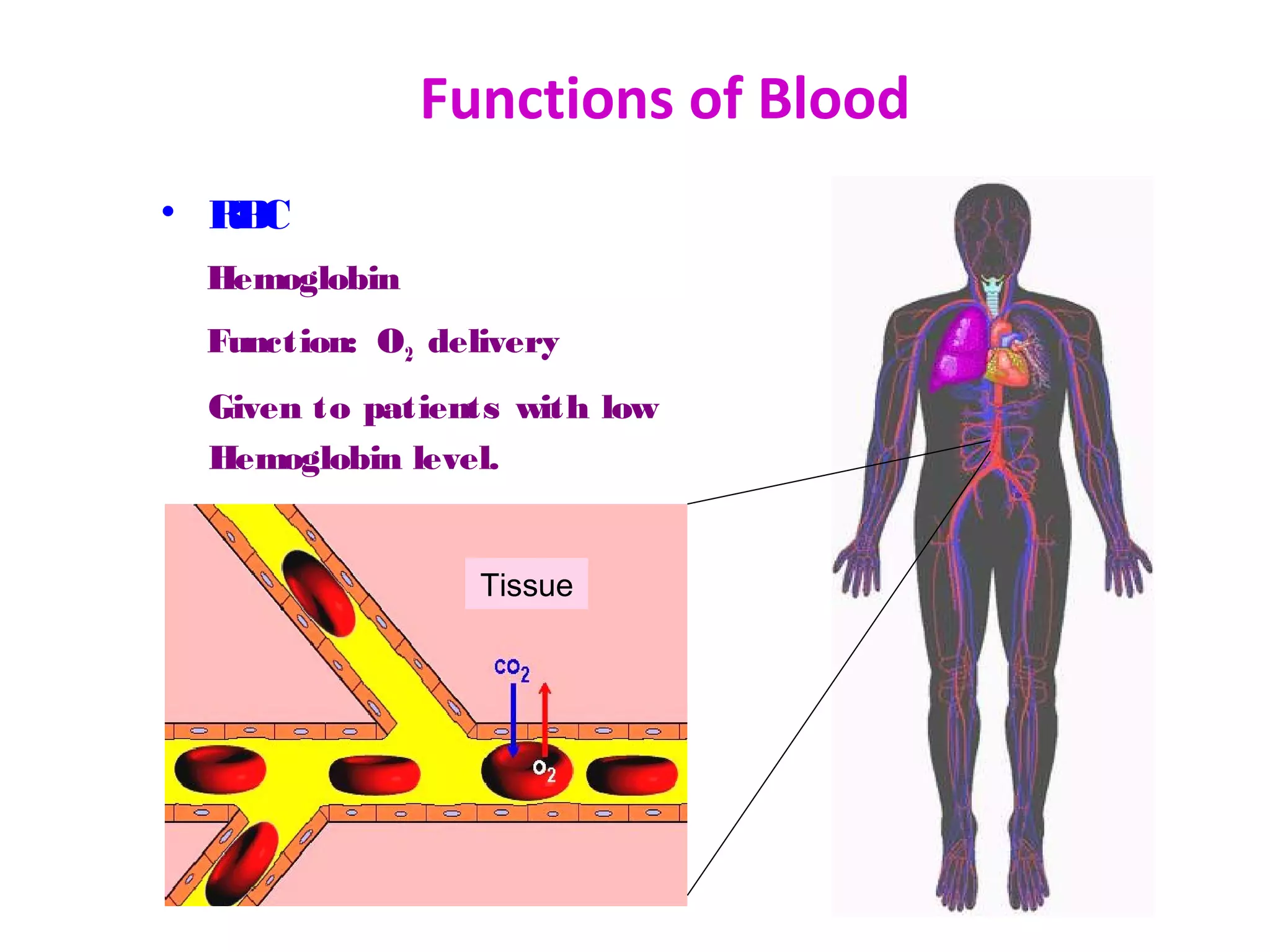
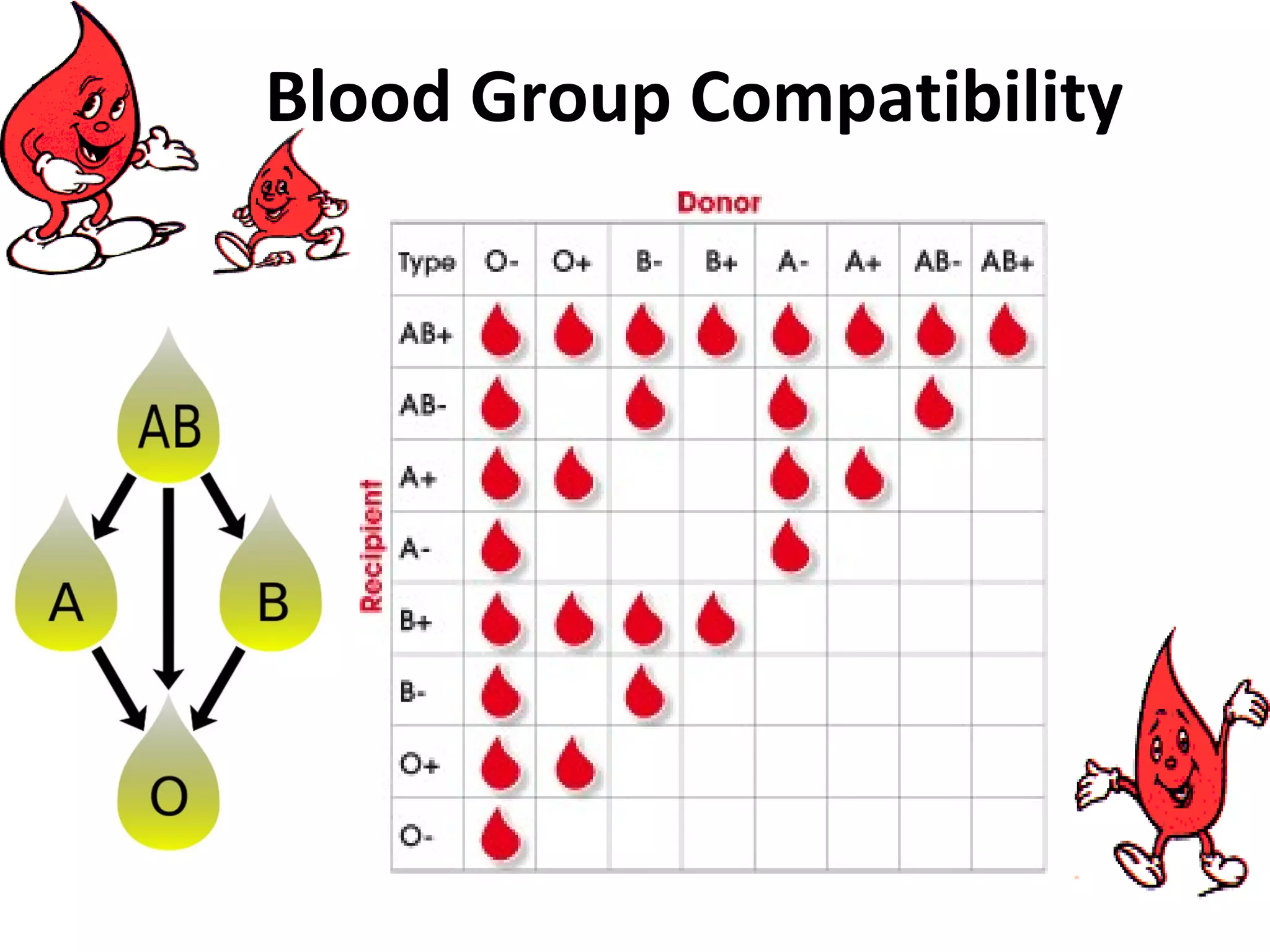
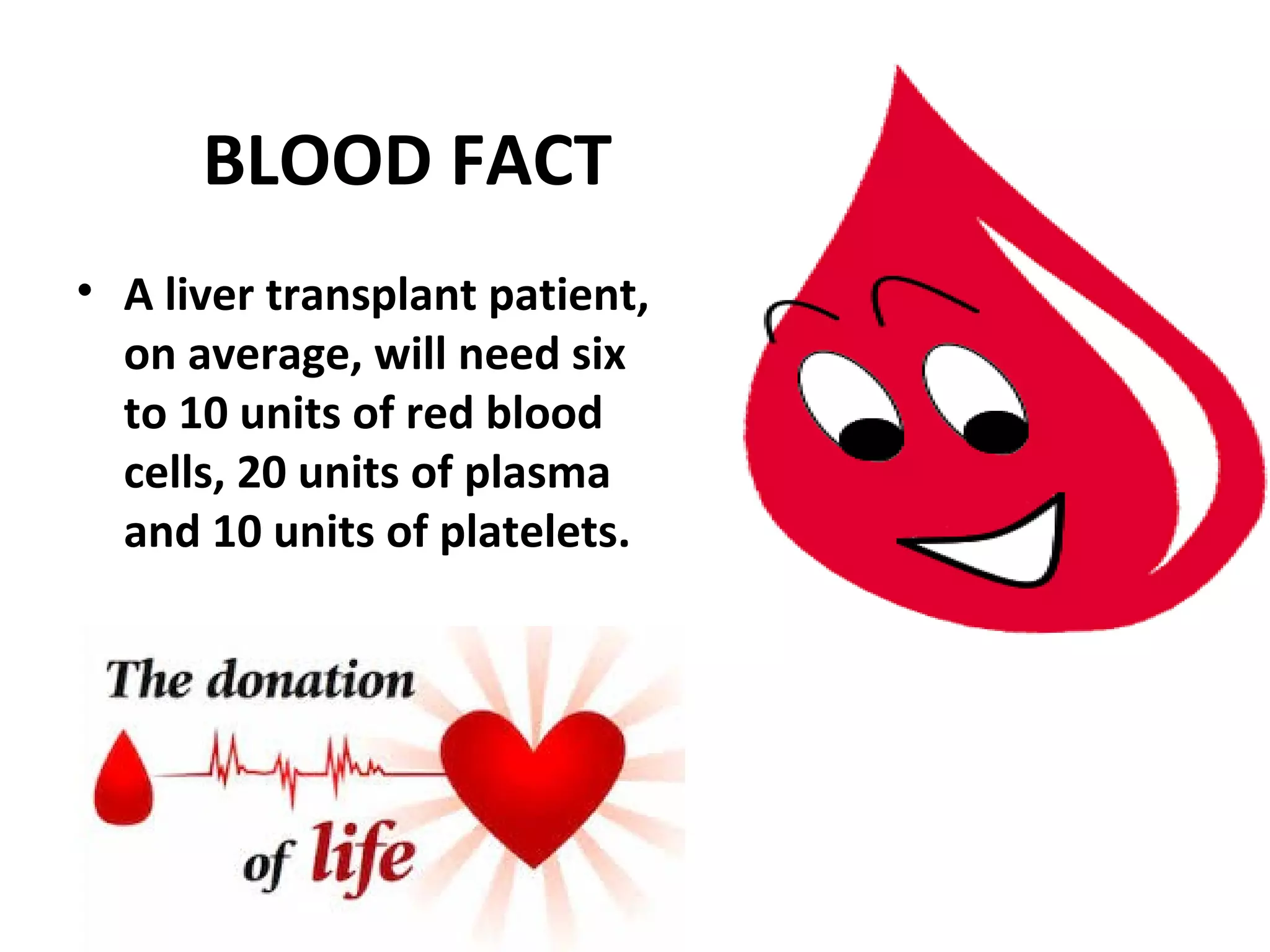
The document discusses the importance of blood donation. It notes that blood is a scarce resource worldwide, with only 16% of the blood supply coming from voluntary donors. Blood carries oxygen, fights infections, and stops bleeding. It is composed of red blood cells, platelets, plasma, and white blood cells. Regular blood donation is beneficial as it helps maintain healthy iron and cholesterol levels. Donating blood can help save lives of accident victims, surgery patients, and those with blood disorders, cancers, or medical conditions. The donation process involves screening, a medical exam, and blood collection that takes less than an hour.