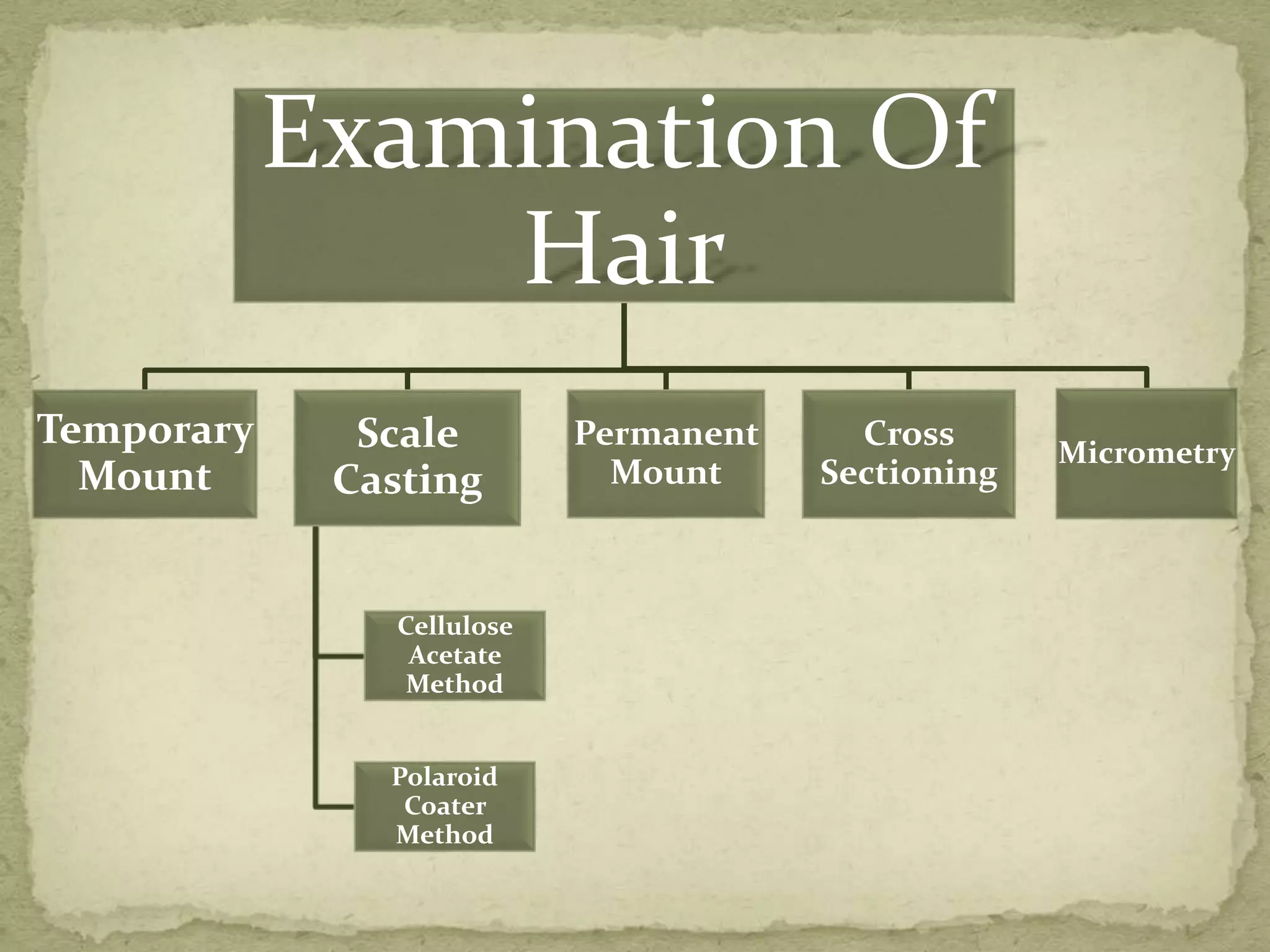
This document provides information on the structure, characteristics, and analysis of human and animal hair. It describes the three main layers of hair - cuticle, cortex, and medulla. The key differences between human and animal hair are discussed, including the width and pigment distribution in the cortex and nature of the medulla. Methods for sampling, examining, and preparing hair samples microscopically are also outlined.