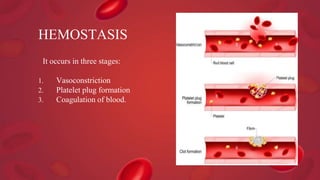
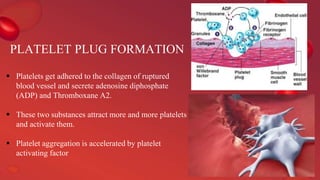
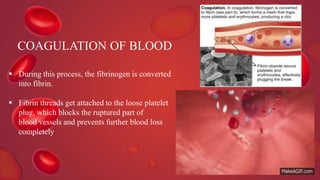
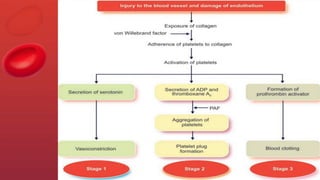
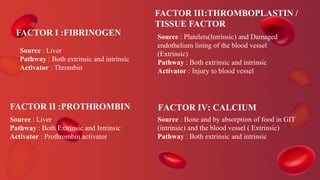
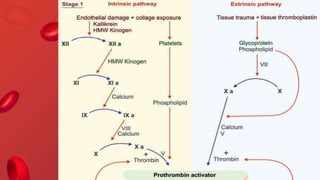
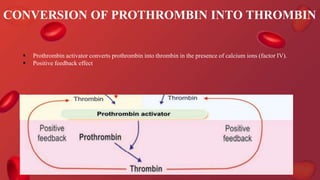
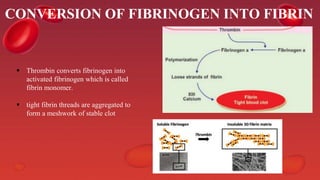
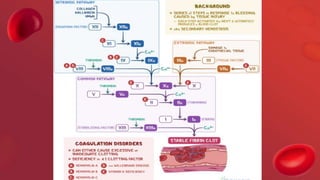
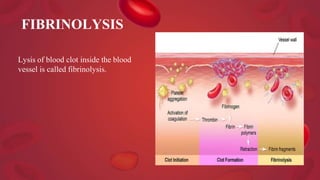
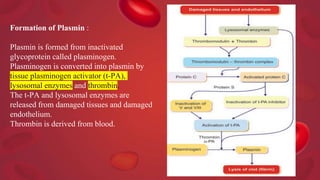
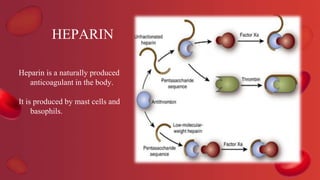
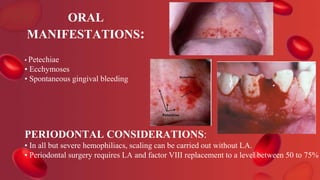
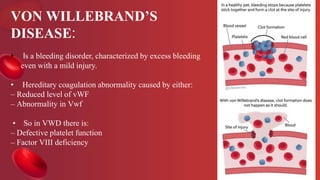
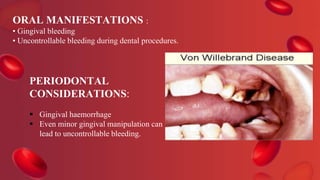
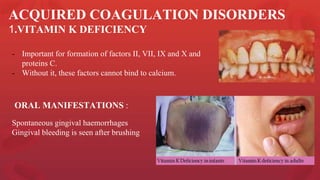
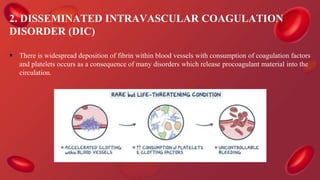
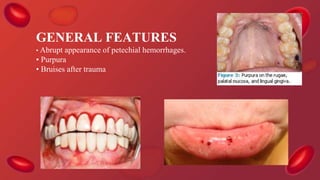
Blood coagulation is a complex process involving multiple coagulation factors that work together in a cascade to ultimately convert fibrinogen into fibrin to form a blood clot. There are two pathways (intrinsic and extrinsic) that lead to the formation of thrombin, which then converts fibrinogen into fibrin. Some bleeding disorders result from deficiencies in specific coagulation factors, such as Hemophilia A and B due to Factor VIII and IX deficiencies. Von Willebrand disease is caused by a defect in von Willebrand factor which is involved in platelet function. Coagulation tests evaluate different parts of the coagulation cascade to identify deficiencies.