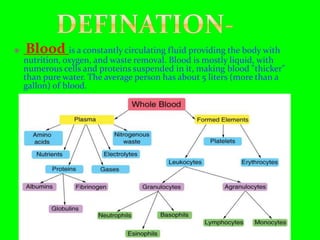
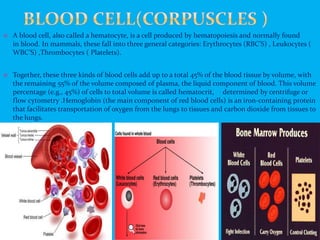
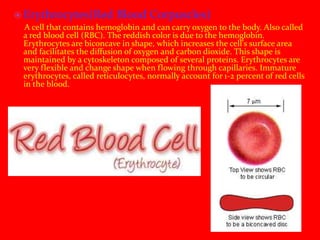
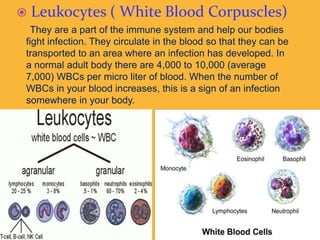
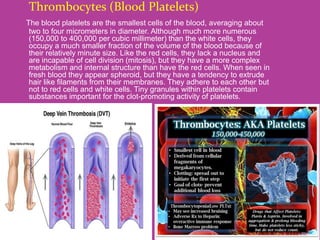
Blood is a circulating fluid composed of plasma and three main types of cells - red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and carry oxygen throughout the body, white blood cells help fight infection, and platelets help the blood to clot and stop bleeding. Together these cells and plasma make up the five liters of blood in the average person that provides nutrients, removes waste, and performs other vital functions.