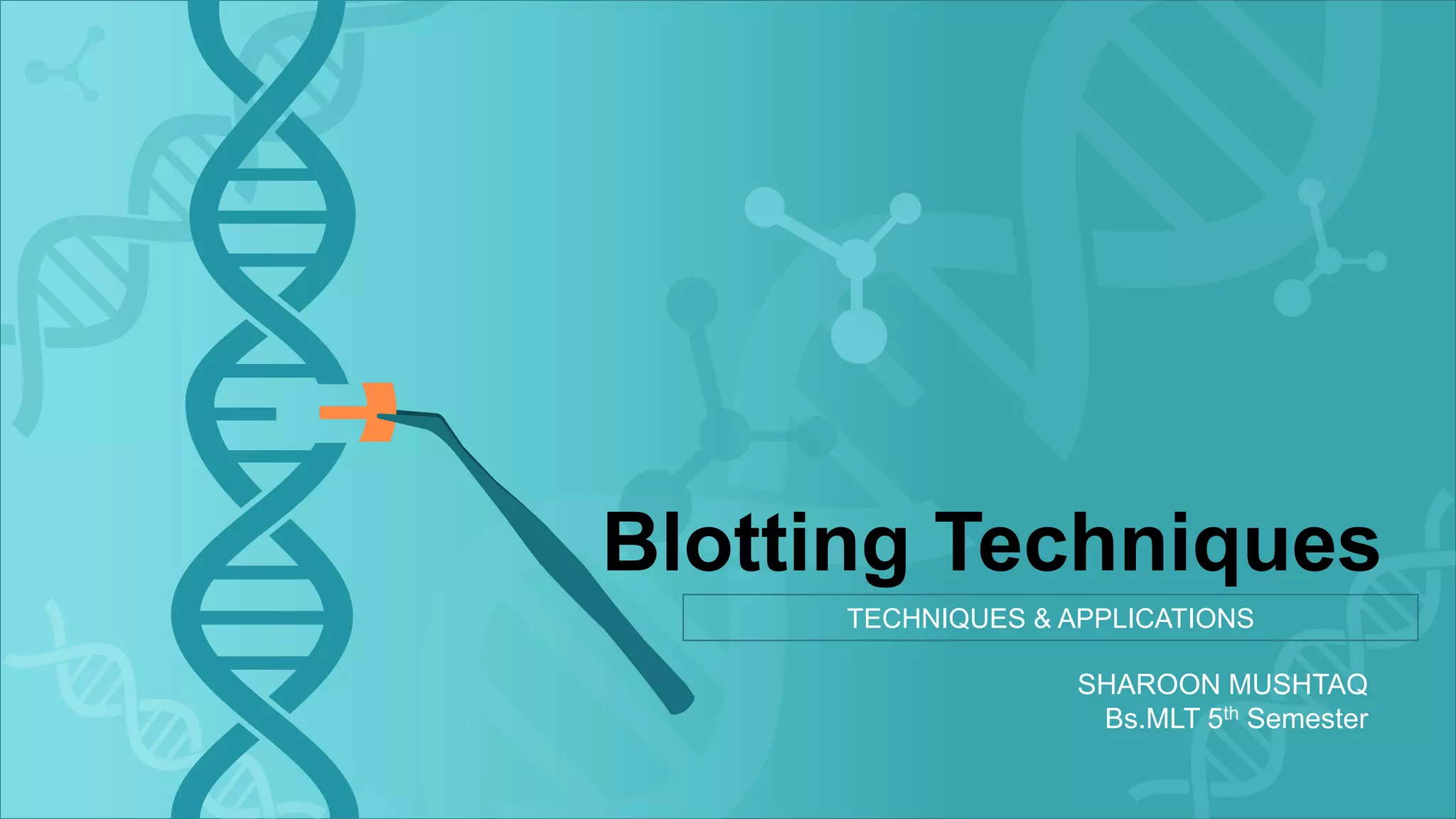
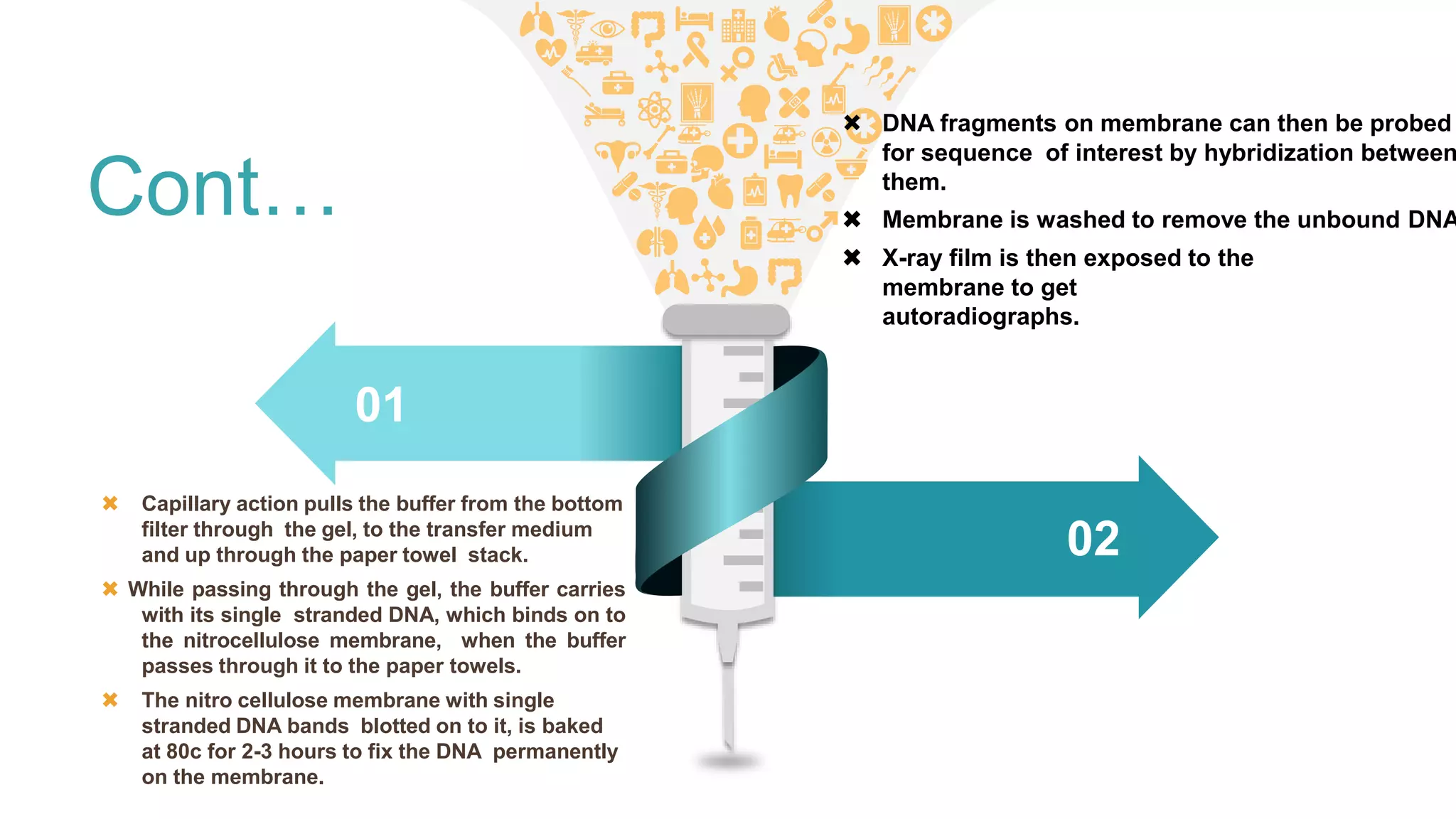
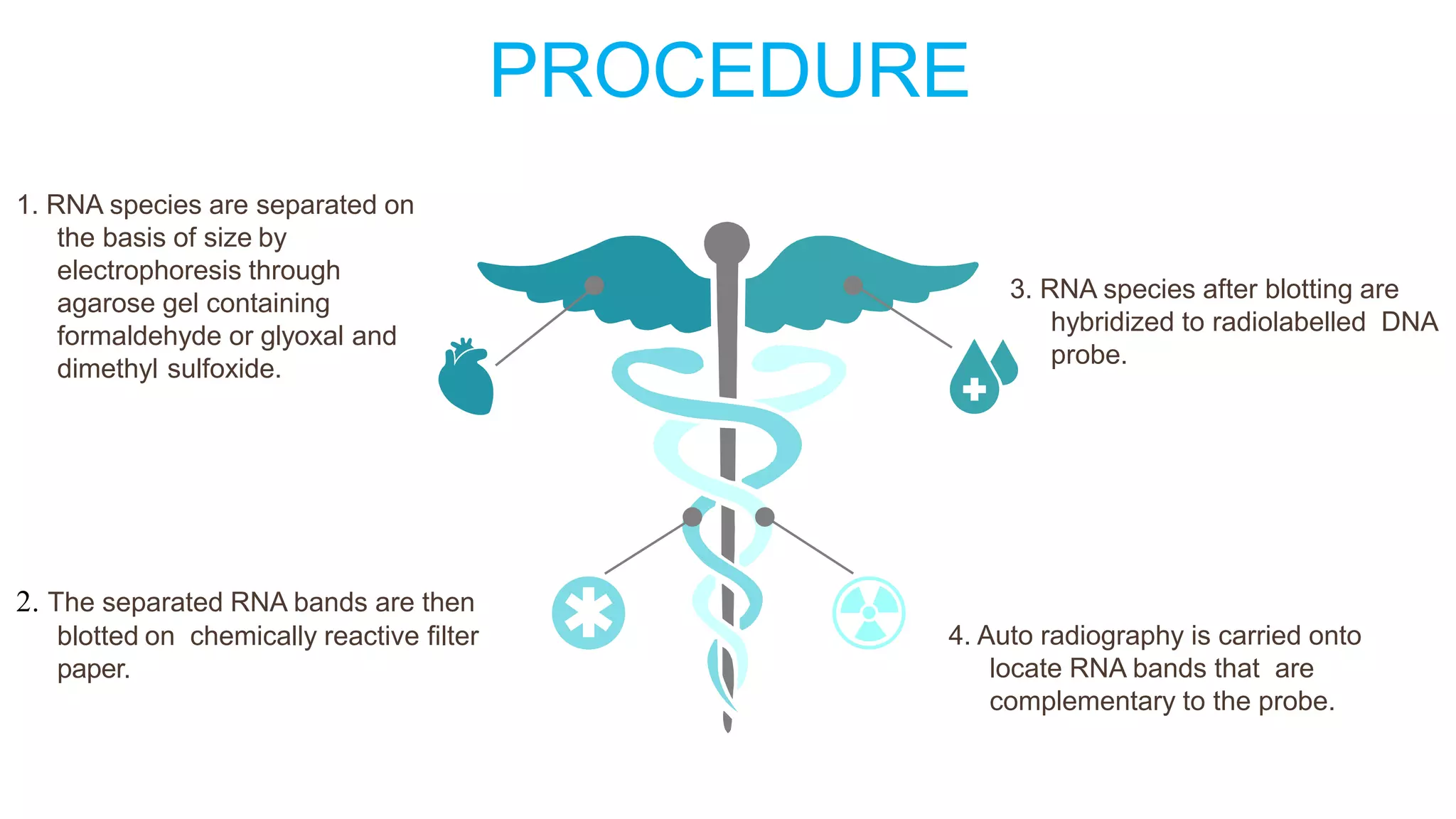
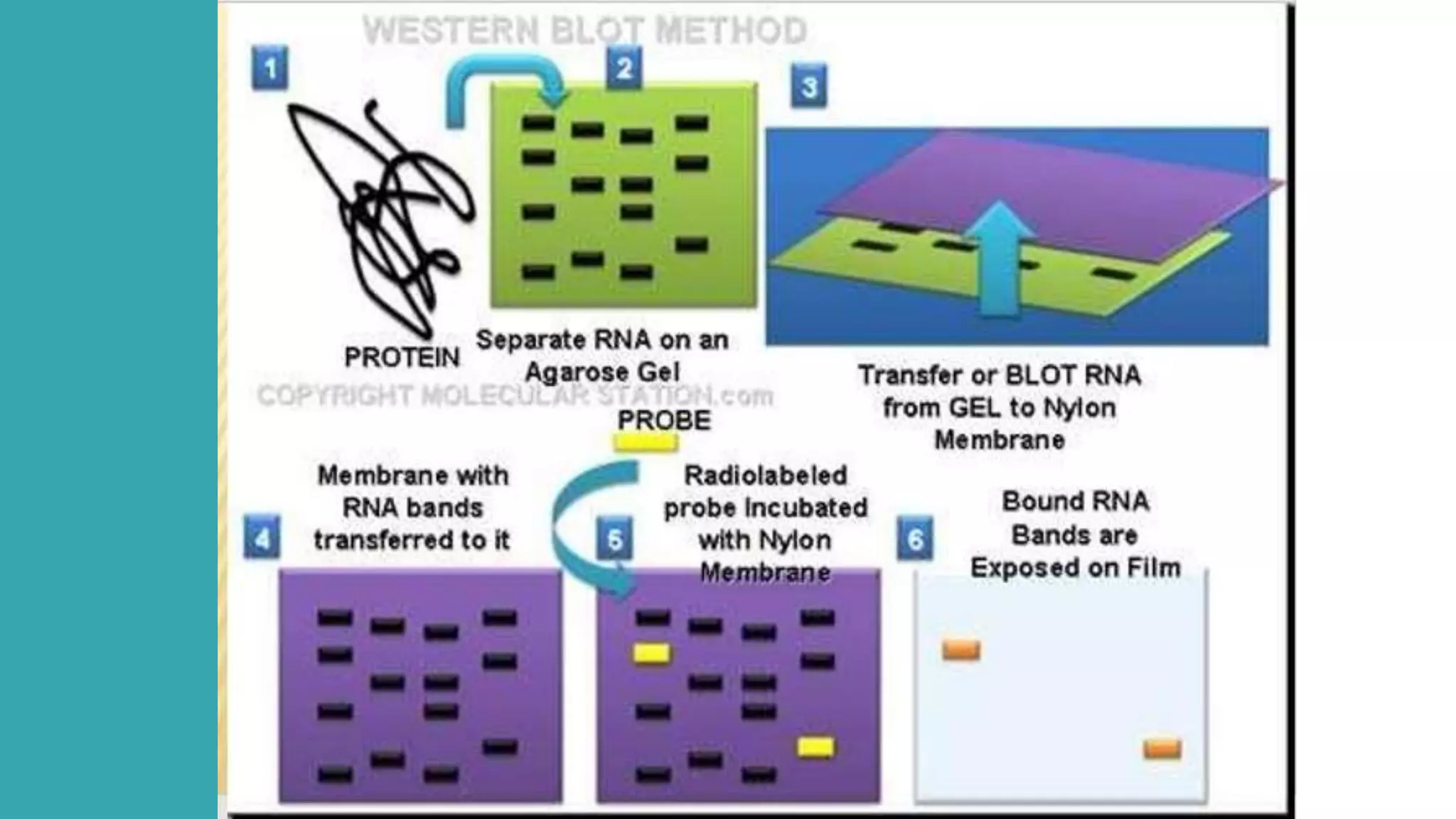
Blotting techniques allow for the detection of specific biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins. Southern blotting detects DNA through electrophoresis, transfer to nitrocellulose, and hybridization with a radioactively labeled probe. Northern blotting is similar but detects RNA. Western blotting detects proteins through electrophoresis, transfer, and incubation with labeled antibodies. These techniques are used for applications like gene mapping, fingerprinting, and confirming infections.