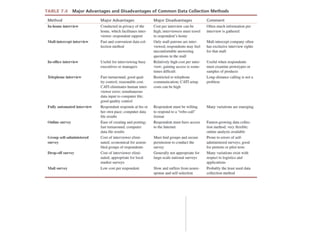
The document discusses different methods for collecting survey data, including in-person, telephone, self-administered, and mixed-mode surveys. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each method, such as lower costs but lower response rates for mail surveys. Researchers must consider factors like time, budget, and infrastructure when choosing the best method to fit their data collection needs.