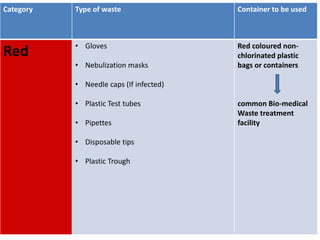
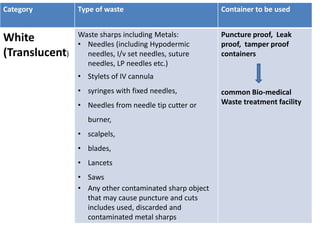
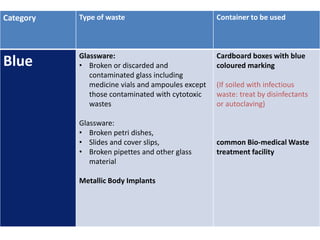
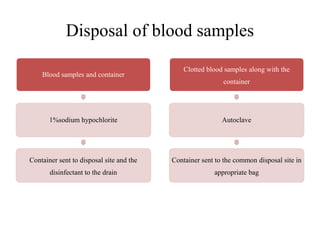
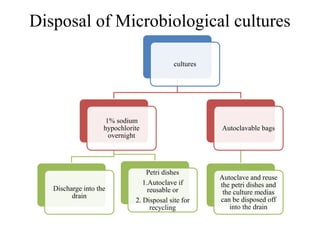
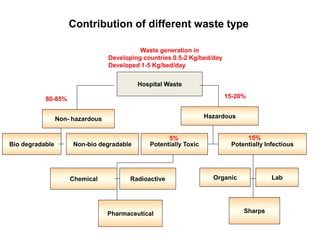
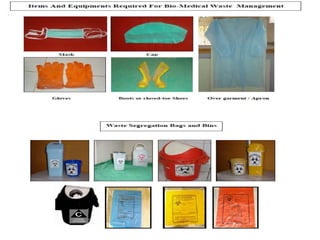
This document discusses biomedical waste management. It defines biomedical waste and notes its various types including hazardous, infectious, pharmaceutical, and sharps waste. It provides details on waste generation rates in developing and developed countries. It outlines the four main categories of waste - yellow, red, blue, and white/translucent - and the types of waste that fall under each category along with the appropriate containers. The document then discusses transportation, treatment, and disposal requirements for different waste types including autoclave conditions and alternatives for sharps containers. It concludes with dos and don'ts for proper waste management.





![Biomedical wastes categories and their
segregation, collection, treatment, processing
and disposal options (Schedule 1)
Category Type of waste Container to be
used
Yellow Human Anatomical Waste: Human tissues,
organs, body parts and fetus below the
viability period (as per MTP act)
[copy of official MTP certificate from
Obstetrician or the MS of hospital or
healthcare establishment must be given]
Yellow coloured
non-chlorinated
plastic bags
common Bio-
medical Waste
treatment facility](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bmwtrainingppt-1-230314141204-77a294fe/85/BMW-Training-PPT-1-ppt-8-320.jpg)