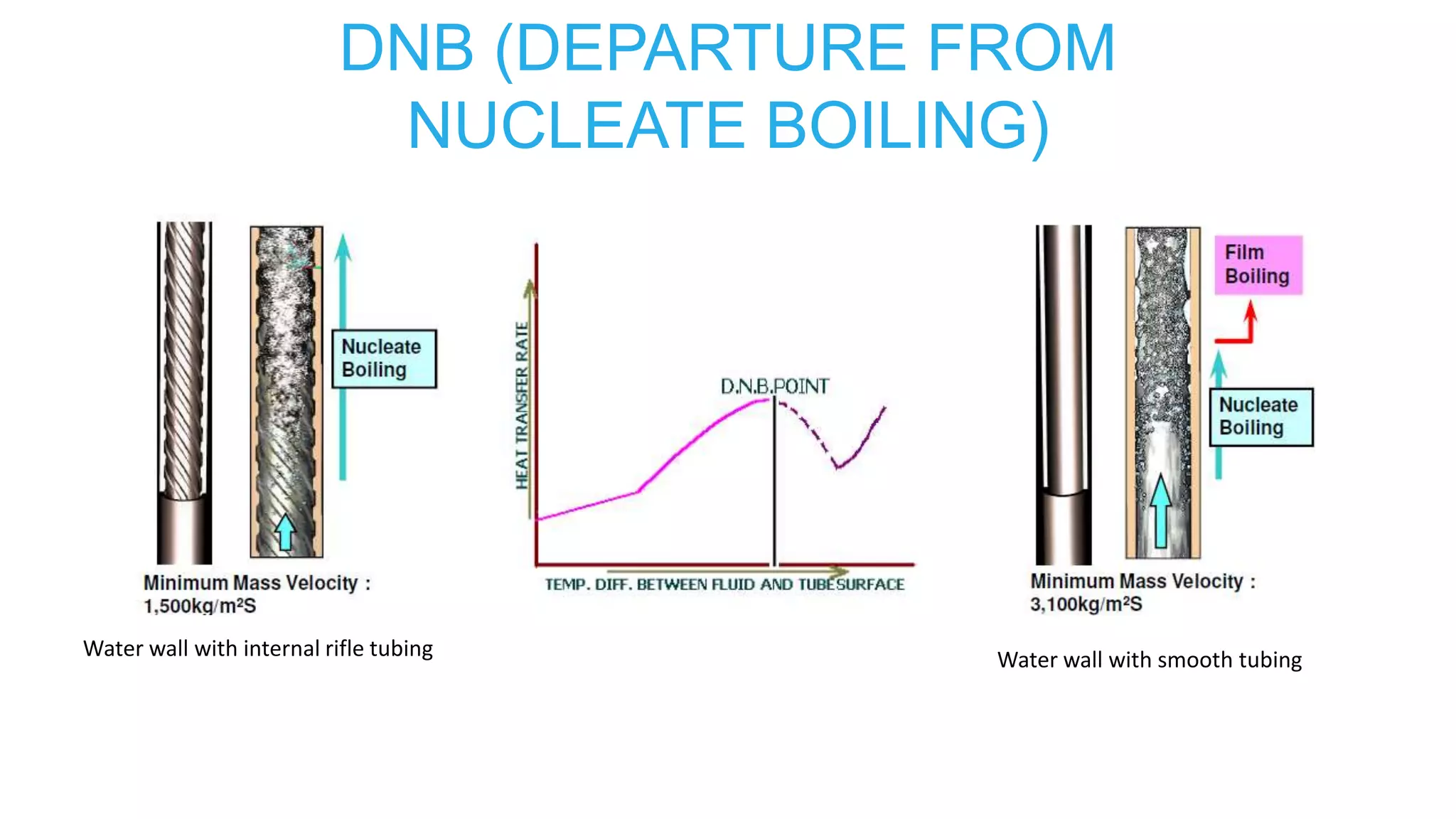
2) Features of boiling like nucleate boiling, critical heat flux, film boiling, and departure from nucleate boiling (DNB).
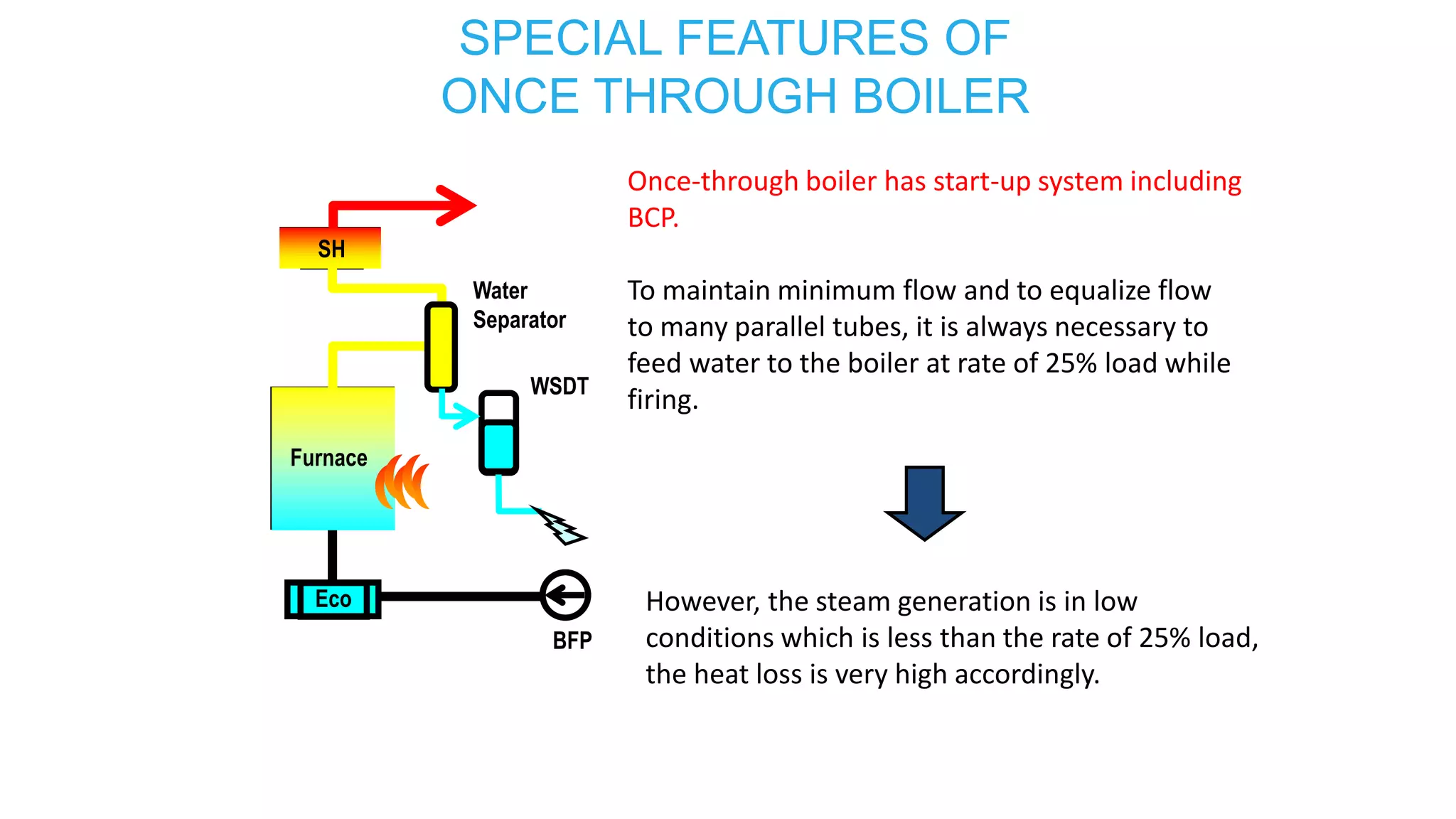
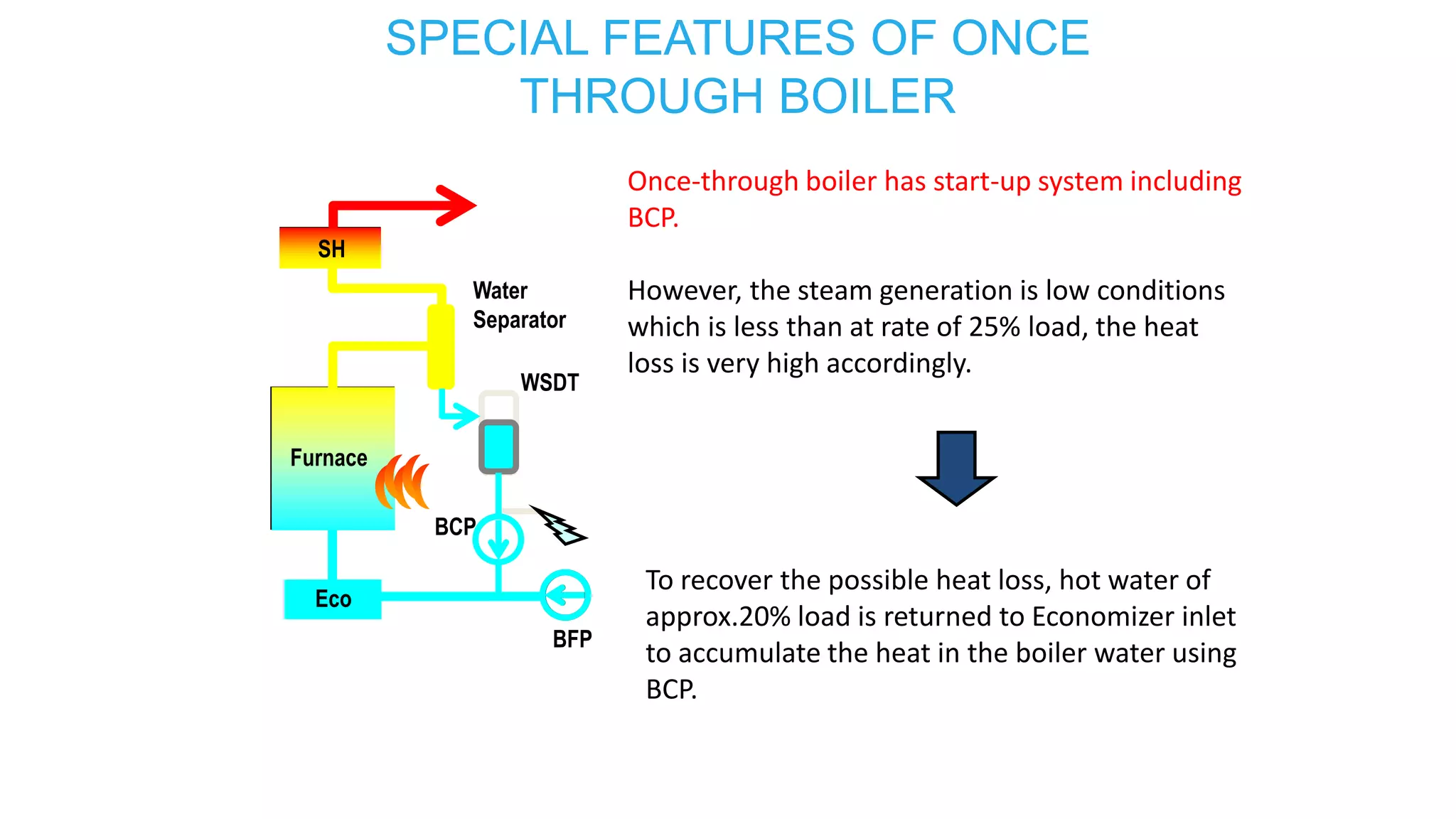
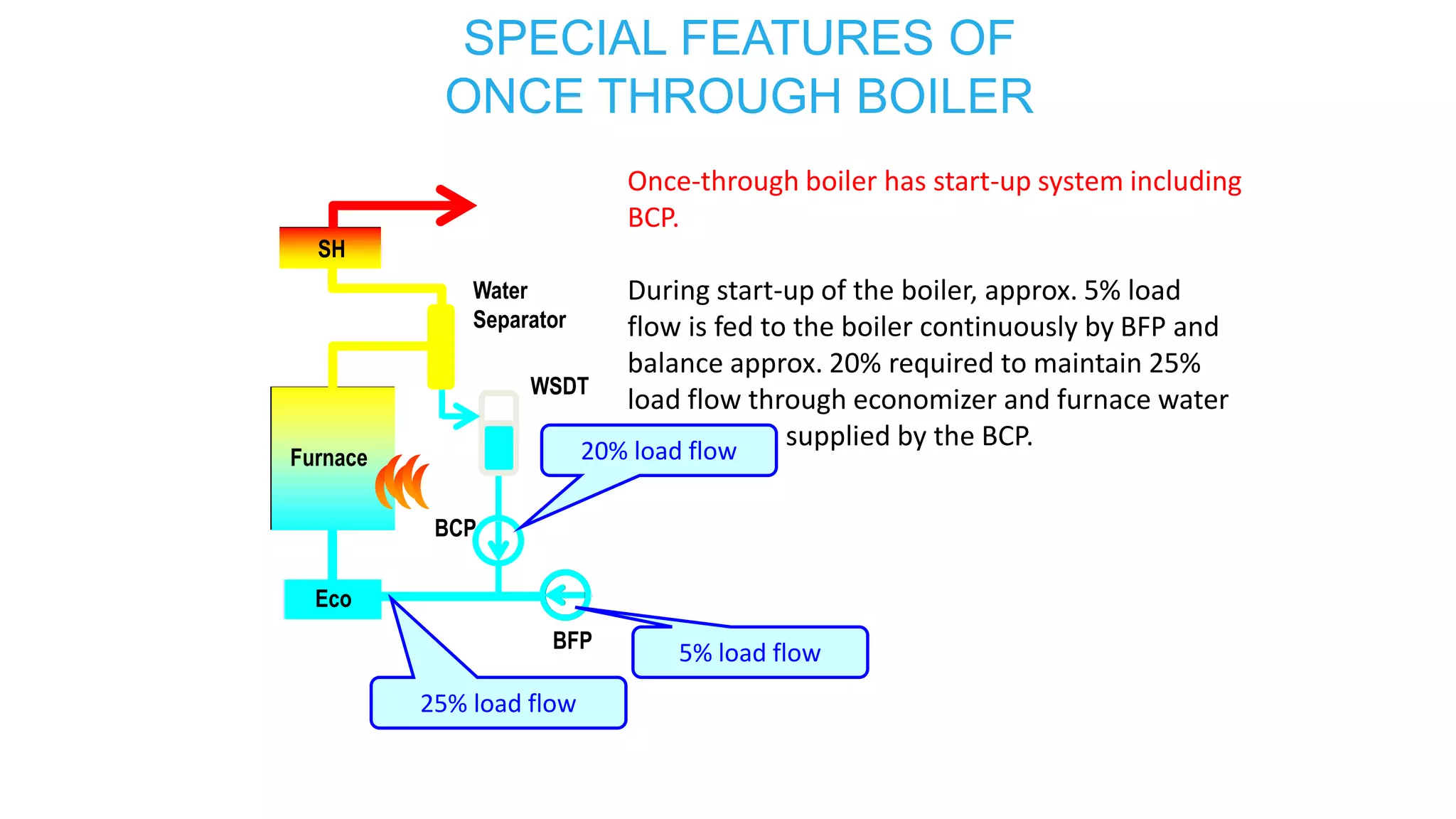
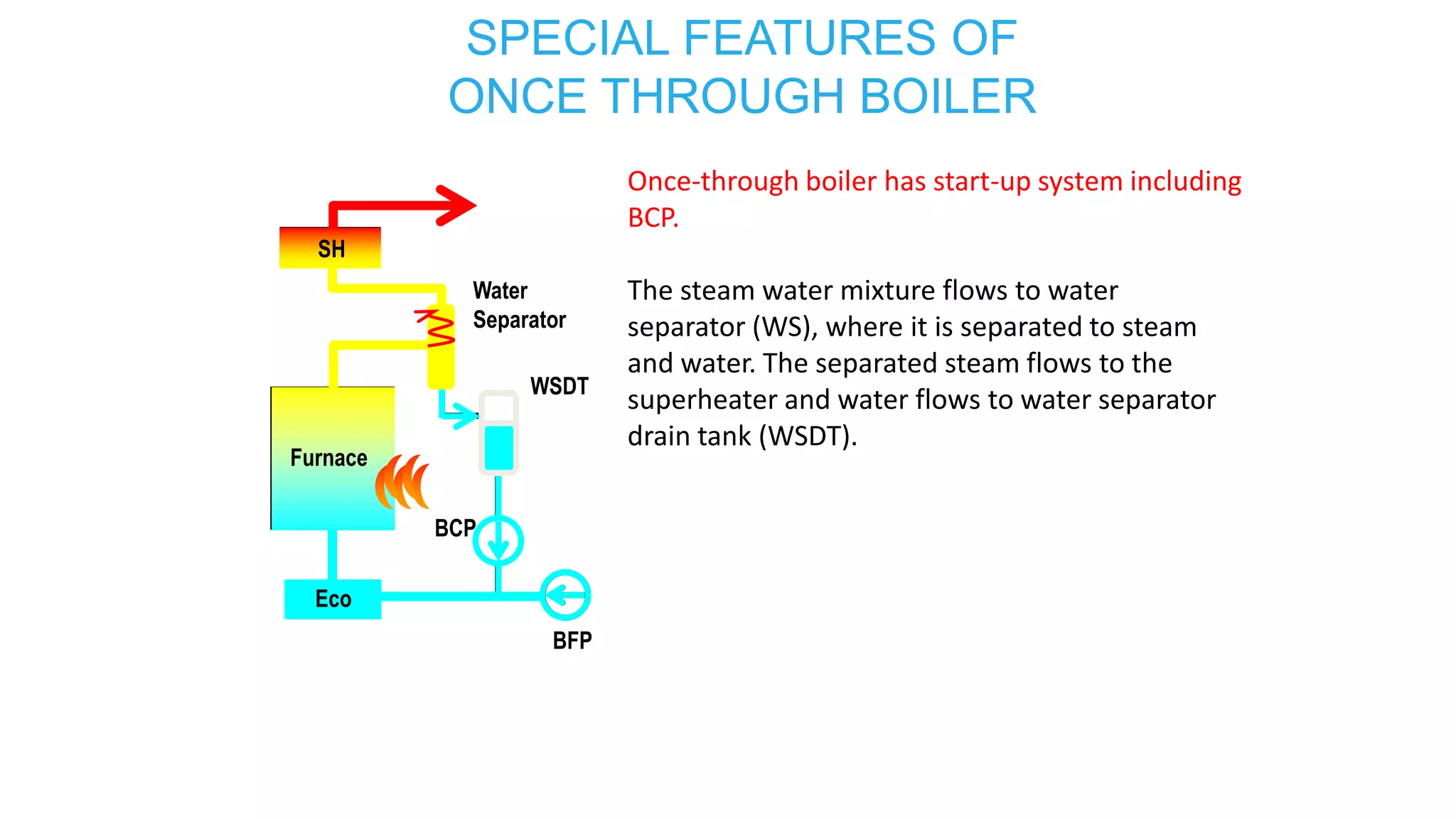
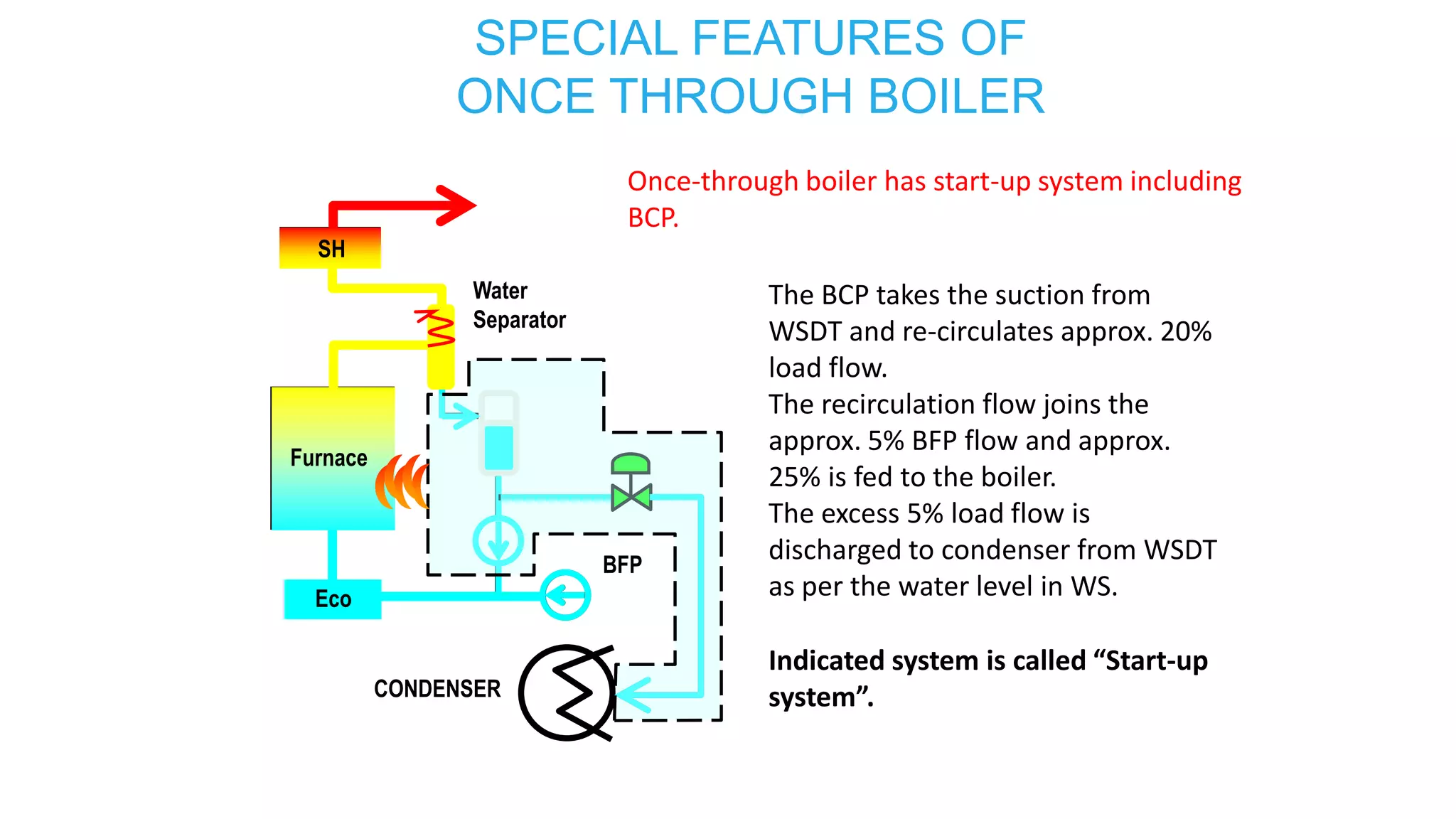
3) Special features of once-through supercritical boilers including their start-up system using a boiler circulation pump (BCP) to maintain minimum flow during low load conditions.