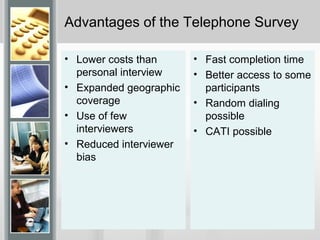
This document discusses various data collection methods and their pros and cons. It covers primary and secondary sources of data. Primary sources include individuals, focus groups, panels, and unobtrusive measures. Secondary sources include existing data that may be out of date or not fully applicable. Common data collection methods include observation, surveys using questionnaires or interviews, and unobtrusive methods. Considerations for each method include costs, reliability, and potential for bias. The document provides guidance on designing questionnaires, pretesting questions, and improving response rates.